What’s the difference between a 6-pin, 8-pin, and 12-pin GPU Cable?
With NVIDIA’s recent announcement of a 12-pin power connector on their new RTX 30 series, we wanted to point out the differences between 6-pin, 8-pin, and 12-pin GPU cables. We also wanted to tell you about our newly developed G-Power™ GPU Power Cable set with Mini 12-pin connector for NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 30 Series.
What is a PCIe x16 connector?
The PCI Express x16 connector is used primarily for high speed data transfer between the graphics card and a motherboard. However, the connector has a handful of pins that allow it to provide up to 75 watts of power through motherboard. While this is enough for many entry-level graphics cards, greater performance will need more power. This is where the pin connectors come in.
What is a 6-pin GPU Cable?
6-pin power connectors are typically found in low and mid-range graphics cards. The 6-pin power connector has 4.2mm pitch and can pull up to 75 watts of power directly from an external power supply, bypassing the motherboard entirely.
When a graphics card needs more power than its PCIe x16 connector can provide, the 6-pin connector comes in as a secondary source of power, allowing the GPU to draw up to 150 watts.
What is an 8-pin GPU Cable?
8-pin power connectors are found in high-end graphics cards. 8-pin connectors have 4.2mm pitch and can deliver up to 150 watts, twice the amount that a 6-pin connector is capable of.
If a 6-pin connector is plugged into an 8-pin slot, the GPU will attempt to draw more power than that cable is rated for, resulting in a fire hazard. To avoid this, we provide any combination of connector types you may need through our selection of GPU Standard Power Cables.
On high-end GPUs, multiple connectors are frequently used to increase maximum power consumption; the table below shows the variety of 6-pin and 8-pin combinations. As power needs have continued to increase, adding more cables has become less feasible as they begin to restrict air flow and interfere with components in tight spaces. This is where the next generation of power connectors begins.
This is where the next generation of power connectors begins.
What is a 12-pin GPU Cable?
The 12-pin power connector is the latest development in power supply for NVIDIA components. The 12-pin connector has a 3.0mm pitch, which means its total physical width is equal to an 8-pin connector. The design of the connector has been simplified, with one row for power and the other for ground.
Our new 12-pin cable with 18AWG wires can carry up to 500 watts, while our premium connector with 16AWG wires carries up to 600 watts. This means Pactech’s 12-pin connectors can handle three to four times the power of an 8-pin connector while taking up the same amount of space.
Introducing our new G-Power
™ 12-Pin GPU Cables.
Say hello to our new G-Power™ GPU Power Cable set with Mini 12-pin connector for NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 30 Series (3090, 3080, 3070, and 3060). These slim and modular cables are designed to directly plug from your power supply unit to your GPU cards.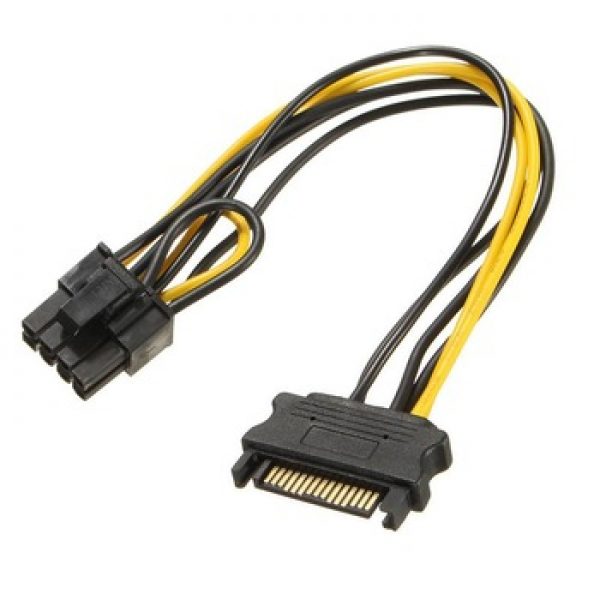 We offer two standard 15-inch cables and two premium 18-inch cables (custom sizes available):
We offer two standard 15-inch cables and two premium 18-inch cables (custom sizes available):
- F01 RTX-PEE18-8812FFF-15 – Black, 15 inches, from 2X ATX/EPS 8-Pin to Mini 12-Pin PSU
- F02 RTX-PPP18-8812FFF-15 – Black, 15 inches, from 2X PCIE 8-Pin to Mini 12-Pin PSU
- F03 RTX-PEE16P-8812FFF-18 (Premium Version) – Black, 18 inches, from 2X ATX/EPS 8-Pin to Mini 12-Pin PSU (w/ Sleeving and Premium Contacts)
- F04 RTX-PPP16-8812FFF-18 (Premium Version) – Black, 18 inches, from 2X PCIE 8-Pin to Mini 12-Pin PSU (w/ Sleeving and Premium Contacts)
We also offer customization options to make sure our new RTX series cables fit into any slim spaces and tight environments, or meet any other clearance restrictions.
Read more about our new GPU Power Cable or contact us to purchase a sample.
GPU Power Connectors Explained [Simple Answer]
An often overlooked yet critical factor when building a PC is power consumption. A top-of-the-line graphics card can place too great a burden on many PSUs, and that is something gamers need to avoid. We have prepared this guide to help you better understand GPU power connectors.
A top-of-the-line graphics card can place too great a burden on many PSUs, and that is something gamers need to avoid. We have prepared this guide to help you better understand GPU power connectors.
Some low-end and mid-range graphics cards can only use the PCI Express x16 slot as a power source, but more demanding cards will need to use 6-pin or 8-pin PCI Express power connectors.
This can be particularly confusing when using a multi-GPU setup, as with the SLI. In that case, the power requirement is the sum of two (or more) connected graphics cards.
Let’s get started!
Table of ContentsShow
PCI Express x16 Connector
Motherboards come with the aforementioned PCI Express x16 slot that can provide a maximum of 75 watts of power. Some feature multiple PCI Express x16 slots in order to connect more GPUs, but, as previously mentioned, this increases the power requirement.
Here are a few examples of GPUs that don’t require external power: GT 1030, GTX 1050 2GB variant, RX 550, RX 460, and many others. As none of these GPUs have a lot of processing power, they don’t need more than 75 watts of power.
As none of these GPUs have a lot of processing power, they don’t need more than 75 watts of power.
6-Pin Connector
A 6-pin connector
This connector can supply the GPU with an additional 75 watts of energy. This means the graphics card will use the PCI Express x16 slot and draw power directly from the PSU (Power Supply Unit).
Despite the fact that 150 watts are enough for most graphics cards, high-end cards such as NVIDIA’s RTX 3080 require more than 320 watts and system power of 750 watts. As 150 watts will be enough for most mid-range cards, these usually feature the 6-pin power connector.
The terms “PCI Express cables” or “PEG cables” (for PCI Express Graphics) can also be used to describe 6-pin connectors.
8-Pin Connector
An 8-pin connector
Although the math might not seem right when compared to the 6-pin connector, the 8-pin connector can deliver 150 watts to a graphics card. If the GPU requires more than 150 watts, it will come with an 8-pin connector or two 6-pin connectors.
As always, there are exceptions. The most power-hungry graphics cards come with a 6-pin and an 8-pin connector. For example, NVIDIA’s GeForce RTX 3060 has both types of connectors. As a result, it has a maximum power consumption of 170 watts.
There are even some exceptional cases where the GPU will have two 8-pin connectors. By adding the numbers together, we get a total of 375 watts, which is an extreme amount. In addition, you still need to power the CPU (another big energy consumer) and the rest of your PC’s components.
In even rarer cases, enthusiast GPUs require three 8-pin connectors. These are usually the manufacturers’ highest-end models made to provide the best possible cooling and overclocking. An example of such a GPU is the GeForce RTX 2080 Ti LIGHTNING Z.
In any case, it’s safe to say that your machine will be properly powered with a good 650 watts PSU. However, if you’re building a gaming rig with an RTX 3080/3090 or want to future-proof it (which is almost impossible), you should choose a more powerful PSU. Be careful because with great power comes a greater risk of overheating.
However, if you’re building a gaming rig with an RTX 3080/3090 or want to future-proof it (which is almost impossible), you should choose a more powerful PSU. Be careful because with great power comes a greater risk of overheating.
There is also a rule of thumb that the PSU runs best when it’s at 50% capacity, but that is a different topic that should be looked at on a case-by-case basis.
12-Pin Connectors
With the release of NVIDIA’s RTX 3000 series, we were introduced to 12-pin power connectors. This move was made out of necessity as NVIDIA desperately needed the extra power for their most powerful cards and came up with a rather elegant solution.
A 12-pin connector is roughly the same size as an 8-pin connector, but it can draw a lot more power. NVIDIA was forthcoming regarding the availability of PSUs with 12-pin connectors, so it released an adapter that allows two 6-pin connectors to interface with its card’s 12-pin slot.
Adapters Or Converters For Connectors
There are often compatibility issues when building a PC, and power connectors are no different. Fortunately, computers are made by engineers who like to modify hardware that isn’t suited to their needs by default.
A company called Molex pioneered these pin connectors all the way back in the late 50s and early 60s, and it has since become synonymous with the term. Don’t be surprised if you hear these being referred to as Molex Adapters or Molex Converters.
4-Pin Molex to 6-Pin PCI-E Adapter Cable
You should use this cable if your graphics card requires a 6-pin power connector, but your PSU doesn’t have it. This is usually a sign of a very old PSU, so it might be time for an upgrade. If you’re determined to keep your existing PSU, know that this sort of adapter sometimes requires one 4-pin connector, but it will most often be two, which is the recommended option.
4-Pin Molex to 8-Pin PCI-E Power Adapter Cable
This cable uses two 4-pin connectors and adapts them to an 8-pin connector. 4-pin to 8-pin is something that will likely be useful with upper-mid-range and high-end graphics cards.
6-Pin to 8-Pin PCI-E Adapter Cable
If you’ve recently purchased a top-class GPU, it will likely require an 8-pin connector, which some PSUs might not have. In that case, the 6-pin to 8-pin adapter is your solution.
2x 8-Pin To 12-Pin PCI-E Adapter Cable
As mentioned earlier, the 12-pin power connector is the latest technology necessary for NVIDIA’s 3000 series graphics cards. Because there were relatively few PSUs with a 12-pin power connector on the launch of the 3000 series, NVIDIA included a dual 8-pin to 12-pin adapter with its product.
SATA to 6-Pin PCI-E Adapter Cable
This cable converts your SATA connectors to a 6-pin connector, but this is generally advised against. There is a chance that SATA won’t be able to handle the power that your graphics card requires, and this is not something that you want to encounter, especially if the cable is labeled as “SATA only“.
There is a chance that SATA won’t be able to handle the power that your graphics card requires, and this is not something that you want to encounter, especially if the cable is labeled as “SATA only“.
SATA to 8-Pin PCI-E Adapter Cable
SATA can also be adapted to an 8-pin power connector. In this scenario, there will be two SATA connectors for one 8-pin connector.
Important Note About Adapters
In most cases, it’s best to upgrade your PSU if you lack connectors, as older PSUs weren’t built with current power requirements in mind. If possible, it’s best to use Molex to Molex for your GPU needs, as they have thicker wires and can transfer more current. A SATA to Molex adapter could be exposed and lead to burnout if the GPU draws more power with a higher load or by overclocking.
Connecting the video card power cable — a description of all types of connectors
The process of assembling a PC can be extremely difficult, since there are quite a few obstacles to overcome. This is, at least in part, due to the many power cables you have to connect and the many components you have to connect them to.
This is, at least in part, due to the many power cables you have to connect and the many components you have to connect them to.
Video cards tend to stand out in this process — are often comically large with huge heatsinks, multiple fans and shrouds that are either black or RGB saturated .
That’s why they’re so enticing, but for those who’ve never really «dealt» with today’s voracious GPUs, the (and more often than not the will be the ) may feel a bit underwhelmed.
And to top it all off, the cable is often so thin that you can’t help but wonder: will it be up to the task of feeding your (potentially rather gigantic) GPU with enough power?
The fact that there are several different power connectors (they all look the same) makes this all much more difficult.
Fortunately, there are a limited number of cables and connectors that can act as a link between your GPU and power supply.
The list is actually rather short , and although it may expand and grow in the future, such changes (or rather additions) are extremely rare and only occur once every ten years.
5
The reason we’re talking about this specific PC build part is pretty simple: you only need to know the difference between those connectors once and you’ll be prepared for years, if not even decades of !
With this little introduction, let’s dive into the finer details!
6-pin graphics card power connector
In absolutely all scenarios, your motherboard will power up to 75W for your GPU via PCI Express x16 slot . However, most graphics cards require a little more than this, and this is where the «basic» 6-pin power connector comes into play.
This cable provides the with an additional 75 watts of , which combined with the above amount gives a total of 150 watts.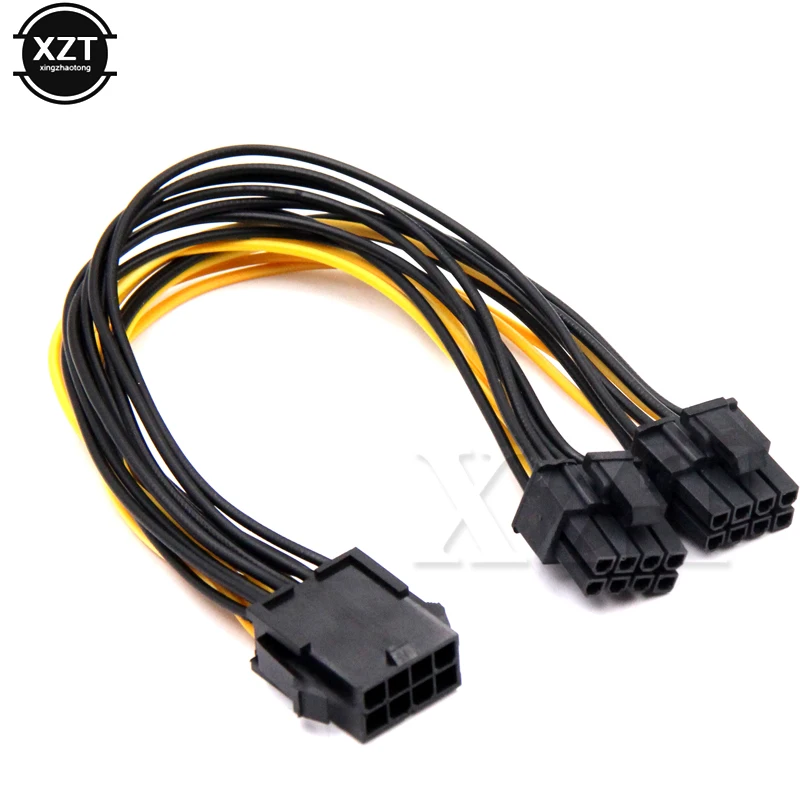 For most entry-level and mid-range graphics cards (especially older ones), will suffice.
For most entry-level and mid-range graphics cards (especially older ones), will suffice.
However, the higher you go in the product stack, the more power hungry GPUs become. In this case, a single 6-pin connector will not help .
6+2-pin and 8-pin video card power connectors
The 6+2-pin connector is essentially an 8-pin connector — it’s just split in two, so you can also use it as a 6-pin connector if needed. contact power cable.
Although he can looks like a like a regular 6-pin cable, this 8-pin cable is rated for a «whopping» 150W, which combined with the 75W from the PCIe slot, makes for a very respectable 225W.
Some video cards require only one 8-pin connector. Others, however, need two . Still others are powered by the 6- and 8-pin connector (300W total).
In the rarest of cases, you may encounter a triple 8-pin configuration, but such things are mostly reserved for the most power-hungry GPUs that are «built» for overclocking.
Note . All power consumption figures shown here are from the ATX power supply specification. And remember, specs are not restrictions. The actual power that a cable will and can transmit depends on a lot more.
For example, short bursts can instantly consume up to 2 times the average power. As you can see below, Vega64, a 250W~ card, boosts power to 420W in 0.3 milliseconds!
Whether your cable can handle all this power depends on the size of the cable and the overall quality of the PSU in question. In addition, the 6+2 Molex Mini-Fit Jr power connector (PCIe plastic power connector) can safely handle up to 288W (8A×3×12V): source.
Precisely because 150W is not the limit, we emphasize the importance of buying good quality power supplies for workstations and other heavily loaded systems . And that’s why is why using pigtails to power video cards is a bad idea . If you have a 400W graphics card and you power it with pigtails, you are sending a whopping 27 amps over a single set of wires. You are just asking for trouble because you rely so heavily on the quality of your power supply. Use two separate cables whenever possible.
You are just asking for trouble because you rely so heavily on the quality of your power supply. Use two separate cables whenever possible.
12-pin graphics card power connector
NVIDIA’s decision to create a dedicated 12-pin power connector for its top-end RTX 3000 series GPUs has been heavily criticized, but at least it’s brought some chaos to the rather outdated PC build segment.
Interestingly, it’s the same width as a standard 8-pin connector because the pins themselves are a bit smaller than we expected.
Luckily, NVIDIA has decided to include an adapter in its Founders Edition GPUs that converts the 12-pin connector to a dual 8-pin connector, making it fully compatible with existing power supplies.
However, it looks like we’ll all have to switch to this emerging new «standard» sooner or later, as future GPUs will require more power than ever before.
How much power each power connector provides
- Your always GPU will be able to draw up to 75 watts from the through the motherboard itself.
 This is the «base» energy.
This is the «base» energy. - One 6-pin power connector provides an additional 75W for a total of 150W.
- Replace it with an 8-pin power connector (150 W) and this number will automatically increase to 225 W.
- You can also get the same with two 9s0003 separate 6-pin connectors — 75W + 75W + 75W.
- 6+8-pin configuration (together with a PCI Express x16 slot) will provide up to 300W of total power.
If your particular model needs more than , you will need to connect two 8-pin connectors to , which combined with the PCIe slot can deliver a whopping 375W of power.
If you’re overwhelmed by this mind-boggling amount of information, here’s a little table with everything classified and laid out:
| Video Card Power Cable Guide | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCIe x16 | 6-pin | 8-pin | 12-pin | Total power |
| 75 W | – | – | – | 75 W |
| 75 W | 75 W | – | – | 150 W |
| 75 W | 2×75W | – | – | 225 W |
| 75 W | – | 150 W | – | 225 W |
| 75 W | 75 W | 150 W | – | 300 W |
| 75 W | – | 2×150W | – | 375 W |
| 75W | – | 3×150W | – | 525 W |
| 75 W | – | – | 600 W | 675 W |
| 75 W | – | – | 2×600W | 1275 W |
This last row is more of a hypothetical one, but given NVIDIA and AMD’s willingness to build huge, voracious behemoths, it’s easy to imagine a future (which isn’t that much and away) in which dual 12-pin power connectors will become the norm — along with 8K / 12K games .
Video Card Power Frequently Asked Questions
Let’s take a look at a few questions you might have about GPU power cables and everything related to them:
How many GPU power connectors are there?
Right now, at the time of this writing, you can only find four different connectors: 6-pin, 6+2-pin, 8-pin and 12-pin .
The two in the middle are the same, but slightly different to ensure maximum hardware and power supply compatibility.
How many power cables does my GPU need?
It depends on your specific model. It needs at least one 6-pin power connector.
If this is a mid-range GPU, it will either have two 6-pin connectors, or alternatively one 8-pin. Both configurations deliver the same power (150W).
The higher you go in the product stack, the more power you have to provide.
Higher-end GPUs most often require the 6- and 8-pin connector, while the most powerful require two 8-pin connectors to function properly and deliver incredibly high frame rates and resolutions.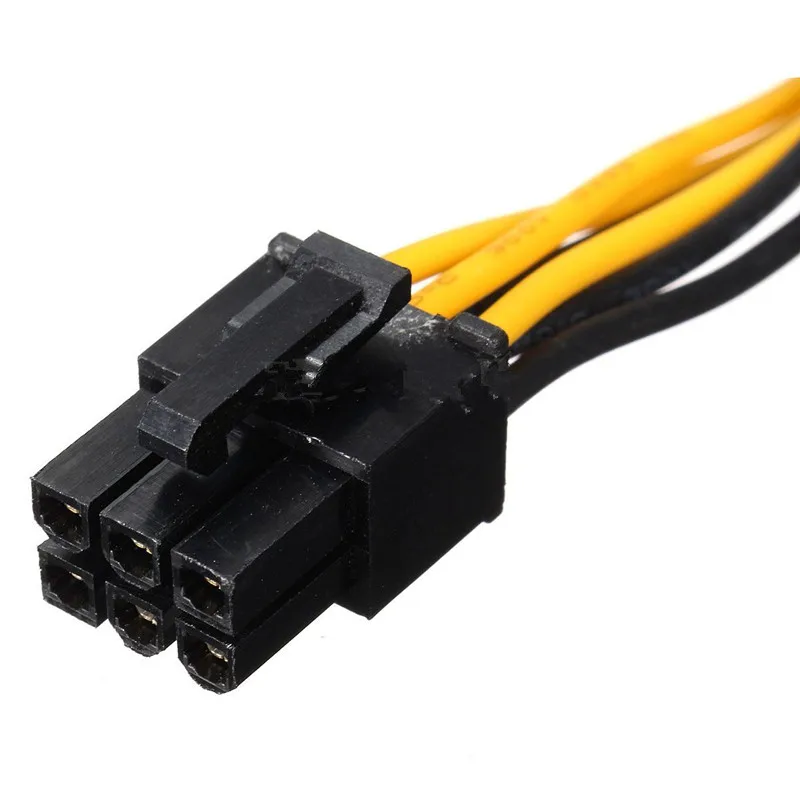
Triple 8-pin connectors are reserved for the best and most power-hungry graphics cards on the market.
Do all graphics cards require additional power?
There are actually quite a few GPUs on the market that not require extra power from your PSU. The motherboard itself always delivers up to 75W of power .
However, these GPUs are on the weaker side. They’re not bad either way, but they’re limited by , when it comes to what they can do and how many frames they can push.
Can I connect the wrong power supply cable to the graphics card?
Fortunately, this is not possible.
Most power supply cables have keys, clips, or both . This, in turn, means that they can only go one way and into the appropriate slots.
CPU and GPU cables may look the same (at least at first glance), but they are by no means interchangeable, and the same goes for all other cables and power supply connectors.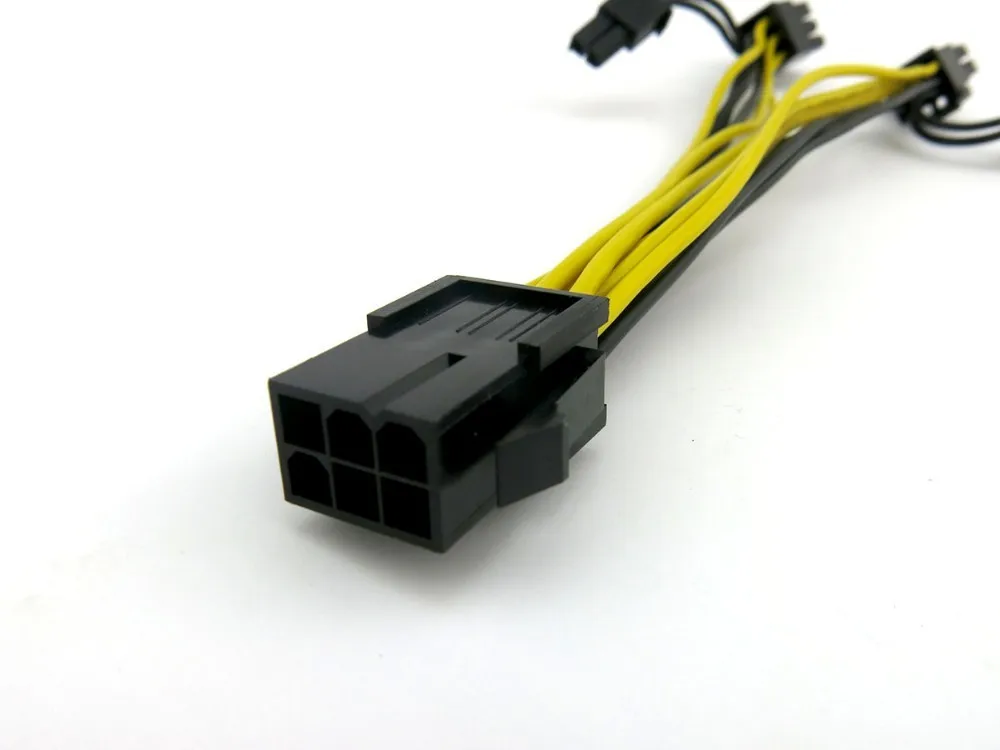
For games and more | PC World
nVidia has released a new line of GeForce GTX 700 series video cards. It would seem that your favorite toys will finally start to “fly”. However, the reality turned out to be not so rosy — the new generation of video accelerators uses the same chip as in the 600th series.
New players have appeared on the modern graphics adapter market — Nvidia has released a line of video cards of the GeForce GTX 700 series. It would seem that happy times have come for real gamers, and their favorite toys will finally start to “fly”. However, the reality turned out to be not so rosy — the new generation of video accelerators uses the same chip as in the 600th series.
For the GeForce GTX 770, a full-fledged version of the well-known GK104 crystal used in a similar edition for the GeForce GTX 680 is used. However, it is worth recognizing that the core, called GK104-425-A2, has been somewhat upgraded — it supports the advanced GPU Boost 2.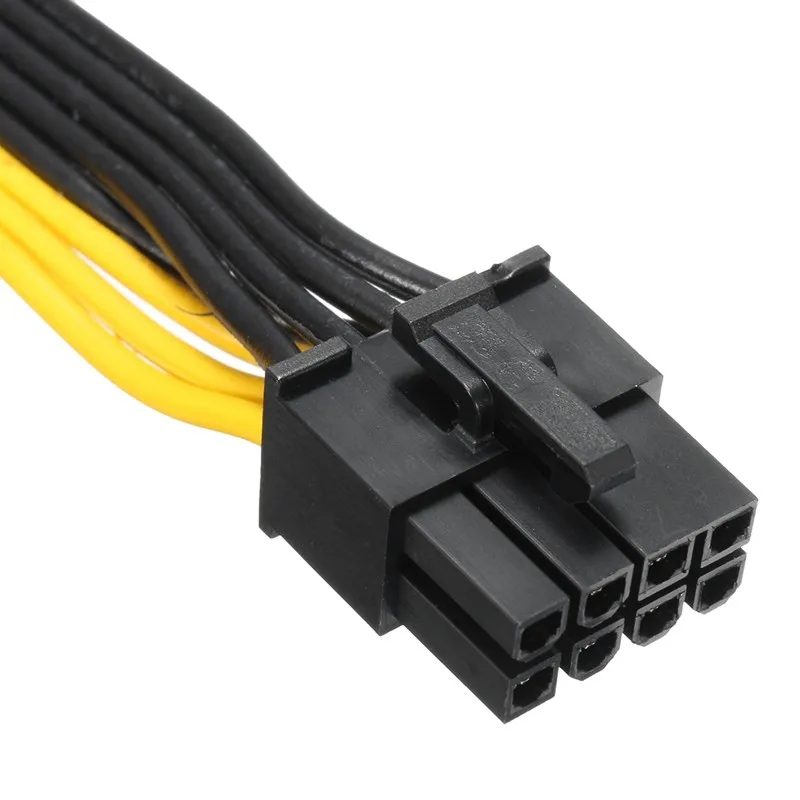 0 dynamic acceleration mechanism. But the number of functional blocks has not changed — the GPU includes 1536 computing processors, 128 texture units and 32 rasterization units.
0 dynamic acceleration mechanism. But the number of functional blocks has not changed — the GPU includes 1536 computing processors, 128 texture units and 32 rasterization units.
The GeForce GTX 760 graphics cards are also based on the GK104 GPU. However, the low-cost version had two of the eight SMX modules disabled. This means that the number of processors has been reduced by 384 compared to the maximum configuration — from 1536 to 1152. In this case, about a quarter of CUDA units are not used, and the number of texture units (TMU) is 96.
Let’s see what products the leading manufacturers offer users. We decided to test six nVidia 770 and 760 series graphics cards to see how different their performance is.
Palit GeForce GTX 760 JetStream
This graphics card comes in a black/green package. It is distinguished not only by the abundance of information about the advantages of this device, but also by the high quality of printing. From the basic information located on the front side of the box, it is worth highlighting the amount and type of video memory used, support for GPU Boost 2.0, nVidia SLI and a number of other technologies. Naturally, there is also a pen.
From the basic information located on the front side of the box, it is worth highlighting the amount and type of video memory used, support for GPU Boost 2.0, nVidia SLI and a number of other technologies. Naturally, there is also a pen.
The bundle is not bad — the video adapter itself comes with a quick installation manual, a software disk, a power adapter, a DVI to D-SUB adapter and an HDMI to DVI adapter.
The cooling system consists of two 90mm fans. The rest of it is covered with a plastic casing. When there is no load, the frequencies of the graphics core and memory are automatically lowered, which reduces power consumption and heat dissipation. At the same time, the fan works almost silently, and the temperature of the graphics core does not exceed 36 o C. The model receives additional power through two 6-pin connectors.
The video adapter is based on the nVidia GK104 (Kepler) graphics chip of the GK104-225-A2 modification, manufactured using a 28-nm process technology. It consists of six active SMX units, 1152 CUDA cores and 32 raster units. The frequency of the graphics core turned out to be increased relative to Nvidia’s recommendations — it is 1072 MHz. Thanks to the support of GPU Boost 2.0 technology, in turbo mode, the frequency of the graphics core reaches 1137 MHz.
It consists of six active SMX units, 1152 CUDA cores and 32 raster units. The frequency of the graphics core turned out to be increased relative to Nvidia’s recommendations — it is 1072 MHz. Thanks to the support of GPU Boost 2.0 technology, in turbo mode, the frequency of the graphics core reaches 1137 MHz.
The amount of video memory is 2 GB. In total, the board contains eight chips of 256 MB each, manufactured by Hynix. Chips are marked H5GQ2h34AFR, according to the documentation, their frequency is 6 GHz. Data exchange between the graphics core and memory is carried out through a 256-bit bus capable of passing information at a speed of 198.4 Gb / s.
Palit GeForce GTX 770 JetStream
The video card comes in a fairly large box with a flip-up lid, under which there is a special viewing window. The top cover traditionally contains key information, from which you can highlight the amount and type of video memory used, support for GPU Boost 2. 0, Nvidia SLI, and a number of other technologies.
0, Nvidia SLI, and a number of other technologies.
The kit includes the graphics card itself, a software CD, a power adapter, a DVI-D-SUB adapter, an HDMI to DVI adapter, a JetStream series logo sticker, and several instruction manuals.
This video card differs from the reference GeForce GTX 770 not only in an alternative cooling system, but also in the presence of a significant factory overclocking of the graphics core. Unlike the recommended value of 1046 MHz, this model operates at a frequency of 1150 MHz, which, taking into account the work of GPU Boost 2.0 technology, gives an average value of 1202 MHz.
Another key difference is the reinforced graphics core power unit — instead of the five channels recommended by Nvidia, eight channels are installed, although the video memory is powered using the usual two.
The model is based on the Nvidia GK104 (Kepler) GPU, manufactured using a 28-nm process technology. It consists of eight active SMXs, 1536 universal shader pipelines (CUDA cores, in Nvidia’s terminology) and 32 ROPs.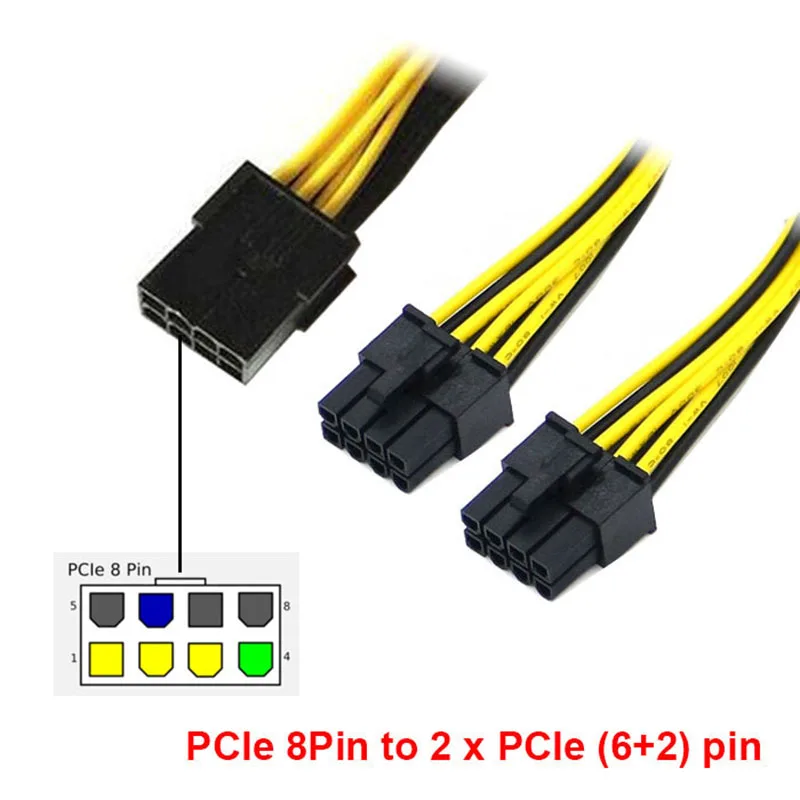 Video memory with a total capacity of 2 GB consists of eight chips manufactured by Samsung with a capacity of 256 MB each. Data exchange between the graphics core and memory is carried out through a 256-bit bus, which can pass 224.4 Gb of information in 1 s.
Video memory with a total capacity of 2 GB consists of eight chips manufactured by Samsung with a capacity of 256 MB each. Data exchange between the graphics core and memory is carried out through a 256-bit bus, which can pass 224.4 Gb of information in 1 s.
The cooling system consists of three fans of different diameters and a radiator based on five heat pipes. A set of outputs on the rear panel is standard — Dual-Link DVI, Single-Link DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort.
Gigabyte GV-N760OC-2GD
The first thing that a potential buyer of this device pays attention to is the packaging. Gigabyte marketers don’t forget about it either — the board comes in a colorful compact box, decorated with all sorts of messages about the company’s achievements.
The proprietary WINDFORCE system with Triangle Cool technology is responsible for cooling. At the same time, the plates that make up the radiator are interconnected by aluminum partitions in the form of a triangle, expanding towards the bottom of the radiator. Therefore, the air flows formed by three 100 mm fans, after passing through the radiator fins, diverge in different directions from the board without heating its surface.
Therefore, the air flows formed by three 100 mm fans, after passing through the radiator fins, diverge in different directions from the board without heating its surface.
The «heart» of the board’s hardware is the Nvidia GK104-225-A2 graphics processor, manufactured using a 28-nm process technology. It consists of 6 active SMX units, 1152 CUDA cores and 32 raster units. The board initially received a noticeable factory overclock. In particular, the base clock speed of the GPU has been increased to 1085 MHz, while in normal mode the GPU clock frequency often rises to 1215 MHz and very rarely drops during normal gaming workload.
Gigabyte GV-N770OC-2GD
The package design of this graphics adapter is made in the classic style for the company with a predominance of blue and black colors. On the front side there are notices about the presence of 2 GB of GDDR5 video memory, the GeForce GTX 760 graphics core, its factory overclocking and, of course, the proprietary WindForce 3X cooling system. The package includes a disk with drivers and proprietary software, a small guide to quickly installing a video card, as well as adapters from a pair of Molex connectors to one 6-pin and from two Molex to one 8-pin.
The package includes a disk with drivers and proprietary software, a small guide to quickly installing a video card, as well as adapters from a pair of Molex connectors to one 6-pin and from two Molex to one 8-pin.
The manufacturer has increased the clock frequency of the GPU, raising its value to 1139 MHz. The board carries on board 2 GB of video memory operating at the recommended frequency. A 256-bit bus is used to access the RAM, and therefore the throughput of the backbone is 224.4 Gb / s.
The basis of the proprietary cooling system is made up of two radiator blocks made of aluminum plates, interconnected by five heat pipes. Another heat pipe passes through the body of the main cooler, increasing its efficiency. The memory chips are covered by an aluminum plate attached to the base of the cooler. The power elements of the VRM are also cooled, and not at the expense of individual elements, but with the help of a common heat dissipation system.
The design of the printed circuit board differs from the reference, and the element base is fully consistent with the concept of Ultra Durable VGA. An 8-channel circuit is used to stabilize the GPU supply voltage.
An 8-channel circuit is used to stabilize the GPU supply voltage.
MSI N760TF 2GD5/OC
This video card comes in a fairly large box with a predominance of black and red colors. On the front side of the package, the main technical features are highlighted — the presence of factory overclocking, a modified Twin Frozr cooling system, and 2 GB of GDDR5 video memory. The delivery set is standard: the video card itself, two PCI-E power adapters, instructions, a disk with drivers and software, and a DVI-VGA adapter.
The modified Twin Frozr IV cooling system is based on heat pipes. Contact with the core is carried out through a copper base, the heat from which is distributed on the main radiator, blown by two 90mm fans.
MSI’s version of the GeForce GTX 760 differs from the reference in overclocking the GPU. In this case, the base frequency of the processor is increased from 980 to 1020 MHz, and the average acceleration value is at the level of 1085 MHz.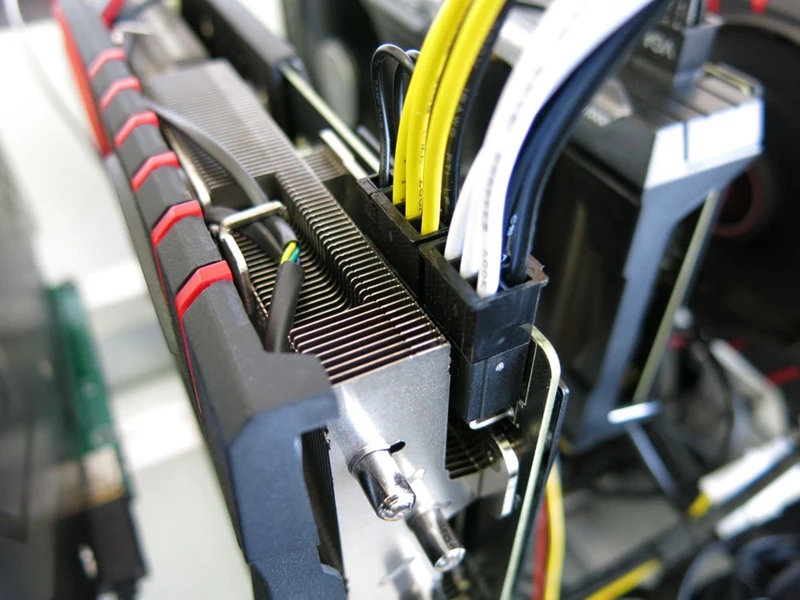 The memory runs at the recommended 6008 MHz.
The memory runs at the recommended 6008 MHz.
Especially for overclockers, MSI has developed a special utility called the Gamming App. This application is very easy to use — a small interface window contains three buttons that allow you to select different modes of the graphics adapter.
ASUS GTX 760 DirectCU II OC
The packaging of this video card can be called usual for the ASUSTeK line — an intricate drawing with traces of claws of an unknown animal, a brief technical specification in a rather small green font, and, of course, a large company logo adorning the top of the box.
The board is sealed in an antistatic bag enclosed in a cardboard clip. In addition to the video adapter, a power adapter, a brochure on choosing a PSU, and, of course, a software CD are supplied.
The graphics chip operates at a frequency of 1006 MHz (instead of the standard 980 MHz). At the same time, the average value of auto overclocking is at the level of 1072 MHz, while for reference models this parameter is 1033 MHz. The adapter is equipped with GDDR5 video memory with a total capacity of 2 GB. It is typed using eight chips of 256 MB each manufactured by Hynix H5GQ2h34AFR-R0C. According to the specification, they are designed to operate at 6000 MHz. Microcircuits are placed on both sides of the printed circuit board, four on each. They are cooled by natural convection.
The adapter is equipped with GDDR5 video memory with a total capacity of 2 GB. It is typed using eight chips of 256 MB each manufactured by Hynix H5GQ2h34AFR-R0C. According to the specification, they are designed to operate at 6000 MHz. Microcircuits are placed on both sides of the printed circuit board, four on each. They are cooled by natural convection.
The model is equipped with a 5-channel (4+1) power stabilizer, which is controlled by a Richtek RT8867A controller. At the same time, an improved element base is used, corresponding to the Super Alloy Power proprietary concept.
Totals
Testing is over, it’s time to take stock. This time, the MSI N760 TF 2GD5/OC graphics card deserved the «Best Buy» award, as it has an excellent price/performance ratio. But the editors’ choice was the Gigabyte GV-N770OC-2GD model — in our opinion, it is the most optimal choice for those who are trying to «squeeze» everything that it is capable of out of the video card.
