Cpu kaputt wenn kein bild kommt? (PC, Hardware)
computertom
Community-Experte
PC, CPU, Hardware
12.07.2022, 16:09
Hallo
Bevor wir hier herumraten, wo der Fehler liegen könnte, wäre es sinnvoll, wenn du mal verrätst, was für Komponenten du da zusammengebaut hast, und zwar möglichst genau, um als erstes ein Kompatibilitätsproblem ausschließen zu können, oder dort bereits den Fehler finden zu können. Erst wenn eine Inkompatibilität ausgeschlossen ist, können wir nach Montagefehlern oder einem möglichen Defekt suchen.
mfG computertom
Nachtrag:
Ich habe mir eben mal dein Profil angesehen und musste feststellen, das du der bist, der seinen Prozessor ohne Kühler betreibt.
https://www.gutefrage.net/frage/kein-bild-beim-pc-nach-zusammenbau
Lüfter dreht sich, Die Gigabyte Audiospur leuchtet orange, also ist das Mainboard eingeschaltet.
Auch wenn du nur das BIOS/UEFI öffnest, läuft der Prozessor bereits mit vollem Takt. Die Stromsparfunktionen werden erst unter einem geladenen Betriebssystem aktiviert, über ACPI Treiber der CPU. Allerdings zieht der Prozessor im BIOS/UEFI, trotz vollem Takt, noch nicht die volle Leistung, weil noch nicht alle CPU Funktionen aktiv sind, nur nutzt das nicht viel, komplett ohne Kühler. Deshalb kann es gut möglich sein, das du so den Prozessor bereits gegrillt hast. Das BIOS hat zwar eine Schutzfunktion und schaltet normalerweise den PC aus, wenn der Prozessor zu heiß wird, aber die Schutzfunktion darf nicht deaktiviert oder die Abschalttemperatur zu hoch eingestellt sein und komplett ohne Kühler kann der Temperaturanstieg auch so schnell erfolgen, das der CPU Kern platzt oder reißt oder wie man das auch immer beschreiben will, noch bevor die Schutzfunktionen greifen. Das Halbleitermaterial der Chips ist Silizium und das ist genau so spröde wie Glas. Langsames aufwärmen = geht so, aber schnelles aufheizen = geht nicht so gut.
Natürlich kann auch was anderes kaputt oder fehlerhaft angeschlossen sein, aber mit hoher Wahrscheinlichkeit ist der Prozessor durch. Du kannst noch mal alle Kabel und Stecker prüfen, es muss unbedingt der 20(+4) polige ATX PSU Stecker am Mainboard stecken und der 4(+4) polige 12V CPU Power Stecker (EPS). An einer Grafikkarte müssen, wenn vorgesehen, auch die 6(+2) poligen PCIe Stecker angeschlossen werden, und zwar so, das alle Anschlüsse an der Grafikkarte vollständig von den Steckern belegt sind. Dann kannst du noch prüfen, ob die RAM Module und die Grafikkarte korrekt sitzen. Ansonsten nacheinander CPU, Mainboard, Netzteil,… usw. austauschen.
mfG computertom
2 Kommentare
2
FreaKLyy99
12. 07.2022, 11:58
07.2022, 11:58
Versuch mal den Monitor direkt ans Mainboard (HDMI, DP) anzuschließen und guck ob du da Bild bekommst!
Siehst du beim Bootvorgang nichtmal den Bootscreen deines Mainboards?
3 Kommentare
3
Mainboard oder CPU defekt? (Computer, PC, Grafikkarte)
Letzte Aktivität: 02.01.2022, 16:20
Details anzeigen
Kurz zu meinem Problem :
Ich habe vorgestern meinen PC teilweise auseinandergenommen um ihn zu reinigen.
Beim Wiedereinschalten hat es kurz verschmort gerochen und er bootete nicht mehr. Auch ins Bios komme ich nicht.
Alle Lüfter drehen, aber ich bekomme kein Bild. Das Mainboard gibt den Piep-Code für Grafikkarten defekt an.
Garfikkarte ausgebaut, Monitore ans Mainboard gestöpselt … selber Fehler.
Die Grafikkartenlüfter drehen und die integrierte LED leuchtet.
Alle Anschlüsse un Steckplätze kontrolliert … sitzt alles da wo es sein soll.
Habe dann die Graka vom 16er auf einen anderen freien PCI Slot gesetzt … gleicher Fehler.
Grafikkarte habe ich im Rechner von einem Freund getestet. Dieser fährt mit meiner Graka hoch und dort bekomme ich auch ein Bild, daher würde ich die Graka als Fehlerquelle vorerst ausschließen.
Auch nach BIOS und RTC Reset keine Änderung, scheinbar funktioniert auch die Onboard Grafik nicht.
zusätzlich leuchtet die DRAM Led auf dem Board, ich habe vorher nie darauf geachtet und weiß nicht ob das so sein muss oder ob auch das ein Fehler ist.
Der RAM sollte aber eigentlich in Ordnung sein, den habe ich kaum berührt.
Ich habe leider keinen Zugriff auf ein passendes Board oder auf eine andere CPU um durch Tauschen zu testen.
Gibt es eine Möglichkeit ohne Ersatzteile herauszufinden ob der Defekt am Board oder an der CPU liegt ?
Falls das hilft, hier noch mein Setup :
Board : ASUS P8Z77V (Sockel: LGA 1155 / h3) CPU : i7 3770k mit Arctic Kühler RAM : 4x8GB Corsair Vengeance Graka : Palit GTX 680 Jetstream Netzteil : 700 Watt
AmokMainz
19.07.2016, 10:53
Hört sich für mich danach an das eine Platine auf dem Board durch geschmort ist. Mit was hast Du ihn gereinigt?
Wenn man es mit den falschen Utensilien macht kann es zu elektrostatischen Aufladungen kommen die das Board beschädigen.
Ich glaube musst ein neues holen
2 Kommentare
2
Blobeye
Topnutzer
im Thema Grafikkarte
19. 07.2016, 11:40
07.2016, 11:40
Erstmal großes Lob für deine umfangreichen Ausschlüsse, so muss das sein 🙂
Wie man nun ohne Tauschen das rausfinden weiß ich nicht, aber ich würde jetzt so vorgehen:
Den Ram könntest du an nem anderen PC via Memtest überprüfen, um den allerletzten Faktor auszuschließen. Wenn der ok ist (vmtl. ist er das), kannste noch das Netzteil wechseln, was vmtl. auch nichts bringen wird (aber man weiß ja nie). Dann würde ich nen günstigen Board kaufen — wenns dann nicht klappt ist das teuerste kaputt…
bloxman
19.07.2016, 11:31
Hallo. Sitzt der Kühlkörper der CPU richtig. Wenn ja, dann weißt du ob es die CPU oder das Mainboard ist. Viel Glück.
19.07.2016, 12:13
Die einzige Möglichkeit, um es sicher auszuschließen ist, das mit Ersatzteilen zu testen. Dafür kannst du entweder Freunde fragen oder zu einem PC-Shop fragen ob sie dir gebrauchte Teile leihen können und die es (vor Ort) testen kannst.
Dafür kannst du entweder Freunde fragen oder zu einem PC-Shop fragen ob sie dir gebrauchte Teile leihen können und die es (vor Ort) testen kannst.
fabsko2001
19.07.2016, 10:54
Versuch mal den Strom auf dem Mainboard oder der CPU zu messen. Wenn die Anzeige auf null steht, oder das Lämpchen am Messgerät nicht leuchtet ist das Mainboard oder die CPU kaputt.
3 Kommentare
3
Faulty Processor Signs and Symptoms
Table of Contents
The central processing unit (CPU), also known as the processor, is considered to be the heart of a computer system. despite the topic of this article, the processor very rarely fails. And if that happens, then there’s nothing a normal user can do about it, anyway. Now we will consider all processor malfunction signs and symptoms .
Now we will consider all processor malfunction signs and symptoms .
Thanks to our post, you will note what are the signs of a processor malfunction and which way to look in order to fix all the problems. The processor is a rather complicated thing, on which almost everything depends. And if he starts to act up, then it’s a disaster. So, let’s begin.
Processor failure signs and symptoms
Processor failure symptoms
By design, modern computers will not boot into an operating system unless a critical component, the processor, is working. In other words, the normal boot process cannot be completed because the POST or Power-On self-test will indicate that a critical component is missing from the system.
Other components such as fans, hard drive, and motherboard in general will continue to work, but the boot process will eventually end with a blue screen of death error. However, there are other observable symptoms before and during CPU crashes that you should be aware of. Knowing them will help you identify the problem faster and reduce downtime.
Knowing them will help you identify the problem faster and reduce downtime.
Lockup and overheating just before PC shutdown If you notice that your computer had locked instances before the final crash, you should be aware that your processor is junk. It may have overheated, causing the system to shut down automatically to prevent further damage.
The processor has its own cooling system — it has a fan with a heatsink that provides cooling, but if the fan fails for any reason, the processor can overheat quite quickly. This is one of the reasons why you should check and clean all fans on your computer once a year.
Dust can sometimes stop normal ventilation, so storing it regularly can destroy the system. If your processor suffers from frequent overheating, consider cleaning its cooling system first. If that doesn’t work, check your BIOS to see if you have a way to lower its RPM. This can have a significant impact on performance,
Be aware that prolonged overheating can permanently damage the processor. If you are 100% sure that the processor is overheating (some motherboards have diagnostic tools to monitor the temperature of the processor). Here — just find a way to lower the temperature of the processor or consult a specialist to find out how to fix it.
If you are 100% sure that the processor is overheating (some motherboards have diagnostic tools to monitor the temperature of the processor). Here — just find a way to lower the temperature of the processor or consult a specialist to find out how to fix it.
Common symptoms of a processor failure
Beeping on startup . As mentioned above, your computer is performing a self-test (POST). Just to check if all peripherals are working or not. If the test detects that the processor is not working, the boot process will be aborted and the motherboard will emit an appropriate beep. The beeps are actually codes that help the technician identify the problem. And so make sure you notice how many beeps and what signals you heard. You can then search Google for what your sound code means.
Charred motherboard or processor . Severe overheating can melt or create a charred appearance on both the motherboard and the processor itself. Try to remove the motherboard from the mounts and disconnect the processor to see if this is the case.
If the overheating was severe, the processor may be damaged, specifically and permanently. In this case, there is nothing you can do about it. Just replace it and everything will work as it should. Depending on the damage, the motherboard may also be rendered useless, so make sure you consider and troubleshoot the motherboard you may have.
Causes of a processor failure
Like any other electronic component, the processor can die for simple reasons. Below are a couple of things that you should fix in the system if you want to extend the life of the processor.
Heat and superheat. A running processor generates heat, but if the heat level is outside the normal threshold, the processor may be damaged by overheating. Again, never underestimate the power of fans. There is a reason why powerful cooling systems are quite expensive. If possible, place the computer in an air-conditioned room so that heat build-up is slower.
Aging . Some processors can outlive all other components, but in most cases, you can expect an old processor to simply fail, at any time. If you have an older system (over 10 years old), the processor may suddenly stop working. Even if everything else is in order and the computer was monitored.
The first component in the CPU assembly that is usually covered is the fan. Over time, it simply reaches its natural limit. And there’s nothing you can do about it. There are millions of transistors in a processor. And if one of them stops working, the processor may malfunction if it is performing a certain task. This is difficult to check directly. Therefore, if you have ruled out all possible causes, the only thing you can do is replace the processor.
What else can cause the processor to crash
Excessive voltage or overclocking . Processors are designed to work based on their clock speeds. Some processors are designed to provide higher clock speeds for better performance, but it’s worth the price. Overclocking can put more stress on the device, shortening its overall lifespan.
Overclocking can put more stress on the device, shortening its overall lifespan.
In other words, you’re playing with CPU longevity for more processing power, which is not entirely a bad thing. If you have the finances to simply buy a faster processor, we advise you to upgrade instead of overclocking.
Power surge or unstable voltage . Many of today’s processors are so reliable that they can run continuously for years without a breakdown. However, if you are in an area with frequent thunderstorms or unstable power lines, a power surge can effectively stagger the processor, if not the rest of the motherboard components.
Avoid connecting the computer directly to a power outlet. If possible, use a surge protector to protect your computer from sudden power surges.
Bad motherboard . The motherboard is a complex interconnection of many different components, and sometimes even one faulty capacitor can cause another component to fail. Try to visually check all the parts on the motherboard. And watch out for leaking or swollen capacitors. If you find anything, there is a high chance that it is causing the processor to crash.
Try to visually check all the parts on the motherboard. And watch out for leaking or swollen capacitors. If you find anything, there is a high chance that it is causing the processor to crash.
How to Troubleshoot Your Processor
Your processor either works… or it doesn’t. When properly installed, the processor will run until it fails, unless something drastic happens. Such as power surge, lightning strike, serious damage to the motherboard. However, if the processor is no longer working, the best thing you can do is to replace it. Essentially, that’s all.
Check if the system is overheating. Before considering removing the processor and installing a new one, you should double check for signs of overheating in the system. Here are some of the specific steps you can try:
- Make sure the airflow is free. Sometimes extra cables inside the case can block important openings.
- Keep your fans under control. I’m talking about their number.
 Too many fans doesn’t necessarily mean it’s better.
Too many fans doesn’t necessarily mean it’s better. - If you can still access the BIOS, make sure it has the latest firmware. The upgrade process depends on the board you are using, so be sure to check the documentation that came with it. You will usually find out the BIOS version by checking the BIOS string that appears during boot. Other motherboards may display their firmware version differently. And so do a little Google search or use the guide.
- Check fan or heatsink. This step is applicable only if you know how to remove and replace the processor. If you do, make sure the push pins are in the correct position. And that the heatsink is properly attached to the motherboard. At the same time, it is necessary to check whether there is a heat-insulating material on the bottom of the radiator. If they are not present, this may be the cause of the computer overheating. Thermal interface material often comes in the form of thermal paste.
If there is silence during loading .
 ..
..
Processor malfunction signs and symptoms. If nothing happens during boot, i.e. the display stays blue or black and you suspect a processor failure, you should follow these steps:
- Verify that the power LED on the motherboard is on or off.
- If the LED is off, check the motherboard or power problems.
- When the LED is on, check if the processor fan is spinning when the system is turned on.
- If the CPU fan is spinning, you should perform a swap test using another running CPU. Make sure other devices are working properly.
How to prevent processor failure
Despite its reliability, you want to know for sure that your computer’s processor is working at full capacity. Because overheating is often the most common cause of a CPU failure. And here’s what you need to do to prevent it.
Monitor processor heat levels . High-end motherboards provide a tool to monitor CPU temperature and fan speed in the BIOS, so be sure to use it. Again, how the monitoring tool is implemented depends on your motherboard. Therefore, for reference, use the accompanying documentation.
Again, how the monitoring tool is implemented depends on your motherboard. Therefore, for reference, use the accompanying documentation.
The monitoring tools in the BIOS are designed to be user friendly. Therefore, you can even use the mouse. Temperature readings are often displayed in a simple way so that you can understand them. And if you’re lucky, there might be an indication of what’s normal and what’s not.
If you cannot set the base temperature, you must determine it yourself. Just noting the temperature of the CPU when it’s idle. After that, you need to boot the processor so you can also take note of its operating temperature. If you’ve run a motherboard monitoring program, set reasonable tripline values for temperatures. And configure the program so that it notifies you when these temperatures are exceeded.
CPU cooler
Use good CPU coolers . Processors bought from retail stores include stock coolers, but if you can afford quality third-party coolers, go for it. Aftermarket coolers tend to be more efficient than stock coolers. But they can also be noisier, so make your choice based on your needs.
Aftermarket coolers tend to be more efficient than stock coolers. But they can also be noisier, so make your choice based on your needs.
If you’re looking for good performance, go with the original coolers. If you are installing a cooler, make sure you properly clean the surface of the CPU before applying thermal paste. Also make sure the heatsink is tight against the processor.
Processor malfunction signs and symptoms
Clean the system unit regularly . This speaks for itself. But then again, we can’t really emphasize the need to minimize dust inside the system unit. Dust can clog the vents, reducing airflow to the processor and other components.
Use thermally enhanced chassis (TAC) . TAC is a buzzword for a more advanced case designed to dissipate extra heat from internal components (outside). TACs can be expensive, but they can be an effective method of minimizing heat inside the case. If you have free finances, we suggest that you use them instead of the standard case.
Location of the system unit . Placing a computer near a heat source in any form is a big problem. A cool, dry place is fine, but a climate-controlled room is even better. Computers would choose a cool room with no sun and air conditioning, so they should help a little with this 🙂 Good luck everyone.
Processor malfunctions signs and symptoms
Views today: 25,966
Related posts
What does buying a VDS server with KVM virtualization give?
The best information portal for users
The versatility of modern network switches
Installing Windows Server step by step
Signs of processor failure and how to prevent them
The central processing unit (CPU), also known as the processor, is considered the heart of a computer system. Despite what the title of this post says, it’s very rare for a CPU to fail, and if it does, there’s nothing the average user can do about it, anyway. This post is intended to educate the user on things to look out for rather than specific steps to get a failed processor working again.
- In this post we will cover the following topics:
- Processor failure symptoms
- Causes of a processor failure
- How to troubleshoot a processor failure
- How to prevent a processor crash
Processor failure symptoms
By design, modern computers will not boot to the operating system if a critical component, the processor, is not working. In other words, the normal boot process cannot be completed because the POST or Power-On self-test will indicate that a critical component is missing from the system. Other components such as fans, hard drive, and motherboard in general will continue to work, but the boot process will eventually end with a blue screen of death error. However, there are other observable symptoms before and during a CPU crash that you should be aware of. Knowing them will help you identify the problem faster and reduce downtime.
Overheating just before shutting down the PC
If you notice that your computer had locked instances before the final crash, you should consider a bad processor. It may have overheated, causing the system to shut down automatically to prevent further damage. The processor has a built-in fan that keeps it cool, but if the fan fails for any reason, the processor may temporarily overheat. This is one of the reasons why you should check and clean all fans on your computer once a year. Sometimes dust can clog the cooler. If your processor suffers from frequent overheating, consider cleaning its fan first. If that doesn’t work, check your BIOS to see if you have a way to lower its RPM. This can have a significant impact on performance,
It may have overheated, causing the system to shut down automatically to prevent further damage. The processor has a built-in fan that keeps it cool, but if the fan fails for any reason, the processor may temporarily overheat. This is one of the reasons why you should check and clean all fans on your computer once a year. Sometimes dust can clog the cooler. If your processor suffers from frequent overheating, consider cleaning its fan first. If that doesn’t work, check your BIOS to see if you have a way to lower its RPM. This can have a significant impact on performance,
Be aware that prolonged overheating can permanently damage the processor. If you are 100% sure that the processor is overheating (some motherboards have diagnostic tools that allow you to monitor the temperature of the processor), find a way to lower the temperature or consult an expert on how to fix it.
Self test detected hardware failure
As mentioned above, your computer is performing a self test (POST) to check if all peripherals are working or not. If the test detects that the processor is not working, the boot process will be aborted and the motherboard will beep. The beeps are actually codes that help the technician identify the problem, so count the number of beeps. You can then search Google for what the beep code means.
If the test detects that the processor is not working, the boot process will be aborted and the motherboard will beep. The beeps are actually codes that help the technician identify the problem, so count the number of beeps. You can then search Google for what the beep code means.
Charred motherboard or processor
Severe overheating can leave a charred mark on both the motherboard and the processor itself. Try removing the motherboard from and disconnecting the processor to see if this is the case (steps below). If the overheating was severe, the processor could be permanently damaged. In this case, there is nothing you can do about it. Just replace it and get on with your life. Depending on the damage, the motherboard may also be rendered useless, so make sure you troubleshoot the motherboard afterwards.
Causes of processor failure
Like any other electronic component, the processor can burn out for simple reasons. Below are the items that you should minimize in the system if you want to prolong the life of the processor.
Heat . A running processor generates heat, but if the heat level is outside the normal threshold, the processor can burn out from it. Again, never underestimate the power of coolers. There is a reason why good cooling systems are expensive. If possible, place the computer in an air-conditioned room so that heat build-up becomes slow.
Aging . Some processors can outlive all other components, but in most cases, you can expect an older processor to simply fail at any time. If you have an older system (over 5 years old), the processor may fail suddenly even if it is taken care of properly. The first component in a CPU assembly that is usually given away is the fan. Over time this moving part just reaches its natural limit and there is nothing you can do about it. There are millions of transistors in a processor and if one stops working, the processor can malfunction if it completes a certain task. It’s hard to test directly, so if you’ve ruled out every possible cause, the only thing you can do is replace the processor.
Excessive voltage or overclocking . Processors are rated based on their clock speeds. Some processors are designed to provide higher clock speeds for better performance, but it’s worth the price. Overclocking can put more stress on the device, shortening its overall lifespan. In other words, you’re trading CPU longevity for more processing power, which isn’t entirely a bad thing. If you have the resources to buy a faster processor, we recommend doing so instead of overclocking.
Power surge or unstable voltage . Many of today’s processors are so reliable that they can run continuously for years without a breakdown. However, if you are in an area with frequent thunderstorms or unstable power lines, a power surge can effectively break the CPU, if not the rest of the motherboard components. Avoid connecting your computer directly to a power outlet. If possible, use a surge protector to protect your computer from sudden power surges.
Faulty motherboard . The motherboard is a complex interconnection of many different components, and sometimes even one faulty capacitor can cause another component to fail. Try a visual check of the hardware on the motherboard and look for a leaking or swollen capacitor. If you find one, there is a high chance that it is causing the CPU crash.
The motherboard is a complex interconnection of many different components, and sometimes even one faulty capacitor can cause another component to fail. Try a visual check of the hardware on the motherboard and look for a leaking or swollen capacitor. If you find one, there is a high chance that it is causing the CPU crash.
How to troubleshoot a processor failure
The processor either works… or it doesn’t. When properly installed, the processor will run until it dies, unless something drastic happens, such as a power surge, lightning strike, serious damage to the motherboard. However, if the processor is no longer working, the best thing you can do is to replace it..0003
Check if the system is overheating . Before considering physically removing a processor and testing a new one, you should double check for signs of overheating in the system. Here are some of the specific steps you can try:
Make sure the airflow is free .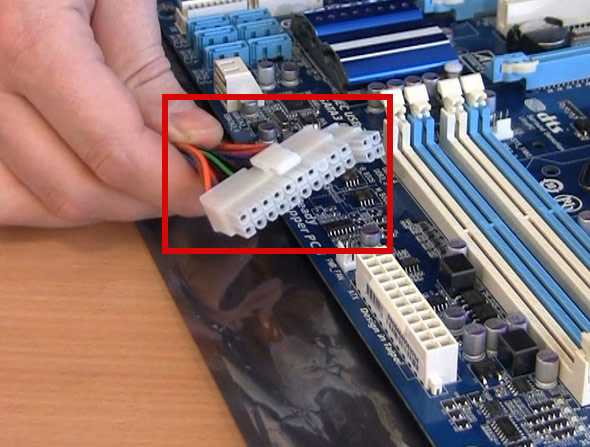 Sometimes extra cables inside the case can block important openings. Keep the number of coolers under control. Too many coolers doesn’t necessarily mean it’s better.
Sometimes extra cables inside the case can block important openings. Keep the number of coolers under control. Too many coolers doesn’t necessarily mean it’s better.
If you can still access BIOS make sure it has the latest firmware installed. The upgrade process depends on the board you are using, so be sure to check the documentation that came with it. You will usually find out the BIOS version by checking the BIOS string that appears during boot. Other motherboards may show their firmware version differently, so do a little Google search or follow the manual.
Check fan or heatsink . This step is applicable only if you know how to remove and replace the processor. If you do, make sure the push pins are in the correct position and that the heatsink is properly attached to the motherboard. At the same time, it is necessary to check whether there is a heat-insulating material on the bottom of the radiator. If they are not present, this may be the cause of the computer overheating.
If nothing happens during boot, i.e. the display remains blue or black and you suspect a processor failure, you should follow these steps:
- Make sure the power indicator on the motherboard is on or off.
- If the LED is off, check the motherboard or power problems.
- If the LED is on, check if the processor fan is spinning when the system is turned on.
- If the CPU fan is spinning, you must run the test using another running CPU. Make sure other devices are working properly.
How to prevent a processor failure
Despite its reliability, you want to make sure that your computer’s processor is running at full capacity. Since overheating is often the most common cause of CPU failure, here is what you should do to prevent it.
Monitor processor heat levels . High-end motherboards provide a tool to monitor CPU temperature and fan speed in the BIOS, so be sure to use it. Again, how the monitoring tool is implemented depends on your motherboard, so use the accompanying documentation for reference. The monitoring tools in the BIOS are designed to be user friendly, so you can even use a mouse. Temperature readings are often displayed in a simple way for you to understand, and if you’re lucky, there may be an indication of what’s normal and what’s not.
The monitoring tools in the BIOS are designed to be user friendly, so you can even use a mouse. Temperature readings are often displayed in a simple way for you to understand, and if you’re lucky, there may be an indication of what’s normal and what’s not.
In case you cannot set the base temperature, you must determine it yourself by noting the CPU temperature when it is idle. After that, you need to boot the processor so you can also take note of its operating temperature. If you run a motherboard monitoring program, set reasonable tripline values for temperatures and set the program to notify you when these temperatures are exceeded.
Use good CPU coolers . Processors bought from retail stores include stock coolers, but if you can afford quality third-party coolers, go for it. Standalone coolers tend to be more efficient than stock coolers, but they can also be noisier, so make your choice based on your needs. If you are installing a cooler, make sure you properly clean the surface of the CPU before applying thermal paste.
