Can i overclock my QuadCore Intel Core 2 Quad Q8300 ?
2012-07-23, 04:43 AM
#1
Hello, i will buy a new one in a couple of months… but meanwhile i`d like to use the most of what i have.
So i tried to OC it but the pc didnt boot, i changed from x333 to x374 and it failed, so before i do some crap ill regreat i`d like some light
My config:
QuadCore Intel Core 2 Quad Q8300, 2500 MHz (7.5 x 333)
Mobo: Gigabyte G41MT-S2P
2x Corsair Vengeance 4 GB DDR3-1866
Satellite SL-X1000EPS 1000W
ATI Radeon HD 5770thanks before hand
Reply With Quote
2012-07-23, 04:56 AM
#2
you just jumped to much into the OC… try going with 10 mhz increments instead until it wont boot… then if you feel comfortable with it.. add voltage… 1 step up at a time till stable.. if not.. back off the mhz till stable. 41mhz to start is just too big of a jump in FSB
Reply With Quote
2012-07-23, 05:51 AM
#3
Dont forget to decrease the RAM multiplier as well, because everytime you increase the FSB , you memory overclock as well.
So this can make your system unstable, so try to stay as close as 1866mhz as possible , if you go way too low , you can always tight the timing.
Also im just wondering if you got an aftermarket cooler , because this is mandatory if you want to OC. Intel stock heatsink is just not good enough to keep your CPU cool, if you increase the voltage and FSB.
Reply With Quote
2012-07-23, 04:55 PM
#4
Originally Posted by mnm
Also im just wondering if you got an aftermarket cooler , because this is mandatory if you want to OC. Intel stock heatsink is just not good enough to keep your CPU cool, if you increase the voltage and FSB.
Aftermarket cooler definitely isn’t mandatory. As far as you watch your temperatures while stress testing there’s nothing wrong with trying. You should actually be able to quite confortably overclock to 2.8-3.
0GHz region with stock cooler. You won’t obviously be as effective with stock as you’d with aftermarket cooler but there should still be some headroom above the stock speeds.
I’d try that 7.5 x 374 again with adjusted voltage, something like 1.3 volts to start with. If it still fails you can try upping it by 0.025 increaments (1.325 -> 1.35 -> 1.375..etc) all the way up to 1.4 area which is still considered safe (if you feel like pushing it, 1.45 is the absolute maximum I’d risk).
If for some reason that still doesn’t boot start reducing the FSB. Controversially, if it works you can up the FSB as long as you stress test between tries and watch the temperatures (75-80 degress during prime 95 would still be reasonable, if it goes above 85-90 I’d definitely abort and reduce either volts or FSB).
You can try to fine tune by reducing RAM speed and/or losen the timings. For more tips and settings to fiddle with try to google «Intel core 2 quad Q8300 overclocking guide), should always yield some additional info.

Good luck and make sure to post results!
Reply With Quote
2012-07-23, 09:23 PM
#5
Thanks for the tips, later today ill test them and post it
———- Post added 2012-07-24 at 12:55 PM ———-
Well i tried it all and the max i could reach was
from 7.5×333 -> 7.5 x 343 now with 1.3 voltsi increased the volatage but didnt pass 343 anyway, othe thing i did was change the memory multiplier.
A lil wierd thing i found was that I did the performance test from Windows 7, and my points went down from 7.2 to 7.1 for the processor and the memory, is this right?Also theres any more i can do or thats my limit? thanks
———- Post added 2012-07-24 at 01:58 PM ———-
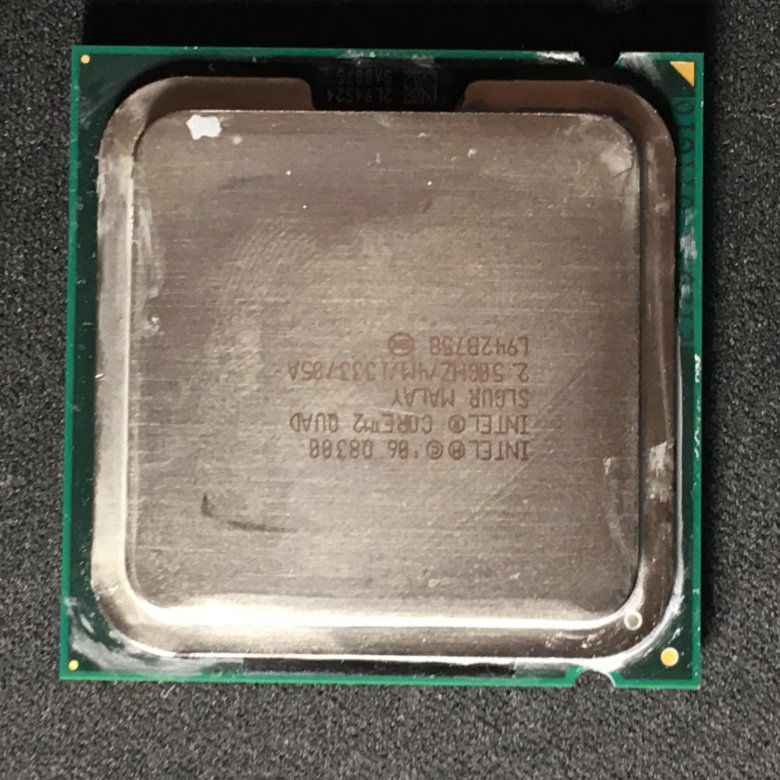
Some pics of what i have now:
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 05:45 PM
#6
i wanna OC my Q8300, and i have the same Mobo, so ill be seeing your results and try myself later.
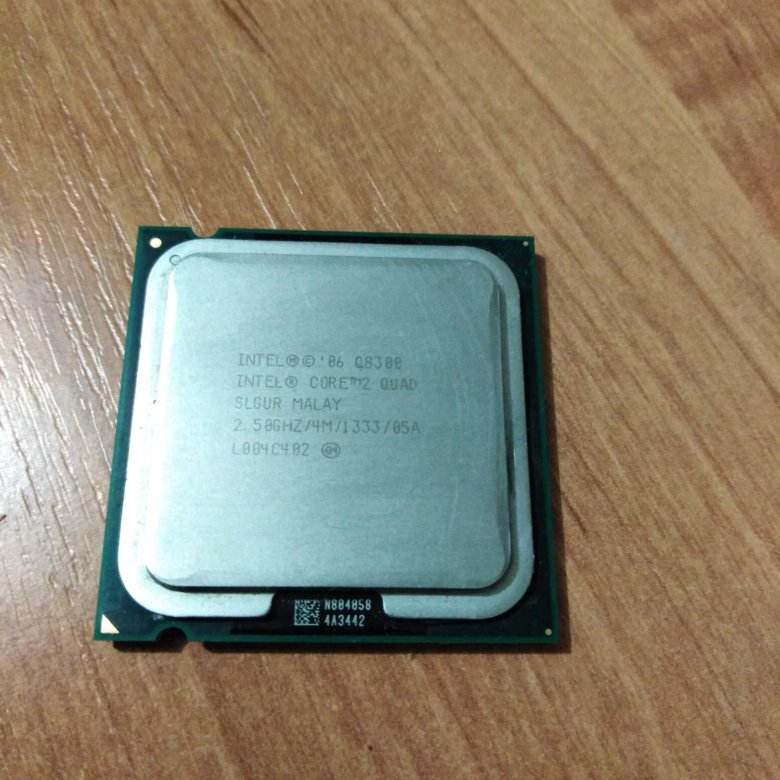

Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 06:02 PM
#7
Originally Posted by Ghâzh
Aftermarket cooler definitely isn’t mandatory. As far as you watch your temperatures while stress testing there’s nothing wrong with trying. You should actually be able to quite confortably overclock to 2.8-3.0GHz region with stock cooler. You won’t obviously be as effective with stock as you’d with aftermarket cooler but there should still be some headroom above the stock speeds.
I’d try that 7.5 x 374 again with adjusted voltage, something like 1.3 volts to start with. If it still fails you can try upping it by 0.025 increaments (1.325 -> 1.35 -> 1.375..etc) all the way up to 1.4 area which is still considered safe (if you feel like pushing it, 1.45 is the absolute maximum I’d risk).
If for some reason that still doesn’t boot start reducing the FSB.
Controversially, if it works you can up the FSB as long as you stress test between tries and watch the temperatures (75-80 degress during prime 95 would still be reasonable, if it goes above 85-90 I’d definitely abort and reduce either volts or FSB).
You can try to fine tune by reducing RAM speed and/or losen the timings. For more tips and settings to fiddle with try to google «Intel core 2 quad Q8300 overclocking guide), should always yield some additional info.
Good luck and make sure to post results!
What? TCASE for Q8xxx is 70c. If he was hitting temperatures of 75-80c, that would be ending the life of said processor rather quickly.
Further, suggesting someone overclock 500Mhz on stock cooling is absurd. Please don’t suggest uninformed users misinformation that could lead to them ruining their hardware.
@ OP — Stop what you’re doing and buy an aftermarket cooler if you wish to overclock. Doing so on stock cooling is a death sentence to your processor.
i7-4770k — GTX 780 Ti — 16GB DDR3 Ripjaws — (2) HyperX 120s / Vertex 3 120
ASRock Extreme3 — Sennheiser Momentums — Xonar DG — EVGA Supernova 650G — Corsair H80i
build pics
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 06:12 PM
#8
Originally Posted by glo
@ OP — Stop what you’re doing and buy an aftermarket cooler if you wish to overclock.
Doing so on stock cooling is a death sentence to your processor.
Really should have been my first change, sorry.
But dou u think the way it is now is a problem for my hardware? or do you suggest me to go to the old configuration?
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 07:19 PM
#9
Originally Posted by glo
What? TCASE for Q8xxx is 70c. If he was hitting temperatures of 75-80c, that would be ending the life of said processor rather quickly.
Further, suggesting someone overclock 500Mhz on stock cooling is absurd. Please don’t suggest uninformed users misinformation that could lead to them ruining their hardware.
@ OP — Stop what you’re doing and buy an aftermarket cooler if you wish to overclock. Doing so on stock cooling is a death sentence to your processor.
I might have been too broad by just speaking of temperatures.
I had no intention to advise him to aim for 75-80c TCase but rather core temperatures at around that area, as quite frankly they are two different things. My mistake.
Never did I suggest him to overclock 500Mhz stright away. Like I said there should be no damage done if you take it slowly and watch your temperatures and stress test in between tries. Doesn’t matter if you had a stock or aftermarket cooler as long as you don’t go crazy and jump the voltage or frequancy to ridiculous amounts.
As far as the «safe» suggested core temps go, the Q8xxx will shut down at around 110c to prevent damage. Even if you listened to no word at all of what I’ve said and managed to hit that, there’d most likely be no permanent damage whatsoever. Most likely as there’s always risk in overclocking. The OP’s exact words were: «i will buy a new one in a couple of months… but meanwhile i`d like to use the most of what i have.». To me that sounds like he’s not trying to make the CPU last for the next ten years but rather make the best do with what he has and be done with it afterwards.

And to be honest here, it’s nearly five years old chip, it’s cheap by todays standard. Better to play with something that’s quite redundant rather than blow your brand new 3960x that’s hundred times as costly don’t you think?
And I’m not trying to promote reckless overclocking here. Just saying that if you are careful it’s just all right to experiment with it and see where’s the limit.
But do u think the way it is now is a problem for my hardware? or do you suggest me to go to the old configuration?
As long as you are within reasonable temperatures and/or voltage it won’t damage anything. Have you stress tested those settings yet? Download Prime 95 and let it run for twenty minutes or so in blend test while watching the temps. If it goes above 80 (watch for core 1,2,3 and 4 temps in your monitoring program), you are stretching it. If it doesn’t you are quite safe.
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 08:20 PM
#10
Originally Posted by Ghâzh
Never did I suggest him to overclock 500Mhz stright away.

I’d try that 7.5 x 374 again with adjusted voltage
It is 300 instead of 500 but still way to much for one go for that CPU.
Best way is to increase the FSB by steps of prob 5, and when it doesnt boot try to increase voltage. That is (i think) the safest way off overclocking.
And i think you can turn the FSB increases for the memory off. So it would only have an impact on the CPU, which should also increase stability.
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 08:48 PM
#11
Originally Posted by Ghâzh
Have you stress tested those settings yet? Download Prime 95 and let it run for twenty minutes or so in blend test while watching the temps. If it goes above 80 (watch for core 1,2,3 and 4 temps in your monitoring program), you are stretching it. If it doesn’t you are quite safe.
after one hour using Prime 95 i got this
Originally Posted by Zeara
And i think you can turn the FSB increases for the memory off.
So it would only have an impact on the CPU, which should also increase stability.
Decrease the FSB for the memory? In the case i got to its limit the way it is now, i still whould go back? I thought the increase was a good thing, seeing the PC looks stable.
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 09:07 PM
#12
Originally Posted by Hayna
Decrease the FSB for the memory? In the case i got to its limit the way it is now, i still whould go back? I thought the increase was a good thing, seeing the PC looks stable.
If it is stable dont touch it
I had an E8400 and tried ocing it, and one of the first things i found was that you should turn that off. Meaning the RAM would just run at it normal speeds, seeing as RAM is usually not the limiting factor, and OCing rarely give any increases in games. Also OCing ram can be pain, AFAIK, which can negatively affect the stability.
Reply With Quote
2012-07-24, 09:32 PM
#13
One thing that i didnt get it is that after these changes the Default Windows 7 Test, my scores for Processor and Ram decreased from 7.2 —> 7.1 , i really thought the would increase =/
Reply With Quote
2012-07-25, 10:47 AM
#14
Windows performance index is just plain inaccurate and can’t be taken seriously. If you want something better use cinebench (free) or such, run a benchmark and compare results. Wouldn’t hold my breath though as thats really mild overclock and different results might just be within margin of error.
Reply With Quote
Core2 Quad Q6600 vs Core2 Quad Q8300 — Red Dead Redemption 2 with GTX 1660 Benchmarks 1080p, 1440p, Ultrawide, 4K Comparison
GTX 1660 with
Intel Core2 Quad Q6600 @ 2.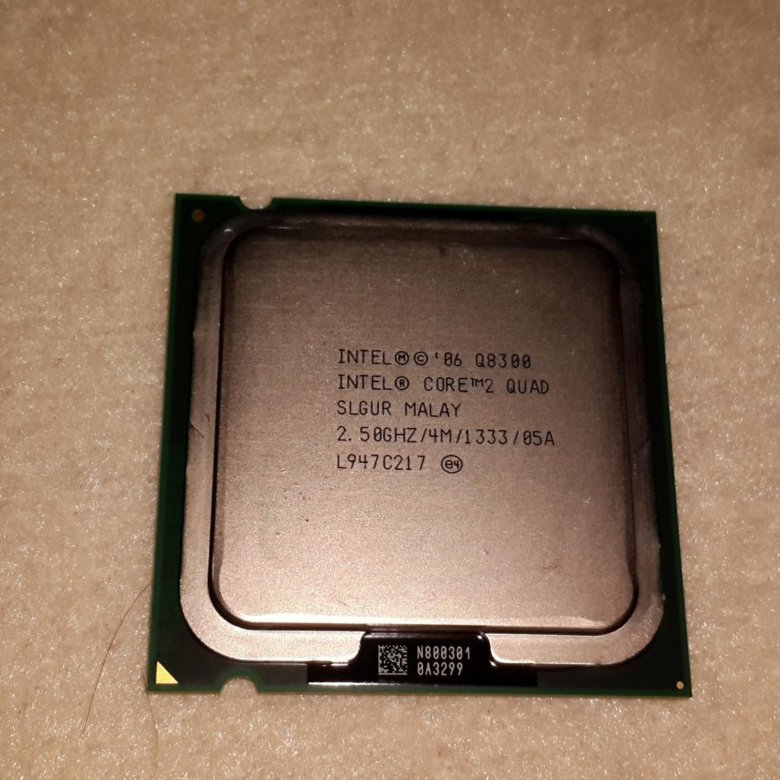 40GHz
40GHz
Red Dead Redemption 2
GTX 1660 with
Intel Core2 Quad Q8300 @ 2.50GHz
Core2 Quad Q6600
Core2 Quad Q8300
Multi-Thread Performance
2955 Pts
2986 Pts
Single-Thread Performance
923 Pts
1057 Pts
Red Dead Redemption 2
Core2 Quad Q6600 vs Core2 Quad Q8300 in Red Dead Redemption 2 using GTX 1660 — CPU Performance comparison at Ultra, High, Medium, and Low Quality Settings with 1080p, 1440p, Ultrawide, 4K resolutions
Core2 Quad Q6600
Core2 Quad Q8300
Ultra Quality
| Resolution | Frames Per Second |
|---|---|
| 1080p |
14.1 FPS |
| 1080p |
16.1 FPS |
| 1440p |
11.5 FPS |
| 1440p |
13.1 FPS |
| 2160p |
7.3 FPS |
| 2160p |
8.3 FPS |
| w1440p |
10. |
| w1440p |
11.5 FPS |
High Quality
| Resolution | Frames Per Second |
|---|---|
| 1080p |
29.1 FPS |
| 1080p |
32.7 FPS |
| 1440p |
24.3 FPS |
| 1440p |
27.3 FPS |
| 2160p |
16.3 FPS |
| 2160p |
18.2 FPS |
| w1440p |
21.7 FPS |
| w1440p |
24.3 FPS |
Medium Quality
| Resolution | Frames Per Second |
|---|---|
| 1080p |
44.1 FPS |
| 1080p |
49.3 FPS |
| 1440p |
37.2 FPS |
| 1440p |
41.5 FPS |
| 2160p |
25.3 FPS |
| 2160p |
28. |
| w1440p |
33.3 FPS |
| w1440p |
37.2 FPS |
Low Quality
| Resolution | Frames Per Second |
|---|---|
| 1080p |
74.2 FPS |
| 1080p |
82.6 FPS |
| 1440p |
62.9 FPS |
| 1440p |
69.9 FPS |
| 2160p |
43.2 FPS |
| 2160p |
48.1 FPS |
| w1440p |
56.5 FPS |
| w1440p |
62.9 FPS |
Core2 Quad Q6600
Core2 Quad Q8300
Compare Core2 Quad Q6600 vs Core2 Quad Q8300 specifications
Share Your Comments 60
Compare Core2 Quad Q6600 vs Core2 Quad Q8300 in more games
Elden Ring
2022
God of War
2022
Overwatch 2
2022
Forza Horizon 5
2021
Halo Infinite
2021
Battlefield 2042
2021
Assassin’s Creed Valhalla
2020
Microsoft Flight Simulator
2020
Valorant
2020
Call of Duty: Black Ops Cold War
2020
Death Stranding
2020
Marvel’s Avengers
2020
Godfall
2020
Cyberpunk 2077
2020
Apex Legends
2019
Anthem
2019
Far Cry New Dawn
2019
Resident Evil 2
2019
Metro Exodus
2019
World War Z
2019
Gears of War 5
2019
F1 2019
2019
GreedFall
2019
Borderlands 3
2019
Call of Duty Modern Warfare
2019
Red Dead Redemption 2
2019
Need For Speed: Heat
2019
Assassin’s Creed Odyssey
2018
Battlefield V
2018
Call of Duty: Black Ops 4
2018
Final Fantasy XV
2018
Shadow of the Tomb Raider
2018
Forza Horizon 4
2018
Fallout 76
2018
Hitman 2
2018
Just Cause 4
2018
Monster Hunter: World
2018
Strange Brigade
2018
Assassin’s Creed Origins
2017
Dawn of War III
2017
Ghost Recon Wildlands
2017
Destiny 2
2017
PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds
2017
Fortnite Battle Royale
2017
Need For Speed: Payback
2017
For Honor
2017
Project CARS 2
2017
Forza Motorsport 7
2017
Ashes of the Singularity: Escalation
2016
Battlefield 1
2016
Deus Ex: Mankind Divided
2016
Doom
2016
F1 2016
2016
Total War: Warhammer
2016
Overwatch
2016
Dishonored 2
2016
Grand Theft Auto V
2015
Rocket League
2015
Need For Speed
2015
Project CARS
2015
Rainbow Six Siege
2015
Counter-Strike: Global Offensive
2012
League of Legends
2009
Minecraft
2009
Overview of the Intel Q8300 processor based on the Yorkfield core / Processors and memory
In virtually every industry, there is a division of products into target categories. There are plenty of cheap products with basic features and functionality; they are intended for the vast majority of users. For a small group of experts and professional users, expensive devices are oriented, with a lot of fine-tuning and specific functions. And the gap between these two groups of users is not as small as it might seem at first glance.
There are plenty of cheap products with basic features and functionality; they are intended for the vast majority of users. For a small group of experts and professional users, expensive devices are oriented, with a lot of fine-tuning and specific functions. And the gap between these two groups of users is not as small as it might seem at first glance.
nine0003
It includes those people who no longer have enough entry-level opportunities; these users, so to speak, have «grown up», and budget products no longer satisfy them. On the other hand, top-end products are quite expensive for them, and in terms of experience, they have not yet «grown up» to it. And it is for this group of people that companies produce various mid-level products with an intermediate set of functions. And it does not matter at all what kind of products we are talking about, whether they are mobile phones or cameras (which are now almost the same thing), stereos or cars.
nine0003
Concluding this thought, we want to emphasize that many novice users often buy mid-range products «for growth». In other words, at the initial stage, they use only basic features, but with the growth of experience, they gradually use more and more functions. Marketers are remarkably successful at exploiting this idea, and in some industries, mid-priced products have the highest percentage.
In other words, at the initial stage, they use only basic features, but with the growth of experience, they gradually use more and more functions. Marketers are remarkably successful at exploiting this idea, and in some industries, mid-priced products have the highest percentage.
Now let’s move on to the subject of our review, namely, the quad-core Intel Q8300 processor based on the Yorkfield core. Initially, all processors with four cores were intended exclusively for workstations used by professional users. The latter use software packages corresponding to their level, which have optimization of multi-threaded calculations. For such users, our recommendation has always remained the same: to achieve the highest performance, you need to purchase the latest platform (with the exception of NetBurst) and use the fastest processor, as well as the maximum possible (corresponding to the capabilities of the OS) amount of RAM.
nine0003
However, besides professionals, there are many other users who sometimes work with multi-threaded programs. Someone studies a new package in the evenings, someone makes a “coven”, and someone develops blanks at home in order to finish them at work the next day. It is these users who need an inexpensive processor with the maximum number of cores.
Someone studies a new package in the evenings, someone makes a “coven”, and someone develops blanks at home in order to finish them at work the next day. It is these users who need an inexpensive processor with the maximum number of cores.
Another group of users is completely far from multithreading and from computers in general. They buy quad-core processors because they are «twice as good as dual-core ones».
nine0003
The situation, in general, is not new — at one time, this is how megahertz bought. It is clear that these buyers do not get any real benefit from four cores, since the vast majority of home applications are not optimized for multithreading. Judge for yourself: after launching the game, you are forced to watch from one to four videos with logos of development companies and licensees. Another video can be introductory. And after the end of all the cutscenes, the game is just starting to load , and does it long enough. Why can’t the game load in parallel while playing the cutscenes? In principle, the answer is clear: programs without optimization are much easier to develop and, most importantly, financially more profitable!
Well, okay, we have said all this more than once in one form or another. Now let’s turn to Intel, which, after switching to a 45-nm process technology, quickly saturated the market with top-level quad-core processors. After that, Intel began to gradually introduce cheaper quad-core processors to the market, with somewhat reduced cache and relatively low clock speeds.
Now let’s turn to Intel, which, after switching to a 45-nm process technology, quickly saturated the market with top-level quad-core processors. After that, Intel began to gradually introduce cheaper quad-core processors to the market, with somewhat reduced cache and relatively low clock speeds.
nine0003
The first such product was the Q8200 processor based on the Yorkfield core, with a clock speed of 2.33 GHz and a 1333 MHz QPB bus. Recall that most of the top 4-core processors of the Q9xxx series have L2=12 MB cache (2x 6 MB), and only the Q9300 model is equipped with L2=6 MB (2x 3 MB). And so that cheaper processors do not outperform more expensive ones, Intel continued the practice of «cutting» the second-level cache, and for the Q8xxx series its volume was set at 4 MB (2x 2 MB). Accordingly, the «table of ranks» of 4-core Intel processors looks like this:
nine0003
| Name |
Core
|
Number of cores
|
Frequency, GHz
|
FSB, MHz
|
Multiplier
|
L2 cache, MB
|
| Core 2 Extreme QX9770 |
Yorkfield |
3. |
400 |
8 |
12 |
|
| Core 2 Extreme QX9650 |
Yorkfield |
4 |
3.0 |
333 |
9 |
12 |
| Core 2 Quad Q9550 |
4 |
2.83 |
333 |
8.5 |
12 |
|
| Core 2 Quad Q9450 |
Yorkfield |
4 |
2.66 |
333 |
8 |
12 |
| Core 2 Quad Q9300 |
Yorkfield |
4 |
2.5 |
333 |
7.5 |
6 |
| Core 2 Quad Q8300 |
Yorkfield |
4 |
2. |
333 |
7.5 |
4 |
| Core 2 Quad Q8200 |
Yorkfield |
4 |
2.33 |
333 |
7 |
4 |
In addition to these specifications, processors have one more parameter that is constantly changing (before the crisis, we would have written down). This is the retail price. For professionals, it does not play a role, but for semi-professional users it still plays. So there is good news for the latter: the Q8300 test processor costs about $230, and its OEM version costs about $200! And, roughly speaking, we get four processors with a frequency of 2.5 GHz for $50 each. From the point of view of professionals — it’s a freebie.
nine0003
So the freebie looks like this:
Reverse side:
The CPU-Z utility provides the following information:
Functionally, this processor is in no way inferior to its older counterparts. That is, the processor supports all extended instruction sets, as well as all modern Intel technologies in terms of energy saving. The only thing that distinguishes the processors of the «eighth» series from the «ninth» is the lack of virtualization technology.
That is, the processor supports all extended instruction sets, as well as all modern Intel technologies in terms of energy saving. The only thing that distinguishes the processors of the «eighth» series from the «ninth» is the lack of virtualization technology.
nine0003
Overclocking
A few words about overclocking. On the one hand, the Q8300 processor should be very attractive in terms of overclocking. This assumption is supported by the fact that the frequency potential of the Yorkfield core is in the region of 4 GHz. Moreover, we reached this frequency even more than a year ago, when we tested the Core 2 Extreme QX9650 processor. Since then, Intel has certainly optimized and improved the process, and the frequency potential has increased.
nine0003
However, there are some negative points to consider. Firstly, we overclocked the QX9650 by increasing the multiplier, which is unlocked for this model. On the contrary, the Q8300 has a locked multiplier, and the relatively high system bus frequency implies a rather low stock multiplier. He, in fact, is such, and is equal to 7.5; Plus, it’s still blocked.
He, in fact, is such, and is equal to 7.5; Plus, it’s still blocked.
As a result, in order to overclock to 4 GHz, the FSB frequency must be around 533 MHz. For most modern motherboards, this frequency is not something transcendental: we constantly reach frequencies of 550 MHz and higher. However, keep in mind that these tests are carried out with a dual-core processor, while a processor with four cores significantly increases the load on the system bus. As a result, the overclocker is forced to significantly increase the voltage on the FSB, increase the voltage of the PLL and adjust the GTL. Still, most enthusiasts face significant problems around 500 MHz. We also faced these problems: the final result is a stable FSB frequency of 480 MHz, which gave the resulting processor frequency of 3.6 GHz.
nine0003
On the one hand, the result can be considered quite good, since Intel uses the «best cores» for the production of expensive high-frequency processors, and what is left for cheap ones. On the other hand, we are left with the strong impression that if the multiplier were unlocked, we would easily run the Q8300 at 4 GHz.
On the other hand, we are left with the strong impression that if the multiplier were unlocked, we would easily run the Q8300 at 4 GHz.
Performance
The following equipment was used in the test system:
nine0003
| Test Equipment | |
| Motherboard | ASUS P5E3 Premium based on Intel X48 chipset Gigabyte EP35-DS4 based on Intel P35 chipset ASUS M3N-HT Deluxe Mempipe on NVIDIA nForce 780a SLI chipset ASUS M4A79 Deluxe on AMD 790FX chipset |
| Cooler | Gigabyte G-Power |
| Video card | ASUS 8800 GT (GeForce 8800 GT; PCI Express x16) Driver version: 180.48 WHQL |
| Sound card | — |
| HDD | Samsung HD160JJ |
| Memory | 2×1024 MB Qimonda DDR3-1333; 2×1024 MB GoodRAM DDR2 GP1066D264L5/2GDC |
| Housing | FSP 550W |
| OS | MS Vista |
First, let’s look at the results of synthetic tests.
Application software tests.
Video encoding (DivX, Xvid) measured in seconds, i.e. less is better.
Data compression (WinRAR) was measured in kb/s, i.e. more is better.
Now — tests of game programs.
Conclusions
In terms of performance, the Q8300 takes exactly the place that Intel marketers assigned it. That is, it is faster and more expensive than the Q8200 processor, but slower and cheaper than other quad-core Intel processors. And a few months ago, the conclusion would have sounded like this: when choosing a 4-core processor, you need to pay attention to Intel products and be guided by your financial capabilities.
nine0003
However, with the release of the new AMD Phenom II processors, the situation has become somewhat more complicated, as the choice has become larger, and it has become more difficult to solve the problem of choosing a processor. The fact is that the specific performance of AM3 processors is almost the same as that of Intel processors. And at the same time, AMD processors are cheaper. In particular, the Phenom II X4 805 retails for about $210 (March 2009). Accordingly, our advice to those users who are starting to work with professional software packages is as follows.
And at the same time, AMD processors are cheaper. In particular, the Phenom II X4 805 retails for about $210 (March 2009). Accordingly, our advice to those users who are starting to work with professional software packages is as follows.
nine0003
At the first stage, it is necessary to evaluate the degree of optimization of the software used for multi-threaded computing. If such optimization is present, then it makes sense to switch to 4-core processors. Then you need to determine which processors the software you use is optimized for, and based on this, purchase a processor from the right manufacturer. And only after that it makes sense to choose a specific processor model based on the cost.
For those users who plan to overclock their processor, we want to remind you again that the Q8xxx series processors have relatively low locked multipliers, and in most cases you will not be able to reach the technology limit of the Yorkfield core.
nine0003
By the way, if overclocking in professional workstations causes an unequivocal condemnation (because 100% stability is important there), then for a home system it is only welcome. The fact is that without significant financial costs, you can significantly increase productivity. At the same time, the loss of data or calculation results will not cause significant harm, since your semi-professional work is a kind of hobby.
The fact is that without significant financial costs, you can significantly increase productivity. At the same time, the loss of data or calculation results will not cause significant harm, since your semi-professional work is a kind of hobby.
— Discuss the material in the conference 95 watts at stock frequencies. When overclocked, the requirements increase.
Thanks to the built-in N/A video core, the computer can work without a discrete graphics card because the monitor is connected to the video output on the motherboard.
Price in Russia
Do you want to buy Core2 Quad Q8300 cheaply? Look at the list of stores that already sell the processor in your city.
family
- Core2 Quad Q8400
- Core2 Quad Q8200
Benchmarks Intel Core2 Quad Q8300
Speed in games
Performance in games and similar applications, according to our tests.
The performance of 4 cores, if any, and performance per core has the greatest impact on the result, since most games do not fully use more than 4 cores.
The speed of caches and working with RAM is also important.
Speed in office use
Performance in everyday work such as browsers and office applications. nine0003
The performance of 1 core has the greatest impact on the result, since most of these applications use only one, ignoring the rest.
Similarly, many professional applications such as various CADs ignore multi-threaded performance.
Speed in heavy applications
Performance in resource-intensive tasks loading a maximum of 8 cores.
The performance of all cores and their number have the greatest impact on the result, since most of these applications willingly use all the cores and increase the speed accordingly. nine0003
At the same time, certain periods of work may be demanding on the performance of one or two cores, for example, applying filters in the editor.
Data obtained from tests by users who tested their systems with and without overclocking. Thus, you see the average values corresponding to the processor.
Thus, you see the average values corresponding to the processor.
Speed of numerical operations
Simple household tasks |
||
|
nine0027 | ||
| Minimum | Average | Maximum |
| 47 | Memory: 65 | 76 9002 |
|
Memory 67.2 |
||
| 31 | 1 core: 38 | 40 |
|
nine0002 1 core
16.4 |
||
| 60 | 2 cores: 76 | 80 |
|
2 cores 16. |
||
Demanding games and tasks |
||
| Minimum | Average | Maximum |
| 95 | 4 cores: 142 | 160 |
|
4 cores 15.5 |
||
| 104 | 8 cores: 145 | 160 |
|
8 cores 8.3 |
Extreme |
||
| Minimum | Average | Maximum |
| 108 | All cores: 146 | 160 |
|
All cores 2. |
Different tasks require different CPU strengths. A system with few fast cores and low memory latency will be fine for the vast majority of games, but will be inferior to a system with a lot of slow cores in a rendering scenario. nine0003
We believe that a minimum of 4/4 (4 physical cores and 4 threads) processor is suitable for a budget gaming PC. At the same time, some games can load it at 100%, slow down and freeze, and performing any tasks in the background will lead to a drop in FPS.
Ideally, the budget shopper should aim for a minimum of 4/8 and 6/6. A gamer with a big budget can choose between 6/12, 8/8 and 8/16. Processors with 10 and 12 cores can perform well in games with high frequency and fast memory, but are overkill for such tasks. Also, buying for the future is a dubious undertaking, since in a few years many slow cores may not provide sufficient gaming performance. nine0003
nine0003
When choosing a processor for your work, consider how many cores your programs use. For example, photo and video editors can use 1-2 cores when working with filtering, and rendering or converting in the same editors already uses all threads.
Data obtained from tests of users who tested their systems both with overclocking (maximum value in the table) and without (minimum). A typical result is shown in the middle, the more filled in the color bar, the better the average result among all tested systems. nine0003
Compare
Benchmarks
Benchmarks were run on stock hardware, that is, without overclocking and with factory settings. Therefore, on overclocked systems, the points can noticeably differ upwards. Also, small performance changes may be due to the BIOS version.
Passmark
Intel Core i3-4030U
1867
Intel Core M-5Y70
1861
AMD A6-3620 APU
1860 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 9000 INTEL CORE ANTE0003
1858
AMD A10-5750M APU
1857
Intel Core2 Quad Q8300
1840
Intel Core i3-2100
1835
AMD Athlon II X3 455
1820
Intel Core i7-2637M
1811
Intel Core2 Quad Q8200
1800
Intel Core i5-2557M
1797
Tests in games Please note that the official requirements of developers in games do not always match the data of real tests.
 Also, the result is strongly influenced by the overclocking of the system and the graphic settings in the game. We test at high settings in FullHD resolution to get numbers close to real gameplay. nine0438
Also, the result is strongly influenced by the overclocking of the system and the graphic settings in the game. We test at high settings in FullHD resolution to get numbers close to real gameplay. nine0438
We’ve put together a list of parts that users most frequently choose when building a Core2 Quad Q8300 based computer. Also with these components, the best results in tests and stable operation are achieved.
The most popular config: motherboard for Intel Core2 Quad Q8300 — bin bin, video card — SVGA 3D, SSD — A400 240GB.
Features
Main
| Socket Installed in motherboards with a suitable socket. Note that a socket is not guaranteed to be compatible. The manufacturer may not add support to the BIOS. nine0027 | LGA 775 |
| Manufacturer Firm | Intel |
Presentation datePresentation in mass media, official information. |
2008-11-30 |
| Code name for the Microarchitecture family. | Yorkfield |
| GenerationCode name for the microarchitecture generation. |
Performance
| Cores The total number of physical cores. | 4 |
| ThreadsNumber of threads. The number of logical processor cores that the operating system sees. | 4 |
| Multi-Threading Technology With Intel’s Hyper-threading and AMD’s SMT technology, one physical core is recognized as two logical cores by the operating system, thereby increasing processor performance in multi-threaded applications. nine0027 | Missing |
Base frequencyThe guaranteed frequency of all cores (P-cores in the case of the corresponding architecture) of the processor at maximum load.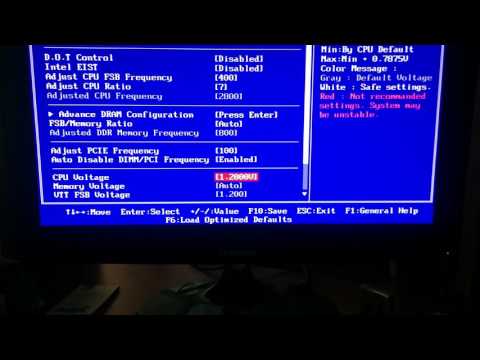 It is important to remember that speed and frequency are not directly related. For example, a new processor at a lower frequency may be faster than an old one at a higher one. It is important to remember that speed and frequency are not directly related. For example, a new processor at a lower frequency may be faster than an old one at a higher one. |
2.5 GHz |
| BCLK System bus frequency. Some motherboards allow you to achieve a good performance boost by slightly raising the bus frequency. Often this has a bad effect on the stability of the system. nine0027 | 333 |
| CPU multiplier. The final CPU frequency is determined by the simple formula BCLK * CPU multiplier. Modern processors instantly change the multiplier of each of the cores, taking into account the type of load, temperature, consumption and settings in the BIOS. | 7.5 |
TDPThermal Design Power is an indicator that determines the heat dissipation in standard operation. The cooler or water cooling system must be rated for a larger value. Remember that with a factory bus or manual overclocking, TDP increases significantly. nine0027 Remember that with a factory bus or manual overclocking, TDP increases significantly. nine0027
| 95 W |
| tCaseMax Allowable IHS (heat spreading plate, «cover») temperature. | 71 °C |
Cache and RAM
| L1 Cache First level cache. Modern processors use a multi-level cache. The first is the fastest, but the smallest. In the case of an L1 access and a miss, the L2 cache is searched for the next stage. | |
| L2 Cache Second level cache. Holds more data, but is slower. | 4MB (shared) |
| Supported type of RAM The type of RAM depends on its frequency and timings (speed), availability, price. | DDR1, DDR2, DDR3 Dual-channel |
Video core
Integrated graphics core Allows you to use your computer without a discrete graphics card. The monitor is connected to the video output on the motherboard. If earlier integrated graphics made it possible to simply work at a computer, today it can replace budget video accelerators and makes it possible to play most games at low settings. nine0027 The monitor is connected to the video output on the motherboard. If earlier integrated graphics made it possible to simply work at a computer, today it can replace budget video accelerators and makes it possible to play most games at low settings. nine0027
| N/A |
PCI
| PCI-E The PCI Express computer bus version. The bandwidth and power limit depend on the version. There is backward compatibility. | Gen 2 |
Details
| Model Official name. | Q8300 |
| ArchitectureCode name for the microarchitecture generation. nine0027 | Yorkfield |
| Chip manufacturer A company that manufactures chips in its own factory. | Intel |
| Number of transistors | 456,000,000 |
Process The manufacturing process, measured in nanometers. The smaller the technical process, the more perfect the technology, the lower the heat dissipation and power consumption. For Ryzen with a chiplet layout, the CCD process is implied. nine0027 The smaller the technical process, the more perfect the technology, the lower the heat dissipation and power consumption. For Ryzen with a chiplet layout, the CCD process is implied. nine0027
| 45 nm |
| Die size Depends on process technology and number of transistors. For chiplet Ryzen, the area of all CCDs is indicated. | 2×82 mm² |
| Socket type | FC-LGA6 |
| Spec Code | SLB5W |
| DescriptionInformation about the processor, taken from the official website of the manufacturer. nine0027 | Intel® Core™2 Quad Processor Q8300 (4M Cache, 2.50 GHz, 1333 MHz FSB) |
| Instructions | 64-bit |
| Bus frequency The speed of communication with the system. | 1333 MHz FSB |
Competitors
| Games | Office | |
|---|---|---|
| Better than | AMD A8-9600 APU (2016 D.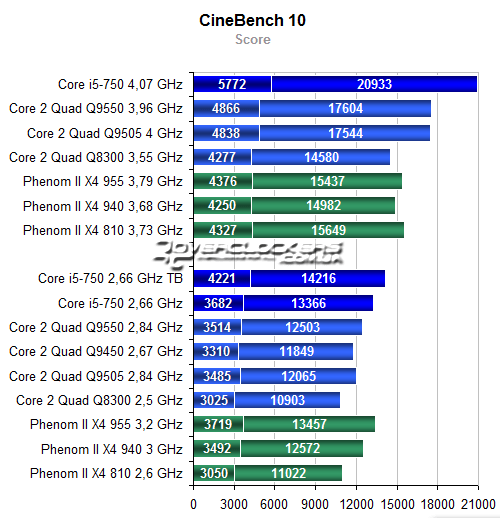
|

 1 FPS
1 FPS 2 FPS
2 FPS 2
2  5
5  5
5  4
4