PCIe 4.0 and PCIe 3.0 — Difference between x8 and x16 with the fastest cards — Where does the bottleneck begin?
Especially after the tests of the B550 motherboards, the justified question about the problem with the split PCIe 4.0 ports naturally arises. PCIe 4.0 with 16 or 8x connection should not show any (serious) difference together with the suitable (AMD) graphics card. But what about the fallback to PCIe 3.0, for example runs an older AMD or current Nvidia graphics card in such a slot?
In order to remain really accurate and reproducible, I must of course limit the test in terms of games and graphics cards. In the pre-test with 12 games and 3 graphics cards of different performance classes the game Assassin’s Creed Odyssey then crystallized out that despite various fluctuations the most consistent results were achieved in the different resolutions. However, in order to see these differences at all, I have to reach for the top shelf of the graphics cards. As CPU I use a Ryzen 9 3950X with PBO in game mode (8 cores), a MSI MEG X570 Godlike and 64 GB Patriot Viper DDR4 3600 Blackout Edition (2x 32 GB). All components are cooled with chiller and 20 °C cold water to avoid temperature-related measurement differences as far as possible.
I have five presets with four resolutions, i.e. 720p, 1080p, 1440p and 2160p in the highest quality settings without antialiasing (AA) and once 2160p with maximum AA in 5 to 7 runs each. For the evaluation in the single graphs I took the run which was closest to the average value of all gebenchmarkten runs. With a total of 128 measurements, one can probably already speak of a reasonably representative result.
| PCIe | Symbolrate pro Lane | PCIe x1 | PCIe x4 | PCIe x8 | PCIe x16 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
3. 0/3.1 0/3.1 |
8 GT/s | 0,985 GByte/s | 3,938 GByte/s | 7,877 GByte/s | 15,754 GByte/s |
| 4.0 | 16 GT/s | 1,969 GByte/s | 7,877 GByte/s | 15,754 GByte/s | 31,508 GByte/s |
| 5.0 | 32 GT/s | 3,938 GByte/s | 15,754 GByte/s | 31,508 GByte/s | 63,015 GByte/s |
Since Nvidia graphics cards currently generally force a fallback to 3. 0, a PCIe 4.0 slot will only run on 3.0, i.e. as PCIe 3.0 x16 @16 and @8, whereby the latter could well lead to limitations and bandwidth limits. But how big is the actual performance loss really? with a constant boost of about 2 GHz, the water-cooled Quadro RTX 6000 24 GB is the fastest Nvidia graphics card currently available alongside the Titan RTX. If there are any limits to be seen at all, then certainly especially with this card.
0, a PCIe 4.0 slot will only run on 3.0, i.e. as PCIe 3.0 x16 @16 and @8, whereby the latter could well lead to limitations and bandwidth limits. But how big is the actual performance loss really? with a constant boost of about 2 GHz, the water-cooled Quadro RTX 6000 24 GB is the fastest Nvidia graphics card currently available alongside the Titan RTX. If there are any limits to be seen at all, then certainly especially with this card.
The check shows the fallback to PCIe 3.0 and the respective bus interface – depending on the BIOS specifications.
With the AMD graphics card, I also use a water-cooled model to eliminate the possible tolerances caused by temperature fluctuations from the outset. Also here I have on average about 2 GHz constantly after a little help with the RBE. In return, the Sapphire RX 5700 XT Nitro Plus, as the fastest Navi card in my archive, performs well as always.
Here again the BIOS counter test, so that nothing goes wrong:
And now it can actually already start, because curiosity dies last, as is well known.
Kann ich eine PCI-e 16x Grafikkarte in einem PCI-e 8x Slot einbauen? (Hardware, Mainboard)
Details anzeigen
Funktioniert die Grafikkarte dann? Und wie groß ist der Leistungsunterschied dann gegenüber.
5 Antworten
compu60
01.03.2016, 14:42
Die Slots von PCIe x16, x8, x4 oder x1 sind alle unterschiedlich lang. Daher kann das nicht passen. Oder meinst du einen x1 Slot der nur mit 8 oder Lanes angeschlossen sind?
Die x16 Slots auf Mainboards mit mehreren x16 Slots sind meist mit absteigenden Anzahl Lanes angeschlossen. Es sollte aber auch immer der erste x16 Slot für eine einzelne Grafikkarte genutzt werden Also immer der erste x16 Slot unter der CPU.
Es sollte aber auch immer der erste x16 Slot für eine einzelne Grafikkarte genutzt werden Also immer der erste x16 Slot unter der CPU.
3 Kommentare
3
Masterman431
01.03.2016, 16:20
Entschuldigung, ich hab mich vertan. PCIe x16 passt in x8.
Performance nimmt angeblich erst bei high-end GPUs wie ner GTX970 oder dual GPUs oder ähnlich in Spielen ab.
ALLERDINGS:
..fehlen dir 8 Lanes und das spürt man, wenn möglichst schnell Daten in den VRAM geladen werden müssen.
4 Kommentare
4
KaeseToast1337
01. 03.2016, 21:59
03.2016, 21:59
Meinst du einen physischen slot oder elektrisxhen? Beim physischen nicht es sei denn er ist nach hinten offen. Beim physich 16x slot ja wenn er 8x unterstütz. Und nein der leistungsabfall ist nicht sehr groß und eigentlich auch nur bei benchmarks wirklich sichtbar.
Roderic
Community-Experte
Hardware
01.03.2016, 15:16
Ja. Kannst du. Einen merkbaren Leistungsunterschied wirst du kaum feststellen.
3 Kommentare
3
Masterman431
01.03.2016, 14:29
Hat du dir mal die Slots angeschaut? Die Grafikkarte passt nicht mal physisch rein.
1 Kommentar
1
Ähnliche Fragen
Kann ich meine Grafikkarte an PCI 8x anschliessen und was ist der unterschied zu 16x?
…zur Frage
Grafikkarte PCI-E 3.0 16x einstellen?
Hi, meine Grafikkarte macht in den Letzten Tagen paar Probleme obwohl sie vorher ganz normal lief…z.b. das sie einfach mal so viel schwächer ist als sonst immer und auch nicht heiß wird. Und jetzt hab ich mal in den Einstellungen nachgesehen und habe gesehen das die aktuelle Busenstellung beim PCI-E 3.0 Slot 8x (Bild) ist obwohl meine Grafikkarte 16x (Bild)ist aber da kenne ich mich auch nicht gerade super aus also kann es vielleicht irgendwie daran liegen?
Mein Setup:
Ryzen 2200g, RX 580 (Bild), MSI B450 Gaming Plus, 16gb Ram, 500W Netzteil
. ..zur Frage
..zur Frage
Grafikkarte egal welcher PCI slot?
Hallo , Ich habe das Msi Mortar B250 leider passt meine GTX 1070 nicht in den ersten PCI slot deshalb hab ich sie in den 2ten gesteckt.Beide Slots sind PCI-E 16 also macht das einen Unterschied in welchem Slot die Karte ist und wenn ja wie groß ist dieser?
…zur Frage
Grafikkarte am richtigen PCI Slot?
Hallo,
Ich hab das Motherboard ASUS Strix x99 gaming Motherboard. Hab seit heute eine 3060 RTX Grafikkarte. Laut GPU-Tech zeigt er mir das hier an:
Hat mein Motherboard kein 16x PCI Slot anschluss? Hab ich da etwas falsch gemacht? Wie genau kann ich das Überprüfen ob ich es am richtigen Slot angeschlossen habe? Das Motherboard hat folgende Slots:
Glaube ich habs falsch reingesteckt, oder?
. ..zur Frage
..zur Frage
Grafikkarte in 2. PCI-Express Slot (Leistungseinbußen)?
Hallo zusammen,
Temperaturbedingt würde ich meine Grafikkarte gerne in den 2. PCI-E Slot stecken. Würde es bei meinen Mainboard zu Leistungseinbußen führen? (GA Z77x D3H) Ein Bild meines Mainboards ist unten auch nochmal angefügt!
Danke schonmal für eure Hilfe, kenne mich damit leider selbst nicht so gut aus und finde in der Beschreibung auch nichts passendes dazu.
…zur Frage
Grafikkarte in unteren PCI-E x16 Slot?
Hallo, Ich habe meine Grafikkarte bis jetzt auf dem oberem PCI-E x16 Slot betrieben, könnte ich meine GPU jetzt ohne Probleme auf den unteren PCI-E x16 Slot stecken? Das würde ich gerne machen, weil die GPU dann einige unschöne Kabel verdecken würde. Meine Bedenken sind, das die Kühlung dann nicht mehr so gut funktioniert. Mainboard: MSI 970 Gaming GPU: MSI R7 370 4G Danke für alle Antworten. 🙂
Meine Bedenken sind, das die Kühlung dann nicht mehr so gut funktioniert. Mainboard: MSI 970 Gaming GPU: MSI R7 370 4G Danke für alle Antworten. 🙂
…zur Frage
Pci-e 4.0 Grafikkarte in Pci-e 3.0 slot?
Ich möchte von einer gtx 750ti auf eine rx 5500 xt Grafikkarte rüsten, aber habe bemerkt, dass die Grafikkarte einen pcie 4.0 slot hat und ich einen 3.0 slot.
1. Kann ich diese trotzdem einbauen?
2. Wenn ja, hat das irgendwelche Nachteile?
3. Würdet ihr es machen, oder nicht
Ich bedanke mich im voraus
…zur Frage
Kann man eine pci 3.0 m.2 ssd auf eine pci 4.0 m.2 slot einbauen?
Also wenn das Mainboard pci 4. 0 m.2ssd unterstützt kann man auf den slot eine pci 3.0 m.2 ssd einbauen
0 m.2ssd unterstützt kann man auf den slot eine pci 3.0 m.2 ssd einbauen
…zur Frage
Grafikkarte verdeckt PCI Slot für Soundkarte, was tun?
Hallo Leute!
Meine Graka verdeckt den Slot für die Soundkarte die ich bald mal einbauen möchte. der andere Slot ist für die Wlankarte- gibt es einen weg das zu ändern?
…zur Frage
Grafikkarte verdeckt aufgrund der dicke 2 PCI-e solts?
Grafikkarte verdeckt 2 PCI Express 1x Anschlüsse da diese zu fett ist. Ein PCI-e 16x Verlängerungskabel käme für mich nicht in Frage.
(mackierte Fläche ist von Grafikkarte bedeckt)
Kann deshalb kein WLAN Karte anschließen da fast alle WLAN Karten einen PCI-e 1x haben. Jetzt bleibt mir nur noch nach WLAN Karten mit PCI-e 16x zu Anschluss zu suchen da dieser noch frei ist. Kennt jemand eine gute und schnelle WLAN Karte mit PCI-e 16x Anschluss ????
Jetzt bleibt mir nur noch nach WLAN Karten mit PCI-e 16x zu Anschluss zu suchen da dieser noch frei ist. Kennt jemand eine gute und schnelle WLAN Karte mit PCI-e 16x Anschluss ????
Vielen Dank im voraus.
…zur Frage
Hat das MS-7848 MoBo ein PCI-E Slot oder gibt es da verschiedene Versionen?
Ist dieses Motherboard mit einer Gtx 1060 kompatibel? Angaben die ich auf E-Bay gefunden habe: Erweiterungssteckplätze: 2x PCI-E 1x 1x PCI-Express 16x
…zur Frage
Grafikkarte verwendet nur PCIe 8x obwohl sie in einem PCIe 16x Steckplatz ist?
Hey Leute kurze Frage.
Laut GPU-Z läuft meine GTX 980Ti mit PCIe 8x. Jedoch ist die Grafikkarte in einem PCIe 16x Slot drinnen. Die Grafikkarte hab ich auch mehrmals umgesteckt jedoch bekomme ich immer wieder die gleiche Anzeige (das Mainboard hat 3 PCIe 16x Steckplätze). Im Moment habe ich es am obersten PCIe 16x Steckplatz (also den am nähesten von der CPU) angeschlossen. (Ich hätte auch keine M.2 SSDs verbaut, welche die Lanes nehmen könnten.)
Hier die GPU-Z Anzeige unter Last. Ich weiß, dass meine Grafikkarte die 8x nicht ausnutzt aber es sollte doch trotzdem in GPU-Z aufscheinen, dass zumindest die 16x möglich sind.
System:
Windows 10 64 bit
CPU: i7- 8700k
RAM: GSKILL 2×8 GB DDR4 2133Mhz (Dual Channel)
PSU: BeQuiet Straight 11 650W
Mainboard: Asrock Z370 Extreme4
Monitor: Asus ROG PG279Q
…zur Frage
PCI-E 2. 0 Grafikkarte in PCI-E 1.0 Slot?
0 Grafikkarte in PCI-E 1.0 Slot?
Hi,
kann ich eine PCI-E2.0 Grafikkarte auch in einen Slot für den PCI-E1.0 stecken? Der Slot ist ja eigentlich zu groß, die Graka passt aber trotzdem rein, es bleibt eben ein Teil vom Slot leer. Kann ich die ohne Probleme ersetzen?
…zur Frage
Kann ich eine PCI-Express wie zB die AMD Radeon R9 270X in mein Motherboard einbauen?
Hallo zusammen,
Es geht darum, dass ich mir eine neue Karte kaufen möchte.
Zurzeit habe ich die AMD Radeon HD 4650 (auch PCI-Express). Am Slot auf dem Motherboard steht PCIe x16 (davon hat das Motherboard 2 Stück, und dazwischen befindet sich ein kleinerer Slot mit der Bezeichnung PCIe x4 — Siehe Bild). Mein Motherboard ist das Pegatron IPMTB-GS.
Bei der Radeon R9 270X steht PCI Express 16x 3. 0 -> was bedeutet dieses 3.0?
0 -> was bedeutet dieses 3.0?
Kann ich problemlos die R9 270x einbauen?
Und noch eine Frage: mein Motherboard hat ja 2 PCIe-Slots. Heißt es, dass ich 2 Grafikkarte zugleich einbauen kann? Könnte ich theoretisch die 2 Grafikkarten nebeneinander laufen lassen, oder wäre das zu viel für das Motherboard? Oder für das Netzteil? Spezifikationen meines Netzteils siehe Bild.
Es sind doch viele Fragen geworden. Danke im Voraus.
…zur Frage
How to Install a PCI Express x16 Video Card in a PCI Express x8 Slot
There isn’t much room to expand the capabilities of a 1U rack server. Is that the installation of an additional PCI Express adapter using an angular riser card, known as a «comb». In the days of Legacy PCI, even this meager solution had universality: all expansion cards were identical in terms of connectors.
The PCIe bus, unlike its predecessor, pleases with variety. Video cards use x16 connectors, other controllers use x8. The developers of the Supermicro X8SIL platform made a sound judgment that for a server board equipped with on-board video, the maximum scaling is an external PCI Express adapter with an x8 bus width.
How to install an additional video card in the current conditions, since both the motherboard and the Riser Card have only a PCI Express x8 slot? Which video adapter to choose, based on size restrictions and strict thermal requirements?
Obviously, the use of the so-called «quiet» solutions from ASUS is up to the task. The EAH6250 is a compact fanless graphics card that meets these requirements quite well. Its radiator with a height of no more than 15 millimeters allows you to install the device in a Riser Card without conflicting with the structural elements of the chassis on the Supermicro X8SIL platform.
Having solved the issue of packaging, let’s consider how to make a PCI Express x16 video card compatible with a PCIe x8 expansion slot? First of all, let’s clarify for ourselves that the performance of the PCI Express bus depends on the successful completion of the following procedures:
- detection of the installed adapter;
- link width detection;
- bandwidth negotiation.

Device Detection
Device detection in PCI Express slots uses a mechanism based on bus signals PRSNT#1 and PRSNT#2 . Their mnemonics speak for themselves: Pr e s e nt means Available .
Fig. 1. Hot-Plug: short lamellas located at the edges of the connector are closed last when installed,
are disconnected first when removed executions in the form of shortened lamellas and, in some cases, placement only along the edges of the connector. Compliance with this condition when connecting devices with different link widths (» link width «) is provided by several copies of signal PRSNT#2 .
Figure 2. PCI Express x8 Riser Supermicro RR1U-E8 cards ready for PCIe x16 adapters contact B81 remains unconnected. Its grounding on the system board will ensure successful detection of the device. To do this, contacts B48 and B49 are shorted.on a PCI Express Riser Card.
To do this, contacts B48 and B49 are shorted.on a PCI Express Riser Card.
Fig. 3. The comb is ready for use:
the connector has been modified to accept PCIe x16 cards,
the jumper between pins B48 and B49 has been soldered.
Compatibility factors
A PCI Express x16 video card installed in a PCI Express x8 slot remains operational due to the PCIe Link Training procedure, which is responsible for determining the link width and bandwidth negotiation.
Fig. 4. Silent PCI Express x16 video adapter from ASUS, model EAH6450 installed in PCIe Riser x8;
due to this, the functionality of the Supermicro X8SIL platform is expanded
This procedure creates the prerequisites for the occurrence of very «insidious» defects: successful start and initialization of the VGA controller are possible even with degradation of the connection parameters.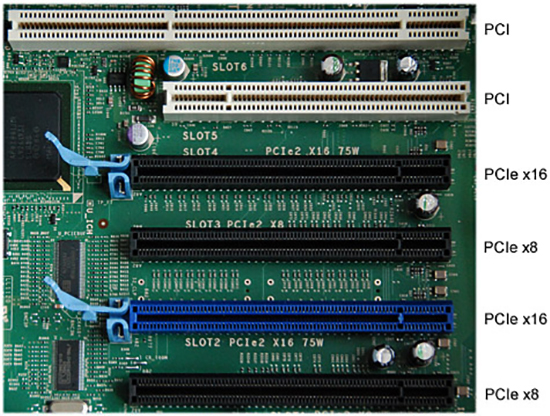 You need to make sure that the construction in question works in x8 mode.
You need to make sure that the construction in question works in x8 mode.
Figure 5. Screenshot: Connectivity diagnostics using custom test demonstrates
platform performance in x8 mode with 2.5 GT/sec throughput
the operability of a PCI Express x16 device in a smaller PCIe x8 slot has been confirmed.
Instead of summary
In most situations, the factors that limit the integral performance of a video adapter are GPU performance and features of the video memory interface. Reducing the width of the PCI Express bus by half will certainly affect the parameters of the video subsystem, but a twofold decrease in the main indicators compared to the x16 variant, all other things being equal, should not be expected, due to the fact that the PCIe port is only one of the fragments of a rather complex circuit transmission and processing of information. The maximum influence of the width of the PCIe link will be noticeable only in synthetic benchmarks that measure the speed of writing to video memory as a dedicated metric.
PCI Express — differences between x1, x4, x8, x16
Author Roman Kolotravov To read 7 min Views 1.8k. Posted by
What is interesting in this article:
- What is a PCI Express bus?
- How lanes affect bandwidth
- Types of devices that use PCI Express x2, x4, x8, x12, x16, and x32
- PCI-E port and lane sizes can vary
The PCI Express standard is one of the foundations of modern computers . PCI Express slots have long taken a firm place on any desktop computer motherboard, supplanting other standards such as PCI. But even the PCI Express standard has its own varieties and connection patterns that differ from each other. On new motherboards, starting around 2010, you can see a whole scattering of ports on one motherboard, labeled as PCIE or PCI-E , which may differ in the number of lines: one x1 or several x2, x4, x8, x12, x16 and x32.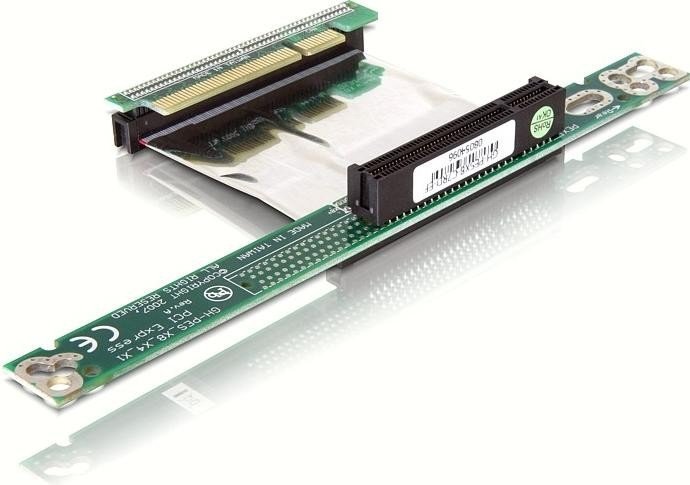
So, let’s find out why there is such confusion among the seemingly simple PCI Express peripheral port. And what is the purpose of each PCI Express x2, x4, x8, x12, x16 and x32 standard?
What is a PCI Express bus?
Back in the 2000s, when the aging PCI (ext. — Peripheral Component Interconnection) standard moved to PCI Express, the latter had one huge advantage: instead of the serial bus, which was PCI, a point-to-point access bus was used. This meant that each individual PCI port and the cards installed in it could take full advantage of the maximum bandwidth without interfering with each other, as they did when connected to PCI . In those days, the number of peripherals inserted into expansion cards was plentiful. Network cards, audio cards, TV tuners and so on — all required a sufficient amount of PC resources. But unlike the PCI standard, which used a common bus for data transfer with several devices connected in parallel, PCI Express, if considered in general, is a packet network with a star topology.
PCI Express x16, PCI Express x1 and PCI on the same board
In layman’s terms, imagine your desktop PC as a small shop with one or two vendors. The old PCI standard was like a grocery store: everyone was waiting in line to be served, having problems with the speed of service, limited to one seller behind the counter. PCI-E is more like a hypermarket: each customer moves for groceries along their own individual route, and several cashiers take orders at the checkout at once.
It is obvious that the hypermarket outperforms a regular store several times in terms of service speed, due to the fact that the store cannot afford the throughput of more than one seller with one checkout.
Also with dedicated data lanes for each expansion card or integrated motherboard components.
Not about PCI, but also interesting:
👉 Why is it important to set a BIOS password, and how to do it?
👉 Dealt with all kinds of computer ports/interfaces and their adapters
The impact of the number of lines on throughput
Now, to expand our metaphor with a store and a hypermarket, imagine that each department of the hypermarket has its own cashiers reserved only for them . This is where the idea of multiple data lanes comes in.
This is where the idea of multiple data lanes comes in.
The
PCI-E has gone through many changes since its inception. Currently, new motherboards usually use version 3 of the standard, with the faster version 4 becoming more common, with version 5 expected in 2019.year. But different versions use the same physical connections, and these connections can be made in four basic sizes: x1, x4, x8 and x16. (x32 ports exist, but are extremely rare on regular computer motherboards).
The different physical sizes of the PCI-Express ports make it possible to clearly separate them by the number of simultaneous connections to the motherboard: the larger the port physically, the more maximum connections it can transfer to the card or vice versa. These compounds are also called lines . One line can be thought of as a track consisting of two signal pairs: one for sending data and the other for receiving.
Different versions of the PCI-E standard allow different speeds on each lane. But generally speaking, the more lanes there are on a single PCI-E port, the faster data can flow between the peripheral and the rest of the computer.
But generally speaking, the more lanes there are on a single PCI-E port, the faster data can flow between the peripheral and the rest of the computer.
Returning to our metaphor: if we are talking about one seller in the store, then the x1 lane will be this only seller serving one client. A store with 4 cashiers already has 4 lines x4 . And so on, you can list cashiers by the number of lines, multiplying by 2.
Various PCI Express cards
Types of devices using PCI Express x2, x4, x8, x12, x16 and x32
For PCI Express 3.0 version, the total maximum data transfer rate is 8 Gb / s. In reality, the speed for the PCI-E 3 version is slightly less than one gigabyte per second per lane.
Thus, a device using a PCI-E x1 port, such as a low-power sound card or Wi-Fi antenna, will be able to transfer data at a maximum speed of 1 Gbps.
A card that physically fits into a larger slot — x4 or x8 , such as a USB 3. 0 expansion card, will be able to transfer data four or eight times faster, respectively.
0 expansion card, will be able to transfer data four or eight times faster, respectively.
PCI-E x16 ports are theoretically limited to a maximum bandwidth of about 15 Gb/s. This is more than enough in 2017 for all modern graphics cards developed by NVIDIA and AMD.
Most modern graphics cards use PCI Express
The PCI Express 4.0 protocol already allows 16 GT/s, while PCI Express 5.0 will use 32 GT/s.
But there are currently no components that can use this amount of bandwidth at maximum bandwidth. Modern high-end graphics cards typically use the x16 PCI Express 3.0 standard. It makes no sense to use the same bandwidths for a network card that will use only one line on an x16 port, since the Ethernet port is only capable of transmitting data up to one gigabit per second (which is about one eighth of the bandwidth of one PCI-E lane — remember: eight bits in one byte).
There are PCI-E SSDs on the market that support the x4 port, but they look like they will soon be superseded by the rapidly evolving new M. 2 standard. for SSDs that can also use the PCI-E bus. High-end network cards and enthusiast hardware such as RAID controllers use a mix of x4 and x8 formats.
2 standard. for SSDs that can also use the PCI-E bus. High-end network cards and enthusiast hardware such as RAID controllers use a mix of x4 and x8 formats.
Port sizes and PCI-E lanes can vary
This is one of the most confusing PCI-E tasks: a port can be made in x16 form factor, but not have enough lanes to pass data, for example, just x4. This is because even though PCI-E can carry an unlimited number of individual connections, there is still a practical limit to the bandwidth of the chipset. Cheaper motherboards with more budget chipsets may only have one x8 slot, even though that slot can physically accommodate an x16 form factor card.
In addition, gamer-focused motherboards include up to four full x16 PCI-E slots and as many lanes for maximum throughput.
For example — ASUS X99-DELUXE II RTL. Motherboard with 4 PCI-E with x16
Obviously, this can cause problems. If the motherboard has two x16 slots, but one of them has only x4 stripes, then adding a new graphics card will reduce the performance of the first one by as much as 75%.
