i7 vs i9 — What’s the Difference?
July 5, 2021
Josh Covington
In previous posts, we’ve discussed Intel’s Core i5 processor vs Core i7. But with the latest generation architecture, Intel introduced a new Core i9. So how has Intel differentiated i7 vs i9? What features does Core i9 have that i7 doesn’t?
What is Intel Core i9
Core i9 is Intel’s naming convention for their top-end set of non-Xeon processors. It’s less of a sub brand, more of a model number and to be honest, it’s a little arbitrary. I9 was first introduced in June of 2017 with 7th Gen Core X release (aka Skylake-X) to go alongside the i7 line. With Skylake-X, all 10-core and higher Core processors were denoted as i9 whereas in previous generations, those processors would have been i7. Then with 9th gen Core (aka Coffee Lake) in 2018, Intel integrated i9 into those higher end models, starting with the 9900k. Prior to this refresh, all Core processors were i7, i5, and i3 only.
i7 vs i9 – How do they compare?
This answer depends on which Intel architecture you’re referring to. As I mentioned, whether a processor is called i9 is a little arbitrary, so it does get confusing, but let’s break it down:
Intel Core series (Alder Lake)
Speaking generally, i9s are simply faster processors than are i7s – more cores, higher clock, more cache. The big differentiator is when it comes to Hyperthreading, the feature that creates two processing threads for every physical core. Depending on the specific processor architecture, this may be a feature exclusive to i9 only, though that’s not the case with 11th and 12th Gen.
Intel Core X-series Processors
Core-X has its own set of rules (thanks, Intel!). Here, the general sentiment is the same, but the rules outlined above go out the window. I9 is still better than i7 with higher core count and cache, but the naming convention is much more arbitrary with no i7 vs i9 feature differences. 10 core or more = i9, 8 core = i7, and that’s it. With 10th Gen Core X though, Intel simply made all processors i9.
10 core or more = i9, 8 core = i7, and that’s it. With 10th Gen Core X though, Intel simply made all processors i9.
Core i7 Pros
- Sometimes higher (or similar) clock and Turbo speeds
- Better value for many applications
Best for – budget conscious builds, single threaded applications, most games
Core i9 Pros
- Higher core count
- More L2/L3 cache
- Highest core speeds – though usually only 100-200Mhz
- All have Hyperthreading
Best for – multithreaded and/or higher demand applications, extreme multitasking
Configure your Core i9 or Core i7 desktop on our Raptor Z55 or Raptor Z95 today!
The following two tabs change content below.
- Bio
- Latest Posts
Josh has been with Velocity Micro since 2007 in various Marketing, PR, and Sales related roles. As the Director of Sales & Marketing, he is responsible for all Direct and Retail sales as well as Marketing activities. He enjoys Seinfeld reruns, the Atlanta Braves, and Beatles songs written by John, Paul, or George. Sorry, Ringo.
He enjoys Seinfeld reruns, the Atlanta Braves, and Beatles songs written by John, Paul, or George. Sorry, Ringo.
Posted in: Hardware
Search for:
Intel Core i7 vs i9: What’s the Difference Between These CPUs?
Search
Home»Hardware
Aug
25
2021
Intel’s two high-end options across desktop and laptop settings might strike a similar pose to business buyers, but each offers distinct benefits depending on the use case.
Ernie Smith is a contributor to BizTech, an old-school blogger who specializes in side projects, and a tech history nut who researches vintage operating systems for fun.
The chipmaker Intel produces a broad array of processors in mobile and desktop settings, offering a diverse range of CPU options.
For professional users, an important distinction emerges between the high-end entries in the Intel Core processor series — the i7 and the i9, which are both seen as premium entries in the x86 chip family.
But not all i7 or i9 chips are created equal, and to understand the value proposition, it’s important to take a step back and look at where these chips came from and why (depending on the context) one might be a better choice than the other when looking to upgrade employees’ technology.
History of the Intel Core i7 and Core i9
The Intel Core i7 and Core i9 are on the high-performance end of the long-running Intel Core processor series. Like other processors in the series, they are known for having multiple distinct processor cores — effectively, multiple processing units on the same die. The Core i7 and Core i9 processors generally have more cores and a higher level of power consumption.
While the Core i7 has been available since the earliest generations of the Core processor series, the Core i9 is relatively new, having launched as a desktop processor in 2017.
REGISTER: Learn about the processors and other tools that can empower a workforce built for the future. Click the banner below to register for the weekly CDW Tech Talk series.
Click the banner below to register for the weekly CDW Tech Talk series.
What Is the Intel Core Processor Series?
The Intel Core processor series, first launched in 2008, is Intel’s main processor line, noted for its reliance on multiple processor cores. An evolution of the earlier Core Duo line of processors for desktop and mobile computers, the series represents Intel’s primary CPU focus.
It’s not the only one, however: The Core series sits between a number of low-end options intended for niche or consumer use cases (the Atom, Pentium and Celeron processor lines) and the high-end Xeon line of server and workstation processors. Most x86 computers sold today utilize some form of Core processor.
It may seem like a lot of choice, but Hernán Quijano of Intel’s Desktop and Workstation Group says that the variety serves a wide range of workloads.
“There is a reason for every product lineup we have — specifically, in our products, for the workstation segment where we serve a lot of different users across many industries,” Quijano says.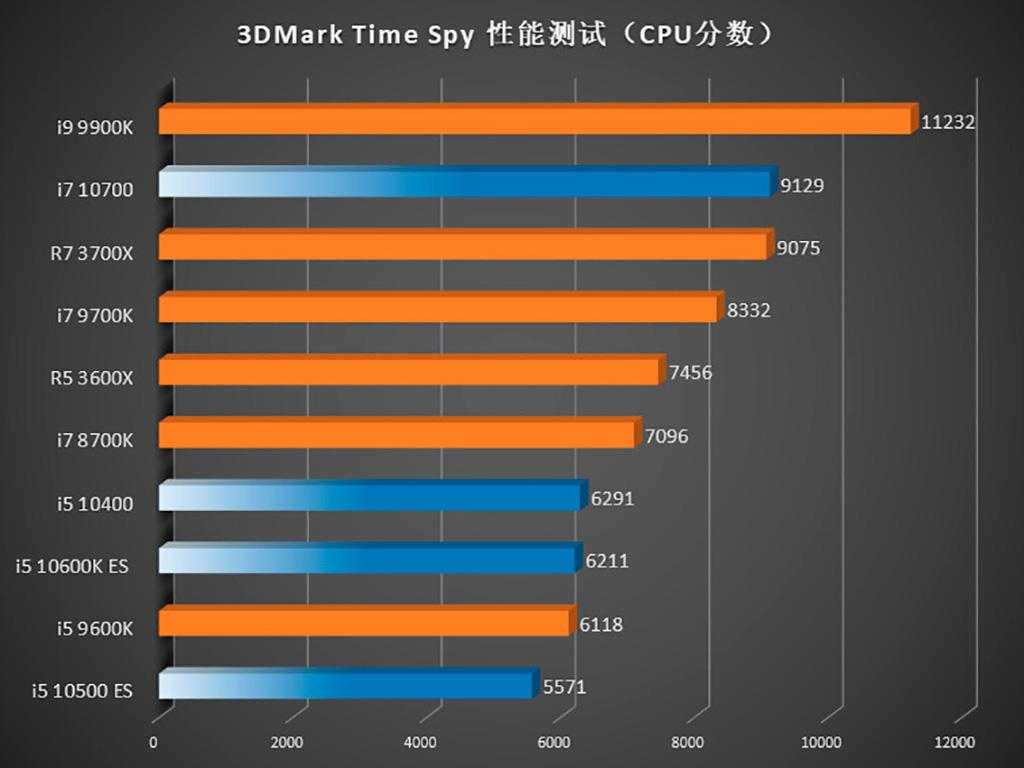
What Are the Different Types of Intel Core Processors for Desktops?
Currently, there are four primary types of Intel Core processors that business consumers may see:
- Core i3: Generally sold with two- or four-processor cores, this low-end model excels at single-threaded tasks such as web browsing and basic office software.
- Core i5: Earlier iterations of the midrange Core i5 came with four processor cores, but more recent models, such as the Rocket Lake-S line, now include six cores and 12 processor threads, making them capable options for graphic-intensive workloads and eSports.
- Core i7: Modern variations of the Core i7 come with as many as eight cores and 16 threads. Core i7s are able to “turbo boost,” providing access to additional processor power as needed. Software development and video editing are two types of tasks that could benefit from a Core i7 or better.
- Core i9: The Core i9 made a big splash in the desktop market with the release of the i9–9900K in 2018, the first i9 processor targeted at consumer platforms.
 Most Core i9 models have 8 cores, but the X-series line of processors offers models with as many as 18 cores.
Most Core i9 models have 8 cores, but the X-series line of processors offers models with as many as 18 cores.
WATCH: Explore the machines that can power a work from anywhere model.
Quijano notes that Intel’s premium desktop lines excel when maximum capabilities are the primary concern — and they can scale up beyond the Core series. Many professionals in entertainment and data sciences, he says, favor the Xeon line of processors, which in its latest iteration can have as many as 56 cores and run in multiprocessor configurations. Apple’s Mac Pro is an example of the Xeon in action.
“There is always a level of performance and expandability that can only be achieved with a powerful fixed or desktop workstation,” Quijano says. “And if you can’t take that system with you, we support technologies to access them remotely in a fast and secure way from your mobile workstation.”
Those purchasing desktop machines should determine whether integrated graphics are necessary; Core processors can be purchased with or without graphics built into the chip, which may negate the need for an additional graphics processing unit (GPU) depending on the workload. Buyers should also consider the power draw of each chip, which generally needs a larger cooling mechanism as processor line evolves.
Buyers should also consider the power draw of each chip, which generally needs a larger cooling mechanism as processor line evolves.
What Are the Different Types of Intel Mobile Processors?
The mobile versions of Intel’s Core processor line also follow the i3/i5/i7/i9 conventions. But there are distinctions among them, with the primary differentiator being power draw. Intel produces three main lines of mobile processors:
- Y Series: Also known as the Core M Series, the Y Series is designed to support ultralow power consumption (below 10 watts), starting with Core m3 and ending with the Core m7. A notable model that uses Y Series processors is the Google Pixelbook Go, a Chromebook.
- U Series: Perhaps the most common chip used in modern laptops, U Series processors consume 15 watts of energy, on average, making them a good match for balancing power consumption and thinness. These processors are generally sold as i3, i5 and i7 models.
 The Microsoft Surface is a good example of a computer that uses a U Series processor.
The Microsoft Surface is a good example of a computer that uses a U Series processor. - H Series: These processors draw the most power among mobile chips, providing the strongest performance available in a portable setting. H Series chips are considered the top mobile processors, with i7, i9 and Xeon processors generally sold in H Series models. The Lenovo ThinkPad P1 and the HP ZBook line of laptops are two notable examples of machines that use H Series processors.
Most modern Intel mobile processors have integrated graphics, with the recent Tiger Lake line of processors providing a significant upgrade through its Xe line of integrated GPUs. (Depending on the need, some users may want something dedicated that offers an NVIDIA GPU, however.)
Beyond laptops, Intel’s mobile line of processors are a fundamental part of many small form factor computers, such as Intel’s own Next Unit of Computing (NUC) line.
What Are the Differences Between a Core i7 and a Core i9?
Apart from varying core counts and processor speeds, differences between the i7 and i9 ultimately reflect the needs of the professional user.
When it comes to processors, there is usually a close relationship between power consumption and performance; an ongoing challenge with the x86 architecture is how to maximize power in a limited power envelope. In desktop and mobile settings, the i7 tends to use less power (and on the mobile side, is available in lower-power Y and U versions), while the i9 generally represents performance without compromise.
Patrick Moorhead, founder and principal analyst of Moor Insights & Strategy, says the i7 and i9 both have a place in the office, but the Core i9 generally makes the most sense for performance-intensive computing (for tasks such as graphics visualization, video production, 3D modeling and multitasking).
“Generally speaking, Intel Core i9 processors offer higher performance because they have more cores, higher frequencies, more cache and draw more power,” Moorhead says. “If you or your users require the highest performance with single-threaded or multithreaded workloads, the i9 is the one to choose. ”
”
Is It Worth Upgrading an i7 to an i9?
In many cases — especially for laptop users — an i7 will deliver more than enough performance. But if you can live without some of the benefits of a less powerful processor, such as longer battery life, it may make sense to go with the i9.
“The trade-off with the i9, generally, is higher power draw, more fan noise and a higher price,” Moorhead says.
Quijano says that, despite the added cost, many businesses are willing to consider the high-end options, as i9 processors strike a good balance between the solid single-core performance of the Intel Core series and the multicore performance that Xeon processors excel at. He adds that mobile workstations, traditionally favored by workers with onsite roles, found a home with many employees during the pandemic, given the need for maximum power on the go.
“The pandemic has made mobile workstations the most flexible systems for many users,” Quijano says. “And as we make plans to go back to our offices one or two days each week, mobile workstations are a perfect solution. ”
”
MARHARYTA MARKO/Getty Images
More On
Related Articles
aaa 1
Register
Security
Best Practices for Deploying Zero Trust In Your Mobile Environment
Digital Workspace
NRF 2023: Photo and Video Highlights from Retail’s Big Show
Trending Now
Copyright © 2023 CDW LLC 200 N. Milwaukee Avenue, Vernon Hills, IL 60061
Do Not Sell My Personal Information
Intel Core i9 or i7
When it comes to choosing a new processor for your computer, it’s important to know the difference. Processors come with different names, and it can be difficult for first-time buyers to figure out what they really need. Generally speaking, the higher the number, the more powerful the processor will be, but that does not mean that it will be the best for the job. When the best Intel processors keep up with the times, what are you going for? i7 vs i9? Well, it obviously depends on what your new PC is actually designed for, so we decided to compare the processor! nine0003
Don’t worry, knowing the essentials will help you make your next purchase. In this article, we will look at the main differences between these two high-end processor families.
In this article, we will look at the main differences between these two high-end processor families.
Content
- Intel Core i7 against i9: What is the difference of
- The main concept
- What is Kesh
- Hyper Threading
- So which processor is better for you
. i9: What’s the Difference
The Intel Core i3, i5, and i7 processor families have been around for more than a decade. The i9 processors were released in 2017. Since their release, these processors have dominated the desktop and laptop market and have witnessed major advances in microarchitecture during that time.
Thus, the 9th generation Intel processors completed Hyper-Threading with i7 and introduced the Intel Core i9 family. As you can see from this comparison, the highly regarded i7 seems to be relegated mainly to gaming and light applications, while the i9 familytakes on enthusiasts.
Core concept
The best Intel i7 and i9 processors have more cores, but does it matter? All Intel 9th Gen i7 and i9 models ship with eight physical cores, just like the older 8th Gen i7 processors. Generally speaking, Core i7 processors have six to eight cores, while all i9 processors ship with a minimum of eight.
Generally speaking, Core i7 processors have six to eight cores, while all i9 processors ship with a minimum of eight.
The main difference between these processors is Hyper-Threading, but we’ll get to that shortly. The number of cores starts to look different when you take into account the HEDT (High Performance Desktop) series models for both processor families. These enthusiast workstation processors will have up to 18 cores. However, if you are looking for a gaming PC, it will be overkill, not to mention expensive. nine0003
What is a cache? The cache, in fact, is the built-in memory of the processor and is responsible for faster access to data. The increased cache size on a multi-threaded processor helps to perform multiple tasks more efficiently. i7 processors have 12 MB L3 cache, while i9 processors are usually equipped with 16 MB. X-series processors can be even bigger, with the i9-9980XE featuring 24.75MB of intelligent L3 cache. nine0003
Hyper Threading
When looking at the key differences between the i5 and i7 processor families, notice that Intel has slightly tarnished the branding of the highly respected i7 processors. This happened because with the release of the 9th generation they removed Hyper-Threading. Now only the mainstream 9th gen i9 models will ship with Hyper-Threading (8c/16t), guiding this line of processors towards multitasking, but there’s still a lot of gaming power there nonetheless. nine0003
This happened because with the release of the 9th generation they removed Hyper-Threading. Now only the mainstream 9th gen i9 models will ship with Hyper-Threading (8c/16t), guiding this line of processors towards multitasking, but there’s still a lot of gaming power there nonetheless. nine0003
Clock speed
Higher clock speed means your processor can process more instructions per second. A higher clock speed usually equates to better performance, but this largely depends on what tasks the processor is performing.
9th Gen Intel Core i7s and i9s mostly ship with base clocks around 3.6GHz, with only the maximum boost rates slightly different (4.9/5.0GHz, respectively). These numbers apply to older models from both processor families and should not greatly influence your decision making. You will find that X-series processors with higher core/thread counts will have much lower clock speeds and higher speeds. This comparison isn’t entirely fair, as HEDT processors are designed to be a bit slower, but they can run a lot more applications without wasting a lot of power. nine0003
nine0003
So which processor is best for you
So i7 vs i9, what are you up to? While there’s an argument that both could be part of an enthusiast’s repertoire, the i9 definitely takes multitasking. Obviously, which family of processors you choose depends a lot on what you plan to use your PC for. It’s not difficult, the Core i7 is definitely a high-end gaming oriented processor, and if you opt for the older 8th gen model, you can also take advantage of some of the Hyper-Threading capabilities. Standard LGA1151 connectors for i9offer much more than just high clock speeds, making them a worthy choice for streamers and content creators.
While I feel like the i9 series is lost among the latest AMD Ryzen desktop processors and Threadripper for multitasking, it still offers reasonable clock speeds to give Intel fans something to think about. The bottom line is that while both processors are powerful, you’ll need the i9 for heavy-duty workstation tasks and the i7 for fast computing and gaming! and gaming! nine0003
The difference between Core i7 and Core i9
Whether you’re upgrading an aging desktop or just want to stay at the forefront of what’s in laptops, the Intel Core i7 and Core i9 processor lineup is loaded with powerful workhorse options . Most of them can handle just about any task you give them. But Intel offers many different processors with slightly different names.
Most of them can handle just about any task you give them. But Intel offers many different processors with slightly different names.
When you’re buying or building a PC, you need to know the really important differences between these two chip lines — a level of nuance that goes beyond just Intel’s i7 vs. i9 marketing approach.. What is the best CPU class for your next machine? Let’s dive into the details of each of them to find out.
Intel Core i7 and Core i9: A Brief History
Intel’s original Core i7 line of high-end desktop processors traces back to the Core line itself, which was launched when the company launched its second-generation desktop chips back in 2008.
Intel Core i7 Processor
Since its inception, the Core i7 line has been anything from Intel’s best mid-range processors to, for a while, the most expensive consumer chips. As far as mainstream processors go, Core i7 offerings have recently been on the edge between low end content creation and high gaming performance. nine0003
nine0003
Although chips such as the 10-core Intel Core i9-10900K are now considered the favorite of PC gamers, when the Core i9 brand first appeared, it was released as a high-performance chip designed for the 7th generation of computers. Intel Core X-Series, a line of desktop processors for workstations.
In the following years, after these first X-series processors were released in the summer of 2017, the Core i9 entered the main Core line (on mainstream Intel sockets, now LGA 1200), and subsequent generations of the Core i9have become first-class options for fans of extreme games. These chips do a decent job at content creation, too, and ultra-tuned options like the Core i9-10900K hold several records as the best processors for maximizing frame rates in games.
Intel Core i9-10900K processor
In 2020, the latest models of the 10th generation Core i9 line span from the mega-core monsters of the Core X-Series, led by the Core i9-10980XE Extreme Edition (18 cores!), to the more mainstream 10-core Core i9-10900K.
As for the Core i7, its reputation for maximum power has been shaken a bit since the release of the 9th Gen Core i7 chips. With these processors, Intel dropped support for Hyper-Threading, a multi-threading technology that allows your computer to run two independent processing jobs on the same core at the same time.
But as the community strongly resists this move, Intel has not only reinstated multithreading in its 10th Gen Core i7 lineup, but has extended threading performance enhancement technology all the way to desktop Core i5 chips. For those who do a lot of content creation, this feature is a must. nine0003
There are differences in the specifications between the Core i7 and Core i9 lines, their complexity differs slightly and in most cases the difference is only a few tenths. But these small differences can sometimes make or break the product you choose. So let’s see how things are today and also take a quick look into the past to see how much they’ve grown.
Intel Core i7 vs. Core i9 Processors: Detailed Specs
To begin the process of comparing processors, it’s always a good idea to first understand what you’re working with on simple specs. We have compiled spec lists for the three major categories of latest processors that Intel has released under the Core i9 badges.and i7, covering the last three generations of chips in three classes: general desktops, high-end desktops (more commonly referred to as «HEDTs»), and laptop/mobile phones. First, the Core i9 processors…
As you can see above and below, almost every chip found in a Core i7 or Core i9 is designed to deliver high performance far beyond the number of cores and capabilities of the processors that occupy the Core i5 or Core i9 lines. Core i3 10th generation. These are powerful chips designed from the ground up for content creators and avid gamers to get the most out of what Intel has to offer in the mainstream desktop, laptop and HEDT markets. nine0003
If you’re wondering what all those letters at the end of each processor mean, here’s a brief description. The Core i7 and Core i9 lines (in major desktop and mobile device families) come with integrated graphics processing units (IGPs), although Intel also offers models without IGPs. Those without an IGP are designated with an «F» suffix. (The entire Core X-Series never offered on-chip IGPs and is an exception to «F»; they all end in «X» or «XE». These processors must be used with a graphics card.
The Core i7 and Core i9 lines (in major desktop and mobile device families) come with integrated graphics processing units (IGPs), although Intel also offers models without IGPs. Those without an IGP are designated with an «F» suffix. (The entire Core X-Series never offered on-chip IGPs and is an exception to «F»; they all end in «X» or «XE». These processors must be used with a graphics card.
Processors without the «F» suffix contain Intel UHD Graphics 630 IGPs in 10th generation chips. Though anyone serious about gaming will pair the processor with a discrete graphics card to get the most out of their chip purchase. This applies to both desktop and mobile systems.
Next are the main desktop chips that have a «T» at the end of the model number. They are what Intel calls its line of «power-optimized» processors that run at lower powers and are designed for smaller or thermally constrained PCs. Then comes «K»: this letter on any of the chip models means that their cores are unlocked for overclocking. Desktop chips K, KF, KS or mobile HK can be overclocked at will. nine0003
Desktop chips K, KF, KS or mobile HK can be overclocked at will. nine0003
«S» denotes a rare special or limited edition CPU, while «H» and «HK» denote high performance variants of Intel notebook processors. Intel Core i9s for laptops is only available in H variants; in the U series, you can see much lower power consumption Core i7 processors designed for thin and light laptops.
«S» indicates a rare special or limited edition processor, while «H» and «HK» both indicate powerful variants of Intel notebook processors. Intel Core i9for laptops only available in H variants; in the U-series, Core i7 processors with significantly lower power consumption, designed for thin and light laptops.
Together, the Core i7 and Core i9 represent the pinnacle of Intel’s consumer-grade processor lineup, at least for pure framerate gaming and single-threaded applications, both of which continue to dominate cost-equivalent offerings from AMD. AMD deals tend to win when all cores come into play because AMD’s Ryzen processors at the same price tend to offer more affordable cores and threads for the same money. nine0003
nine0003
In general, you’ll find a greater variety of Core i7 processors in the notebook and mobile market, while the Core i9 line is more focused on desktop and HEDT offerings.
Core i7 vs. Core i9: desktop performance
The Core i7 and Core i9 chip lines only truly stretch their legs in desktop systems due to their high power consumption and heat dissipation (compared to options in the Core i3 and i5 lines) . Their serious power is better managed in desktop PC builds, which can use custom cooling and beefier PSUs. nine0003
Here’s a side-by-side look at Core i7 and Core i9 desktop processors that have been tested over the past few years in four key benchmarks that determine pure processor power with all cores and threads in games.
As expected, in Intel’s top consumer and HEDT processors, it performs directly to specifications for their respective price ranges. It’s rare that you’ll see any of the company’s processors perform faster than the more expensive option.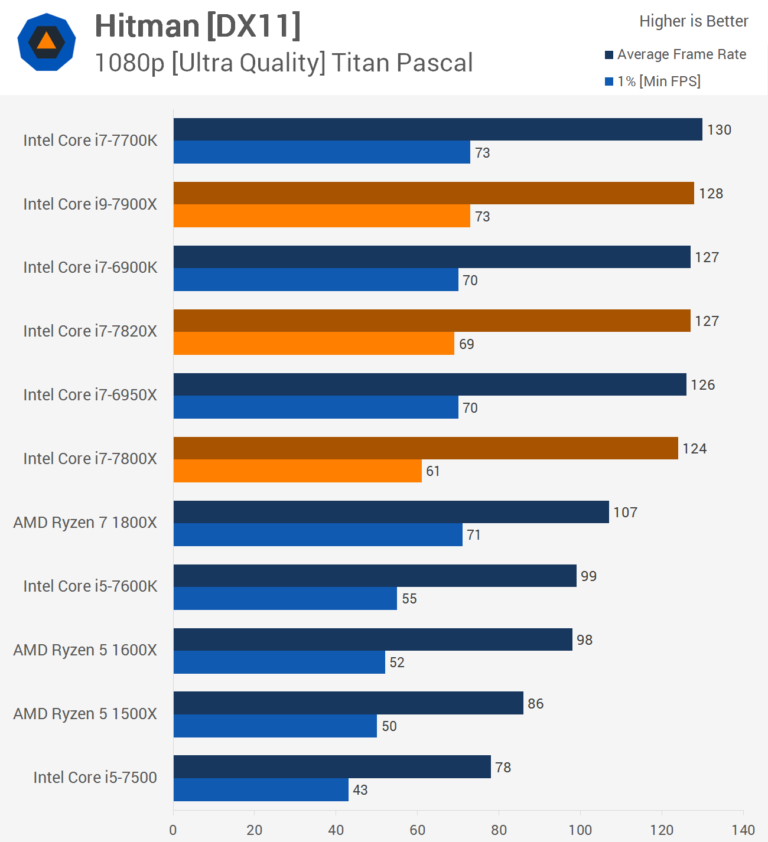 nine0003
nine0003
These four benchmarks scale well with more cores and threads, and you can see how Core i9 Core X-Series chips (on socket LGA 2066) far outperform mainstream Core i9 chips on LGA 1151 and now on LGA 1200. In a way, the lesson to be learned from this — aside from how the Core i7 chip series stacks up against the Core i9 — is how Core i9 on a single desktop platform (HEDT) can far outperform Core i9 chips on more mainstream desktop platforms. Intel. nine0003
But one of the few exceptions to this rule is the Core i9-9900KS, which was a limited edition Core i9-9900K that was tested to run at high clock speeds on more cores. However, it has not received wide distribution. Essentially, Intel picked its best 9900Ks and sold them at a small premium.
As you can see from the diagrams above, there is not that much variation between different chip models in each Core i7 or i9 line on the same platform. The big leap has been from mainstream processors to Core X-Series HEDT processors. And the actual performance gains can vary depending on the type of workload you give the processor the most. nine0003
And the actual performance gains can vary depending on the type of workload you give the processor the most. nine0003
Core i7 and Core i9 laptops: it’s all about the H series
The laptop market now offers far fewer options than desktop PCs when it comes to Core i9 processors. As mentioned earlier, Intel’s mobile processors for powerful laptops are called the H-Series, whose names end in «H» or «HK». Core i9 chips only appear in this series, as do some Core i7s. You’ll also see plenty of Core i7 processors in Intel’s U-series, but they’re designed for thin laptops, not powerful machines. nine0003
In its current lineup of 10th generation H-series chips dubbed «Comet Lake-H», Intel only offers the Core i9-10880H and i9-10980HK (for large and powerful laptops that can fit them), while how Core i7 machines are more common. You’ll see Core i7 models pick up performance as Intel’s 11th Gen «Tiger Lake» laptop processors roll out, but for now, they’re all low-power processors. The company has yet to make any official announcements about the 11th Gen H-series processors for Core i7 or Core i9 laptops.. Intel has announced plans to release an octa-core Tiger Lake chip in the future, but right now the most powerful confirmed mobile Intel processor you can find is the Core i7-1185G7.
The company has yet to make any official announcements about the 11th Gen H-series processors for Core i7 or Core i9 laptops.. Intel has announced plans to release an octa-core Tiger Lake chip in the future, but right now the most powerful confirmed mobile Intel processor you can find is the Core i7-1185G7.
Laptop with Tiger Lake Core i7-1185G7
In general, while Core i7 and i9 processors are useful in heavy-duty performance or gaming laptops, their higher power consumption and higher thermal output often mean heavier designs that are not as portable like i3 or i5 chips. Let’s leave it up to you to decide what’s right for you, but in general for gaming laptops and mobile workstations, it’s almost exclusively the world of Core i7 H-Series processors. nine0003
Note. AMD’s latest offerings in Ryzen 4000 H-Series laptop processors (AMD uses the same «H» and «U» nomenclature) have often outperformed anything Intel has offered in its 10th Gen line (e.g. in laptops like MSI Bravo 15).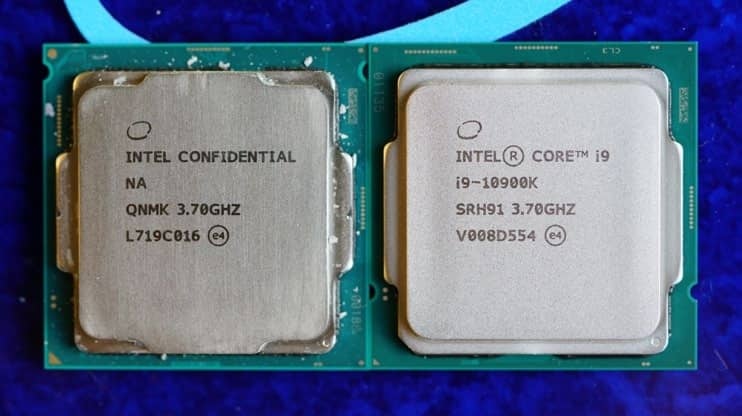 This story could quickly change if the 11th Gen Tiger Lake H-Series laptops arrive.
This story could quickly change if the 11th Gen Tiger Lake H-Series laptops arrive.
Gaming: Do you need a Core i7 or Core i9 for your desktop PC?
For most gamers i7 and i9 chip linea little overkill to justify their higher price compared to the i3 and i5 chips. This is because while having eight or 10 cores is great for task performance and content creation, few games know how to take advantage of more than four cores at once. Gaming test results speak for themselves…
In both synthetic graphics benchmarks like 3DMark and AAA gaming benchmarks like Far Cry 5, the Intel Core i5-10600K is only slightly slower than the Core i9-10900K in 1080p results, and at 4K resolution there is almost no difference.
Games like GTA V , do have the ability to use up to six cores at the same time in difficult situations, and Civilization series games will use as many cores as you can provide them. But, in general, these games are an exception to the rule of four cores.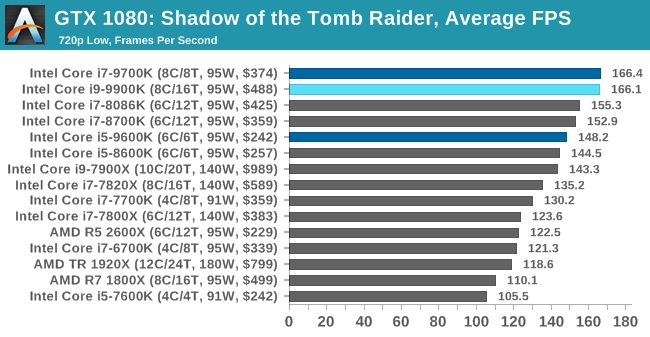
This may change as gamers update their new PlayStation 5 and Xbox One Series X game consoles globally to the new AMD-based octa-core processors. However, both the PS4 and Xbox One originally shipped with octa-core processors, and it’s been seven years since they were released, and there’s no sign that developers are building their games to push the processors beyond the comfortable maximum usage of four cores. nine0003 Intel Core i9-9900KS
Also, while the Core i7 is the best choice for gamers who want to maximize the performance of their next build on a budget, they might also consider options like the Core i5-10600K. With six cores and 12 threads, the Core i5-10600K is more than well equipped to handle just about every PC game on the shelves, and it costs a lot less than the current model’s desktop chips in the Core i7 or i9 lines.
However, Core i9The -10900K is still the best of the best when it comes to straight wins in games, posting record-breaking results in almost every test. If budget isn’t an issue and all you want is the fastest gaming processor on the shelves in the second half of 2020, the Core i9-10900K is the current king.
If budget isn’t an issue and all you want is the fastest gaming processor on the shelves in the second half of 2020, the Core i9-10900K is the current king.
Intel Core i7 vs. Core i9: which processor level is better?
When it comes to Core i7 vs. Core i9, the differences between the two don’t make one clearly «better» than the other across the board. Rather, it comes down to which platform makes the most sense for your energy needs, your budget, and the type of work you plan to do most often. And by «platform» we don’t mean Core i7 versus Core i9generally; we’re talking about the i7 and i9 chips in the Intel Core X-Series versus the i7 and i9 chips on the mainstream chip maker platforms.
The i9 line is the pinnacle of Intel’s consumer segment, representing the pinnacle of what Intel can do on both desktops and laptops, while the i7 fills a niche, more modestly priced professional content creation engine and reliable driver for games all over the world. Pretty much the same as the i9. .. but slightly smaller in specs, price and, as expected, performance. But sometimes stepping down is the right choice if you don’t need the power that the Core i9 provides.. The money you save will allow you to spend more on another part of the PC, such as an SSD, for more tangible benefits.
.. but slightly smaller in specs, price and, as expected, performance. But sometimes stepping down is the right choice if you don’t need the power that the Core i9 provides.. The money you save will allow you to spend more on another part of the PC, such as an SSD, for more tangible benefits.
However, in the second half of 2020, not Core i7 vs. Core i9, but Core i7 vs. Ryzen 7 or Core i9 vs. Ryzen 9. Outside of the world of esports gaming, neither the Intel Core i7-10700K nor the Core i9-10900K are too competitive with AMD’s current cost-comparative options, namely the Ryzen 7 3700X and Ryzen 9 3900X.
Ryzen 9 processor3900X
Core i9-10900K, as the 12-core, 24-thread Ryzen 9 3900X has been found to outperform it so regularly in content creation that in 2020 Ryzen is usually the smartest option. For gamers, the Core i9-10900K’s clear framerate win might be tempting at first, but in our opinion, the results aren’t far enough ahead of the 3900X to make any Core i9 processors a clear recommendation over what AMD would offer at the same price.
