Should you upgrade your Samsung tablet?
-
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8
If you’ve already got a Tab S7, the Tab S8 won’t feel like a particularly large upgrade for you. If you’re on an older Tab S6, though, there’s a lot to be gained by springing on this upgraded tablet, including a 120Hz display and considerably longer software update support.
See at Samsung See at Best Buy
-
Samsung Galaxy Tab S7
If you’re happy with your Samsung Galaxy Tab S7, there’s not much reason to upgrade right now. Its Snapdragon 865 chipset is more than enough for light use, and the tablet’s 120Hz display is still great.
See at Amazon
-
Samsung Galaxy Tab S6
The Samsung Galaxy Tab S6 is starting to show its age. If you’re getting tired of the tablet’s 60Hz display or the performance of its Snapdragon 855 is starting to feel inadequate, it may be time to upgrade.
See at Amazon
Samsung produces many of the best Android tablets in the US. The Korean manufacturer makes excellent hardware and lacks serious competition here in the States. With so many similarly named devices available, you may find it hard to keep track of what’s new, what’s old, and what’s different between Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 models.
Samsung’s tablet offerings are a maze of slabs that all look alike, so it can be tough to know whether upgrading from a previous model is worthwhile when the latest and greatest hits the shelves. If you’d like to make sense of the never-ending list of features spread across the last four generations of Samsung’s Tab S tablets (covering the Galaxy Tab S5e, Tab S6, Tab S6 Lite, Tab S7, Tab S7+, and Tab S7 FE) while comparing hardware, software, performance, accessories, and pricing against the Galaxy Tab S8 line, read on.
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 vs. Tab S7 and Tab S6: Pricing and deals
Samsung’s newest Galaxy Tab S8 series launched globally in February 2022. The Samsung Galaxy S Tab 7 series launched in September 2021 and the Galaxy Tab S6 series was released two years before that, in August 2019. The Galaxy Tab S6 and S6 Lite are getting harder and harder to find, and they’re not really worth it when compared to Samsung’s 2020-2021 A-series tablets. However, the Galaxy S7 series and even the most recent Galaxy Tab S8 series are seeing regular deals.
The Galaxy Tab S6 and S6 Lite are getting harder and harder to find, and they’re not really worth it when compared to Samsung’s 2020-2021 A-series tablets. However, the Galaxy S7 series and even the most recent Galaxy Tab S8 series are seeing regular deals.
To help you decide whether a given sale is a good deal for you or just a «normal» price, here are the MSRPs and typical discounts for the Samsung Galaxy Tab S6, S7, and S8 series:
|
Model Name (Wi-Fi) |
64GB |
128GB |
256GB |
512GB |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 |
N/A |
$550 (from $700) |
$650 (from $780) |
N/A |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8+ |
N/A |
$750 (from $900) |
$850 (from $980) |
N/A |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 Ultra |
N/A |
$1,000 (from $1,100) |
$1,080 (from $1,200) |
$1,100 (from $1,400) |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S7 FE |
$400 (from $530) |
N/A |
$579 (from $680) |
N/A |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S7 |
N/A |
$585 (from $650) |
$650 (from $730) |
$830 |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S7+ |
N/A |
$700 (from $849) |
$775 (from $930) |
$1,030 |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S6 Lite |
$225 (from $349) |
$275 (from $430) |
N/A |
N/A |
|
Samsung Galaxy Tab S6 |
N/A |
$550 (from $650) |
$630 (from $730) |
N/A |
Given how similar the Galaxy Tab S8 and S7 series are, once you choose the size you want, watch both the new and old models. Each model should see a decent deal within a month or so. You can also go by which has the better discount today. If you’re willing to go with a larger screen, the Galaxy Tab S7 FE can also be a great way to save money while getting a quality tablet, as long as you find it on sale.
Each model should see a decent deal within a month or so. You can also go by which has the better discount today. If you’re willing to go with a larger screen, the Galaxy Tab S7 FE can also be a great way to save money while getting a quality tablet, as long as you find it on sale.
After shopping for tablets for a while, the hardware might start to blur together, especially Samsung’s Tab S models, which mainly offer similar bezels and shapes. Still, there are always differences, even if you don’t notice them at first.
The Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 and Samsung Galaxy Tab S8+ offer the same form factor as the Tab S7, Tab S7+, and Tab S7 FE. So if you’re looking to upgrade your Tab S7 device over its appearance and appearance alone, then you’re better off sticking with your S7 to save some money (though there are still hardware differences — more on that in a bit).
Going further back to the Tab S5e, Tab S6, and Tab S6 Lite, the differences in design from the S7 and S8 series are a bit clearer. For example, the Tab S5e, S6, and S6 Lite offer slightly larger bezels than the S7 and S8 models, with beveled edges (instead of the newer flat edges of the Tab S7 and S8 lines). Still, all three of these tablets look relatively similar, so what’s best for your needs will ultimately come down to specs.
For example, the Tab S5e, S6, and S6 Lite offer slightly larger bezels than the S7 and S8 models, with beveled edges (instead of the newer flat edges of the Tab S7 and S8 lines). Still, all three of these tablets look relatively similar, so what’s best for your needs will ultimately come down to specs.
Being the newest, the Tab S8 line offers the most up-to-date hardware, packing a Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 in all models (though there is some throttling), along with a minimum of 8GB of RAM. So if you’re shooting for pure power, the S8 line is the way to go, especially when the S7 line offers older chips and less RAM.
Still, the S7 and S7+ are no slouches; both offer high refresh rate screens at 120Hz (TFT LCD for the S7, OLED for the S7+) and Snapdragon 865 chipsets. So if you’re using a Tab S7 right now, there’s probably no need to upgrade, especially if you picked up a model with 8GB RAM. However, the mid-range Tab S7 FE (with a Snapdragon 778) doesn’t offer a high refresh screen, which would mean moving to an S8 of any kind would represent an upgrade that could be worth the cost of a new device.
The S5e and S6 pack OLED screens, but the S6 Lite is TFT LCD. All three are limited to 60Hz refresh rates. The regular S7 also offers a TFT screen, but it’s a high refresh rate screen that supports 120Hz, comparable to the S8’s screen.
With the exception of the Galaxy Tab S7 FE, which has a 60Hz LCD, all Galaxy Tab S7 and Galaxy Tab S8 devices have 120Hz displays. The smallest models in each family — the Tab S7 and Tab S8 — are LCD panels. The Tab S7+, Tab S8+, and Tab S8 Ultra are OLED.
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 vs. Tab S7 and Tab S6: Software and features
Samsung is pretty much the leader in the high-end Android tablet market, and software is a big part of this equation. Something as simple as the Samsung Internet Browser is a standout app (as far as Android web browsers go), and it comes packed in with every Samsung device.
Then there’s DeX mode, a proprietary software feature from Samsung that lets you switch your tablet to a desktop-like interface that works with a mouse, keyboard, and a bottom taskbar design similar to Windows. Every Tab discussed in this guide supports DeX, although the newer the model, the better the performance. If you’re looking for a new tablet and require solid DeX mode performance to get work done on an external screen, an upgrade to an S8 may be in order, even though an S7 should do a fair job.
Every Tab discussed in this guide supports DeX, although the newer the model, the better the performance. If you’re looking for a new tablet and require solid DeX mode performance to get work done on an external screen, an upgrade to an S8 may be in order, even though an S7 should do a fair job.
Another notable software feature is S Pen support. The Galaxy S8 line offers the lowest latency when using the S Pen, so there’s an advantage here that older models can’t compete with. The S Pen support on the S7 lineup does an excellent job, especially if you’re taking notes and drawing. But if you’re a professional who requires the lowest latency and superior palm rejection, the S8 is a better option.
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 vs. Tab S7 and Tab S6: Performance and updates
Performance is often subjective — different use cases demand different processing power. Sure, you can dip into benchmark apps, such as Geekbench, but in the particular case of the Tab S8 line, Samsung has changed how its latest tablets report their performance, which makes nailing down said performance difficult.
If you’re more worried about real-world use, there’s good news: The Tab S8 line is plenty powerful. It chews through apps and games with little noticeable slowdown. Sure, this is what you’d expect from the newest high-end Samsung tablets, but if pure performance is your goal, don’t let the Geekbench snafu dissuade you. The Tab S8 line is the cream of the crop regarding tablet performance on Android. You will pay for the privilege, however.
Then again, the Tab S7 line is no slouch, thanks to chips such as the Snapdragon 865, Snapdragon 778G, and 750G. These might be more upper-mid-range chips instead of high-end chips, but they use less power than something like a Snapdragon 888 or 888+ (the last gen’s high-end). So there are some battery savings with the lower performance, which is precisely why Samsung ran with these chips in the S7 series.
Still, most people won’t be able to tell the difference between a Snapdragon 865 and a Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 when using a tablet for everyday use, like browsing websites and watching videos. The difference will be more apparent if you often use demanding apps like image or video editors, play heavy games, or want to use multiple apps at once.
The difference will be more apparent if you often use demanding apps like image or video editors, play heavy games, or want to use multiple apps at once.
Even the Tab S6 or S6 Lite are still pretty handy in everyday use. Keep in mind the Lite packs a Samsung-made Exynos 9611 chipset instead of a Snapdragon. So moving beyond an S6 might not be necessary if you don’t throw demanding apps at your tablet, though even basic tasks will be smoother on an S8 than on an older tablet.
Regarding updates, Samsung does an excellent job keeping its tablets on the latest software, though the Tab S5e is limited to Android 11 and OneUI 3.1. On the other hand, the Tab S7 and S8 lines have started receiving updates to Android 13-based One UI 5 in various parts of the world, which should mean the update is coming stateside soon.
The S8 series will see the lengthiest update cycle now that Samsung is updating its devices in four-year stretches. So even if you own an S7 model, your update cycle won’t compare to the S8 line’s four years of Android updates and five years of security updates — ending in February 2026 and 2027, respectively.
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 vs. Tab S7 and Tab S6: Accessory compatibility
The Tab S8 line is still pretty recent, so there aren’t many third-party solutions for Tab S8 accessories yet. That’s especially true of the Tab S8 Ultra since it offers a brand-new footprint, thanks to its enormous 14.6-inch OLED screen. The good news is that the Tab S8 and S8+ are the same sizes as the Tab S7 and S7+, which means cases and keyboards will work between these two models, whether they’re first- or third-party.
There are some slight savings if you pick up a Tab S8 or S8+ and purchase older Tab S7 accessories. Plus, there are savings when upgrading from a Tab S7 to an S8, as all your peripherals will work with the newer tablet and eliminate the need to buy a new case or keyboard just because you changed devices.
Beyond the compatibility between a few Tab S7 and S8 models, options are more plentiful and less expensive for older tablets. For example, cases and styluses can be snagged on most online stores for much less than the newest items for the Tab S8 line.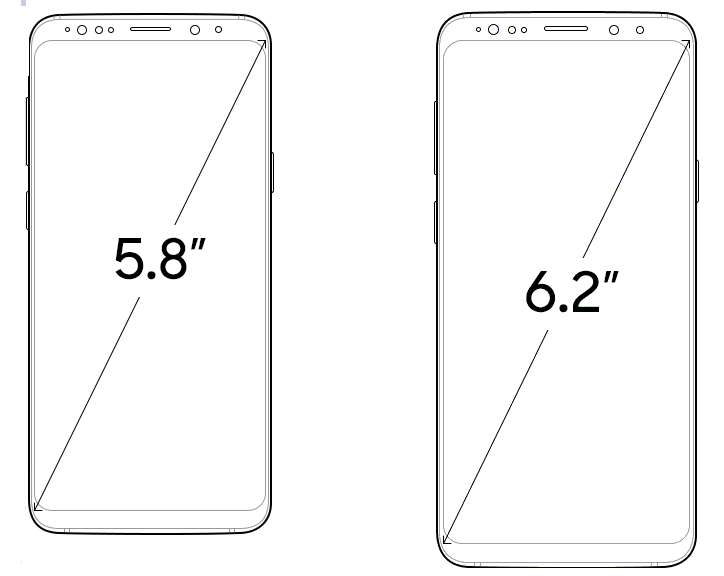
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 vs. Tab S7 and Tab S6: Should you upgrade?
Whether you should upgrade your Samsung Galaxy Tab depends on how your current device is holding up and what you want to use your tablet for. The Tab S7 models are still powerful and handy, even though they don’t have the latest chipsets. Unless you’re a professional who edits video, audio, or images on your tablet, the extra cash spent on an S8 model won’t make a huge difference, especially when form factors between the S7 and S8 series are the same. Sure, perhaps the 14.6-inch Tab S8 Ultra is calling you. And that’s fair, as no other tablet compares in size.
But if you’re coming from an earlier model, say a Tab S5e or one of the Tab S6 models, there is a lot to gain from upgrading to an S8 or S7 — like access to Android 13 and, in the case of the newer S8 series, future OS updates.
There’s also the newer hardware to consider. Not only do all the S7 and S8 tablets have high refresh rate screens, but you also get a newer CPU/GPU and more RAM. And again, the S8 line will get software updates much longer than the S7 line.
And again, the S8 line will get software updates much longer than the S7 line.
The choice of whether to upgrade comes down to your personal needs. There may not be much of a difference between the S7 and S8 models beyond a bump in specs and lengthier update support, but if you’ve been running out of RAM on an older S7 during your heavier tasks, then the extra two gigs in the entry-level S8 models may be worth the upgrade.
Still, the tablet market moves a little slower than the phone market, so it’s not like these tablets are going anywhere anytime soon. You have time to decide which model is best for you, and you may even catch a sale.
Samsung Galaxy Tab S8
The Samsung Galaxy Tab S8 features a premium design, a 120Hz display, an S Pen stylus, a powerful Snapdragon 8 Gen 1 chipset, and enough RAM to handle any task you’re likely to need from a tablet. This is one of the best Android tablets you can buy.
See at Samsung See at Best Buy
Samsung Galaxy Tab S7
The Samsung Galaxy Tab S7 is still a great tablet. Its Snapdragon 865 chipset isn’t the fastest around anymore, but it’s plenty for basic computing, and the S7’s 120Hz display still looks very nice by today’s standards.
Its Snapdragon 865 chipset isn’t the fastest around anymore, but it’s plenty for basic computing, and the S7’s 120Hz display still looks very nice by today’s standards.
See at Amazon
Samsung Galaxy Tab S6
With an aging Snapdragon 855 chipset, a 60Hz display, and limited software update prospects, the Samsung Galaxy Tab S6 is getting ripe for replacement.
See at Amazon
Samsung Galaxy S6 32GB vs Samsung Galaxy S7 vs Samsung Galaxy S8: Compare Specifications, Price
Edition
IN
- IN
- US
Fri, Feb 03, 2023 | Updated 02.41PM IST
News
Tech NewsSocialMobilesPCsAppsGamingMore GadgetsTelecomFAQsAppliancesWearablesDevice Care
Compare
Compare Mobile PhonesCompare LaptopsCompare TabletsCompare CamerasCompare TelevisionsCompare Power banksCompare Smart watchesCompare Air conditionersCompare Washing machinesCompare RefrigeratorsCompare Fitness bandsCompare EpilatorsCompare HaircurlersCompare TrimmersCompare HairstraightenersCompare HairdryersCompare Bluetooth SpeakersCompare HeadphonesCompare Air PurifiersCompare Water PurifiersCompare IronsCompare FansCompare Air FryersCompare Air CoolersCompare Hand BlendersCompare Food ProcessorsCompare Room HeatersCompare Chimneys
Gadgets
Mobile PhonesTabletsLaptopsCamerasTelevisionsPower banksSmart watchesAir conditionersWashing machinesFitness bandsPersonal GroomingHome AppliancesKitchen AppliancesAudio
Slideshows
Reviews
Device Care
More
VideosRechargeVisual StoriesUSHow ToBrandsTop GadgetsFeaturedDeals
Trending Topics
Make a perfect choice for yourself by comparing Samsung Galaxy S6 32GB, Samsung Galaxy S7 and Samsung Galaxy S8 on the basis of their specifications and features on our compare mobile phones page. On Gadgets Now, we let you compare up to 4 mobiles at a time on the basis of different criteria like price, RAM, storage, camera, display,battery, and more. The comparison results help you in understanding how one mobile is better than others so that you can make a wise buying decision
On Gadgets Now, we let you compare up to 4 mobiles at a time on the basis of different criteria like price, RAM, storage, camera, display,battery, and more. The comparison results help you in understanding how one mobile is better than others so that you can make a wise buying decision
.
| Specifications | Samsung Galaxy S6 32GB | Samsung Galaxy S7 | Samsung Galaxy S8 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | ₹ 49,900 | ₹ 48,900 | ₹ 57,900 |
| Display | 5.1 inches (12.95 cm) | 5.1 inches (12.95 cm) | 5.8 inches (14.73 cm) |
| Camera | 16 MP And 5 MP | 12 MP And 5 MP | 12 MP And 8 MP |
| OS | Android v5.0.2 (Lollipop) | Android v6.0 (Marshmallow) | Android v7.0 (Nougat) |
| Battery | 2550 mAh | 3000 mAh | 3000 mAh |
FacebookTwitterLinkedin
Specifications
Summary (8)
| Variants |
Samsung Galaxy S6 32GB |
— | — | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| User Rating | 4. 0Read User Review 0Read User Review |
5.0Read User Review | 4.0Read User Review | — |
| performance | Samsung Exynos 7 Octa | Samsung Exynos 8 Octa | Samsung Exynos 9 Octa | — |
| display | 5.1″ (12.95 cm) | 5.1″ (12.95 cm) | 5.8″ (14.73 cm) | — |
| storage | 32 GB | 32 GB | 64 GB | — |
| camera | 16 MP | 12 MP | 12 MP | — |
| battery | 2550 mAh | 3000 mAh | 3000 mAh | — |
| ram | 3 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | — |
special features (4)
| heart rate monitor | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fingerprint sensor position | Front | Front | Rear | — |
| other sensors | Light sensor, Proximity sensor, Accelerometer, Barometer, Compass, Gyroscope | Light sensor, Proximity sensor, rgbw sensor, Accelerometer, Barometer, Compass, Gyroscope | Light sensor, Proximity sensor, Accelerometer, Barometer, Compass, Gyroscope | — |
| fingerprint sensor | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
general (10)
| quick charging | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| operating system | Android v5. 0.2 (Lollipop) 0.2 (Lollipop) |
Android v6.0 (Marshmallow) | Android v7.0 (Nougat) | — |
| sim slots | Single SIM, GSM | Dual SIM, GSM+GSM | Dual SIM, GSM+GSM | — |
| model | Galaxy S6 | Galaxy S7 | Galaxy S8 | — |
| launch date | April 10, 2015 (Official) | March 18, 2016 (Official) | May 5, 2017 (Official) | — |
| custom ui | TouchWiz UI | — | — | — |
| brand | Samsung | Samsung | Samsung | — |
| sim size | SIM1: Nano | SIM1: Nano SIM2: Nano (Hybrid) | SIM1: Nano SIM2: Nano (Hybrid) | — |
| network | 4G: Available (supports Indian bands), 3G: Available, 2G: Available | 4G: Available (supports Indian bands), 3G: Available, 2G: Available | 4G: Available (supports Indian bands), 3G: Available, 2G: Available | — |
| fingerprint sensor | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
multimedia (3)
| loudspeaker | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| fm radio | No | No | No | — |
| audio jack | 3. 5 mm 5 mm |
3.5 mm | 3.5 mm | — |
performance (5)
| chipset | Samsung Exynos 7 Octa 7420 | Samsung Exynos 8 Octa 8890 | Samsung Exynos 9 Octa 8895 | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| graphics | Mali-T760 MP8 | Mali-T880 MP12 | Mali-G71 MP20 | — |
| processor | Octa core (2.1 GHz, Quad core, ARM Cortex A57 + 1.5 GHz, Quad core, Cortex A53) | Octa core (2.3 GHz, Quad core, M1 Mongoose + 1.6 GHz, Quad core, Cortex A53) | Octa core (2.3 GHz, Quad core, M2 Mongoose + 1.7 GHz, Quad core, Cortex A53) | — |
| architecture | 64 bit | 64 bit | 64 bit | — |
| ram | 3 GB | 4 GB | 4 GB | — |
design (5)
| thickness | 6.8 mm | 7.9 mm | 8.0 mm | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| width | 70.5 mm | 69. 6 mm 6 mm |
68.1 mm | — |
| weight | 138 grams | 152 grams | 155 grams | — |
| height | 143.4 mm | 142.4 mm | 148.9 mm | — |
| colours | Black, Blue, Gold, White | Black, Gold, Silver | Midnight Black, Orchid Gray, Coral Blue, Arctic Silver, Maple Gold, Burgundy Red | — |
display (8)
| display type | Super AMOLED | Super AMOLED | Super AMOLED | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| aspect ratio | 16:9 | — | 18.5:9 | — |
| pixel density | 576 ppi | 576 ppi | 568 ppi | — |
| screen protection | Corning Gorilla Glass v4, Scratch-resistant glass | Corning Gorilla Glass v4 | Corning Gorilla Glass v5 | — |
| screen to body ratio calculated | 70.76 % | 72.18 % | 84.57 % | — |
| screen size | 5. 1 inches (12.95 cm) 1 inches (12.95 cm) |
5.1 inches (12.95 cm) | 5.8 inches (14.73 cm) | — |
| screen resolution | 1440 x 2560 pixels | 1440 x 2560 pixels | 1440 x 2960 pixels | — |
| touch screen | Yes Capacitive Touchscreen, Multi-touch | Yes Capacitive Touchscreen, Multi-touch | Yes Capacitive Touchscreen, Multi-touch | — |
storage (4)
| user available storage | Up to 25 GB | Up to 24.4 GB | Up to 52.3 GB | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| internal memory | 32 GB | 32 GB | 64 GB | — |
| expandable memory | No | Yes Up to 256 GB | Yes Up to 256 GB | — |
| usb otg support | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
camera (13)
| camera setup | Single | Single | Single | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| settings | Exposure compensation, ISO control | Exposure compensation, ISO control | Exposure compensation, ISO control | — |
| image resolution | 5312 x 2988 Pixels | 4000 x 3000 Pixels | 4000 x 3000 Pixels | — |
| video recording features | Dual Video Recording | Dual Video Recording | — | — |
| autofocus | Yes Phase Detection autofocus | Yes Phase Detection autofocus | Yes | — |
| shooting modes | Continuos Shooting, High Dynamic Range mode (HDR) | Continuos Shooting, High Dynamic Range mode (HDR) | Continuos Shooting, High Dynamic Range mode (HDR) | — |
| resolution | 5 MP f/1. 9 Primary Camera 9 Primary Camera |
5 MP f/1.7, Wide Angle Primary Camera(22 mm focal length, 4.1″ sensor size, 1.34µm pixel size) | 8 MP f/1.7, Wide Angle Primary Camera(25 mm focal length, 3.6″ sensor size, 1.22µm pixel size) | — |
| video recording | 3840×2160 @ 30 fps, 1920×1080 @ 60 fps, 1280×720 @ 120 fps | 1920×1080 @ 30 fps | 1920×1080 @ 30 fps | — |
| camera features | Digital Zoom, Auto Flash, Face detection, Touch to focus | Digital Zoom, Auto Flash, Digital image stabilization, Face detection, Smile detection, Touch to focus | Wide Angle Selfie | — |
| sensor | CMOS | CMOS | Exmor-RS CMOS Sensor | — |
| physical aperture | F1.9 | F1.7 | F1.7 | — |
| optical image stabilisation | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
| flash | No | No | Yes Screen flash | — |
battery (7)
| user replaceable | No | No | No | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| talktime | Up to 17 Hours(3G) | Up to 22 Hours(3G) | Up to 20 Hours(3G) | — |
| quick charging | Yes Fast | Yes Fast | Yes Fast | — |
| usb typec | No | No | Yes | — |
| wireless charging | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
| type | Li-ion | Li-ion | Li-ion | — |
| capacity | 2550 mAh | 3000 mAh | 3000 mAh | — |
network connectivity (12)
| wifi | Yes Wi-Fi 802. 11, a/ac/b/g/n/n 5GHz 11, a/ac/b/g/n/n 5GHz |
Yes Wi-Fi 802.11, a/ac/b/g/n/n 5GHz, MIMO | Yes Wi-Fi 802.11, a/ac/b/g/n/n 5GHz, MIMO | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wifi features | Wi-Fi Direct, Mobile Hotspot | Wi-Fi Direct, Mobile Hotspot | Mobile Hotspot | — |
| bluetooth | Yes v4.1 | Yes v4.2 | Yes v5.0 | — |
| mobile highdefinition linkmhl | Yes | — | — | — |
| usb connectivity | Mass storage device, USB charging, USB Host, microUSB 2.0 | Mass storage device, USB charging, microUSB 2.0 | Mass storage device, USB charging | — |
| hdmi | Yes via microUSB | — | — | — |
| sar value | Head: 0.293 W/kg | Head: 0.322 W/kg | — | — |
| nfc | Yes | Yes | Yes | — |
| network support | 4G (supports Indian bands), 3G, 2G | 4G (supports Indian bands), 3G, 2G | 4G (supports Indian bands), 3G, 2G | — |
| gps | Yes with A-GPS, Glonass | Yes with A-GPS, Glonass | Yes with A-GPS, Glonass | — |
| sim 1 | 4G Bands:TD-LTE 2300(band 40) FD-LTE 2100(band 1) / 1800(band 3) / 2600(band 7) / 900(band 8) / 700(band 28) / 1900(band 2) / 1700(band 4) / 850(band 5) / 700(band 17) / 850(band 18) / 850(band 19) / 850(band 26)3G Bands: UMTS 1900 / 2100 / 850 / 900 MHz2G Bands: GSM 1800 / 1900 / 850 / 900 MHz 4G Speed: 50 Mbit/s ? 300 Mbit/s ? (LTE category 6)3G Speed: HSDPA 42. 2 Mbit/s ?, HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s ?GPRS:Available EDGE:Available 2 Mbit/s ?, HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s ?GPRS:Available EDGE:Available |
4G Bands:TD-LTE 2600(band 38) / 2300(band 40) / 2500(band 41) / 1900(band 39) FD-LTE 2100(band 1) / 1800(band 3) / 2600(band 7) / 900(band 8) / 700(band 28) / 1900(band 2) / 1700(band 4) / 850(band 5) / 700(band 13) / 700(band 17) / 850(band 18) / 850(band 19) / 800(band 20) / 1900(band 25) / 850(band 26)3G Bands: UMTS 1900 / 2100 / 850 / 900 MHz2G Bands: GSM 1800 / 1900 / 850 / 900 MHz 4G Speed: 50 Mbit/s ? 450 Mbit/s ? (LTE category 9)3G Speed: HSDPA 42.2 Mbit/s ?, HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s ?GPRS:Available EDGE:Available | 4G Bands:TD-LTE 2300(band 40) FD-LTE 2100(band 1) / 1800(band 3) / 2600(band 7) / 900(band 8) / 700(band 28) / 1900(band 2) / 1700(band 4) / 850(band 5) / 700(band 17) / 800(band 20)3G Bands: UMTS 1900 / 2100 / 850 / 900 MHz2G Bands: GSM 1800 / 1900 / 850 / 900 MHz 4G Speed: 150 Mbit/s ? 1024 Mbit/s ? (LTE category 16)3G Speed: HSDPA 42.2 Mbit/s ?, HSUPA 5.76 Mbit/s ?GPRS:Available EDGE:Available | — |
| sim size | SIM1: Nano | SIM1: Nano, SIM2: Nano (Hybrid) | SIM1: Nano, SIM2: Nano (Hybrid) | — |
More Details (2)
| Price | ₹ 49,900 | ₹ 48,900 | ₹ 57,900 | — |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Details | Samsung Galaxy S6 32GB full specification | Samsung Galaxy S7 full specification | Samsung Galaxy S8 full specification | — |
Treatment of radicular syndrome of the cervical spine in Moscow at the Dikul clinic: prices, appointments cervical spine.

Cervical radiculopathy is much less common than lumbar radiculopathy. The annual incidence is approximately 85 cases per 100,000 population. In a younger population, radicular syndrome (radiculopathy) of the cervical spine is the result of a herniated disc or an acute injury that causes a local effect on the nerve root. Disc herniation accounts for 20-25% of cases of cervical radiculopathy. In older patients, cervical radiculopathy is often the result of narrowing of the intervertebral joints due to the formation of osteophytes, reduced disc height, and degenerative changes in the uncovertebral joints. Treatment of radicular syndrome of the cervical spine can be either conservative or surgical, depending on the clinical picture and the genesis of compression.
The spinal roots (C1 — C8) emerge from the cervical spine and then branch out to innervate the muscles of the upper extremities (shoulders, arms, hands) to enable them to function. They also carry sensory fibers to the skin, which provides skin sensitivity in the zone of innervation.
When the roots of the cervical spine are irritated, with inflammation or compression, pains appear in the neck with irradiation to the hands, sensitivity disorders, muscle weakness in the zone of innervation of the damaged root.
Symptoms of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine may develop suddenly or gradually, and periods of exacerbation are followed by remission.
Causes of Cervical Radiculopathy
Any condition that in some way compresses or irritates a nerve root in the cervical spine can cause cervical radiculopathy.
The most common causes are:
- Herniated disc. If the internal material of the intervertebral bulges and irritates the nearby root in the cervical region, then the development of radicular syndrome (cervical radiculopathy) is possible. If a young person (20 or 30 years old) has cervical radiculopathy, the most likely cause is a herniated disc.
- Cervical spinal stenosis. As part of the degenerative process of the cervical spine, changes in the spinal joints can lead to a reduction in space in the spinal canal.
 Spinal stenosis is a common cause of symptoms of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine in people over 60 years of age.
Spinal stenosis is a common cause of symptoms of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine in people over 60 years of age. - Osteochondrosis (degenerative disc disease). As the discs in the cervical spine degenerate, the discs become flatter and stiffer and do not support the spine. In some people, this degenerative process can lead to inflammation or damage to a nearby nerve root. Cervical degenerative disc disease is a common cause of radiculopathy in people over 50 years of age.
- Cervical radiculopathy may be caused by other conditions that compress the nerve roots or cause damage to the cervical nerve roots, such as: tumors, fractures, infections or sarcoidosis, synovial cyst, synovial chondromatosis of the facet joints, giant cell arteritis of the radicular vessels.
- Factors associated with an increased risk of cervical radicular syndrome include: heavy manual labor requiring more than 10 kg lifting, smoking, and prolonged driving or working with vibrating equipment.

Symptoms
Symptoms of radicular syndrome of the cervical spine usually include pain, weakness or numbness in areas that are innervated by the affected root. Pain may be felt in only one area, such as the shoulder, or may radiate throughout the arm and into the fingers.
The type of pain can also vary. Some patients describe dull, constant pain. However, other patients describe the pain as sharp (knife-like) or intense burning.
Patients may experience tingling in the fingers, which may also be accompanied by numbness. A feeling of numbness or weakness in the hand can also affect the ability to grasp or lift objects, as well as perform other daily tasks such as writing, putting on clothes.
Certain neck movements, such as back extension of the neck, neck tilt, or rotation, may increase pain. Some patients report that the pain is relieved when they put their hand behind their head; movement can relieve pressure on the nerve root, which in turn reduces symptoms.
Types of cervical radiculopathy
Symptoms of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine depend on which root is subjected to cervical compression. For example, C6 radiculopathy occurs when the nerve root that emerges above the C6 vertebra is damaged.
While specific symptoms can vary widely in any given patient, there are characteristic symptoms for each level of root involvement:
- C5 radiculopathy — can cause pain and/or weakness in the shoulders and arms. A characteristic symptom is discomfort around the shoulder blades, numbness or tingling is rare.
- C6 radiculopathy (one of the most common) causes pain and/or weakness along the entire length of the arm, including the biceps, wrist, thumb and index finger.
- C7 radiculopathy (most common) causes pain and/or weakness from neck to hand and may involve triceps and middle finger.
- Radiculopathy C8 causes pain from the neck to the arm. Patients may experience weakness in the arm, and pain and numbness may radiate along the inside of the hand, ring finger, and little finger.

- If several roots are affected simultaneously, a combination of symptoms is possible
- Symptoms may worsen with certain activities, such as prolonged sitting with the neck tilted (working on a computer) and lessen at rest.
- But in some cases, symptoms may become permanent and not improve when the neck is in a supported rest position.
To select an adequate tactics for the treatment of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine, it is necessary to correctly identify the cause of the symptoms. For example, cervical radiculopathy and carpal tunnel syndrome can have similar symptoms, such as arm pain and numbness, so it is necessary to accurately determine the genesis of the symptoms in order to target the actual source of the problem.
Diagnosis
If symptoms such as neck pain or associated symptoms such as tingling, weakness, or numbness in the shoulder, arm, and/or hand are present, the doctor will likely start with the following:
- Patient history.
 The doctor collects detailed information about the presence of any previous or current diseases or conditions, accidents or injuries, family history and lifestyle. This allows you to get a better idea of what may be required for further examination.
The doctor collects detailed information about the presence of any previous or current diseases or conditions, accidents or injuries, family history and lifestyle. This allows you to get a better idea of what may be required for further examination. - Physical examination. The doctor, based on examination and palpation, determines the presence of anomalies, painful areas, as well as the range of motion and strength of the neck muscles.
- The Spurling test allows the physician to determine whether compression of the cervical spine may provoke or (temporarily) worsen a patient’s radicular symptoms. This test is usually performed as follows: the patient tilts the head to the side where the symptoms appeared, and then the doctor applies gentle pressure to the top of the head with his hand. This process leads to narrowing of the foraminal openings from which the nerve roots exit and this leads to the reproduction of the radicular symptoms experienced by the patient.
 If the Sperling test reproduces radicular symptoms, then cervical radiculopathy probably occurs.
If the Sperling test reproduces radicular symptoms, then cervical radiculopathy probably occurs.
- In patients who already have evidence of cervical myelopathy (spinal cord compression) or radicular symptoms after an injury episode (and therefore may have fractures), the Spurling test is not recommended.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
- X-ray of the cervical spine is usually the first method for diagnosing radicular syndrome and allows you to detect the presence of injuries, osteophytes, narrowing of the space between the vertebrae. Radiography is considered the most appropriate initial investigation in all patients with chronic neck pain.
- CT (MSCT)
-
CT scan provides good visualization of bone morphology and can be a useful diagnostic tool for evaluating acute fractures. The accuracy of diagnosing herniated discs in the cervical spine with CT imaging ranges from 72-91%.
CT scan with myelography has an accuracy approaching 96% in the diagnosis of cervical disc herniation.
 In addition, the use of a contrast material makes it possible to visualize the subarachnoid space and assess the condition of the spinal cord and nerve roots.
In addition, the use of a contrast material makes it possible to visualize the subarachnoid space and assess the condition of the spinal cord and nerve roots. - MRI
-
MRI has become the method of choice for imaging the cervical spine and can detect a significant proportion of soft tissue pathologies, such as disc herniation. MRI can detect torn ligaments or sequestered disc herniation that cannot be detected with other imaging modalities. An MRI can visualize the entire spinal cord, nerve roots, and spinal column well. MRI has been found to be a fairly informative method for assessing the amount of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) surrounding the spinal cord in the examination of patients with spinal canal stenosis:
- EMG (ENMG)
-
Electrodiagnostic methods of research are important for the detection of physiological disorders of the nerve root and the exclusion of other neurological causes of the patient’s symptoms. An EMG (ENMG) study has been shown to be useful in the diagnosis of radiculopathy and correlates well with myelography and surgical findings.

Treatment
Non-surgical treatment of cervical radicular syndrome may include the following treatments:
Rest or change of activity . Wearing a cervical collar during acute pain syndrome. Often, cervical radiculopathy resolves on its own, especially if symptoms are mild. Limiting strenuous activities such as playing sports or lifting heavy objects or improving posture while sitting or driving may sometimes be sufficient as a treatment.
exercise therapy. Exercise and stretching may help relieve symptoms. An exercise therapy doctor can develop an individual plan for a particular patient. Exercise therapy is the most effective treatment for radicular syndrome in both the short and long term. Foramen opening exercises are the best choice for reducing the effect of compression on the root. Exercises such as contralateral rotation and lateral flexion are among the simplest forms of exercise that are effective in reducing the symptoms of radicular syndrome and increase range of motion in the neck. Muscle strengthening exercises can also be done to improve neck stability and reduce the risk of future nerve root irritation, unless the root compression is due to reasons why exercise therapy is not curative. In the initial stages of treatment, muscle gain should be limited to isometric exercises in the involved upper limb. Once the acute symptoms are resolved, progressive isotonic strengthening can begin. Initially, resistance exercises should be done with light weights and high reps (15-20 reps). It is necessary to engage in exercise therapy for a long time, periodically adjusting the volume and intensity of the loads with the exercise therapy doctor.
Muscle strengthening exercises can also be done to improve neck stability and reduce the risk of future nerve root irritation, unless the root compression is due to reasons why exercise therapy is not curative. In the initial stages of treatment, muscle gain should be limited to isometric exercises in the involved upper limb. Once the acute symptoms are resolved, progressive isotonic strengthening can begin. Initially, resistance exercises should be done with light weights and high reps (15-20 reps). It is necessary to engage in exercise therapy for a long time, periodically adjusting the volume and intensity of the loads with the exercise therapy doctor.
Medicines . To reduce the symptoms of pain, it is possible to use various anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, movalis, ibuprofen) muscle relaxants.
If drugs in this group do not have an effect, it is possible to connect opioids for a short period of time.
Cervical epidural steroid injections are used in patients who are refractory to other treatments. When performed correctly by experienced doctors under x-ray control, in most cases of radicular syndrome in the cervical region, a fairly good effect can be achieved.
When performed correctly by experienced doctors under x-ray control, in most cases of radicular syndrome in the cervical region, a fairly good effect can be achieved.
Manual therapy . Manipulations during manual therapy can remove blocks and improve the mobility of motor segments and thus reduce symptoms.
Traction therapy . Skeletal traction is often used in the treatment of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine. Tractions are performed on specialized traction tables with controlled load. Traction allows you to slightly reduce the compression of the root by increasing the distance between the vertebrae. •
Acupuncture , along with other methods, is used in the treatment of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine. This treatment method improves conduction in nerve fibers, reduces pain and restores sensitivity.
Physiotherapy . Modern methods of physiotherapy, such as cryotherapy or Khivamat, as well as traditional methods (electrophoresis, phonophoresis) are widely used both in the acute stage of radicular syndrome and in the complex of rehabilitation techniques.
Surgery
If conservative treatments fail to relieve pain, or if neurological symptoms such as hand numbness and weakness continue to progress, then surgery may be considered.
The following surgical techniques are most commonly used in the treatment of cervical radiculopathy:
Anterior cervical discectomy and fixation . This operation is performed through a small incision in the front of the neck to remove a herniated disc, and then fixation of this motor segment of the cervical spine is performed, which allows for the stability of the spine. This is the most common operation for root decompression.
Intervertebral disc replacement with artificial disc . This technique allows you to replace the fixation of the vertebrae. A potential advantage of this technique is that it aims to maintain mobility at this level of the cervical spine rather than fusing two vertebrae.
Surgical treatment of radicular syndrome in the cervical spine can effectively reduce symptoms and restore conduction along nerve fibers. According to statistics, the efficiency ratio is from 80% to 90%. As with any surgery, there are some risks, but more often than not, the benefits of surgery outweigh the risks.
According to statistics, the efficiency ratio is from 80% to 90%. As with any surgery, there are some risks, but more often than not, the benefits of surgery outweigh the risks.
S6 — C7 of the cervical intervertebral disc, treatment, surgery, symptoms
7 January 2020
94037
3.5 out of 5
Tladpin
- 1 Types of the cervical spine
- 4 Conservative therapy
- 4.1 Medical treatment
- 4.2 Traction therapy
Initially, a protrusion is formed, i.e. a slight deformation of the disc while maintaining the integrity of the fibrous ring. If C6–C7 cervical herniation is not treated at this stage, the annulus fibrosus will become thinner and eventually rupture. The consequences of such changes can be quite deplorable, since the dural sac with the spinal cord and nerve endings pass in close proximity to the intervertebral discs.

C6–C7 disc herniation is the second most common. It is second only to hernias of the lumbar spine.
Types of hernias of the cervical spine
A protrusion can form towards the spinal canal, then a posterior or dorsal hernia is diagnosed, or outwards — an anterior hernia. The greatest danger is the first scenario, since with the growth of the protrusion, the spinal cord and nerves may suffer.
Depending on which side of the C6–C7 disc hernia is formed, there are:
- median — the protrusion is located strictly in the center of the posterior surface of the disc and can provoke alternating disorders on the right and left sides of the body;
- paramedian — a hernia is localized closer to the left or right side of the intervertebral disc, which causes, respectively, the prevalence of symptoms on the left or right;
- foraminal — a protrusion is formed in a very narrow opening of the spine, where many nerve roots pass, which, even with a small hernia, provokes severe neurological symptoms;
- diffuse — the formation occupies the entire posterior surface of the disc, which causes severe pain on both sides of the body.

If treatment is not started when the first symptoms of a hernia of the cervical spine of the 6th and 7th vertebrae appear, part of the nucleus pulposus may separate. This condition is called a sequestered hernia, which requires urgent surgical intervention.
Symptoms
The classic manifestations of a hernia of the neck are pain in the neck, radiating to the arms, shoulders, head, dizziness and limited mobility of the neck. But since the nerves responsible for the innervation of the eyes and the back surfaces of the hands pass in the region of the 6th and 7th vertebrae of the cervical spine, when they are compressed by a hernia, the corresponding symptoms may occur:0003
- pain on the back of the arm;
- weakening of the triceps reflex;
- numbness of the hand;
- decreased vision and hearing.
In severe cases, when the formation mechanically compresses the blood vessels, there may be symptoms of impaired brain function and jumps in blood pressure.

Diagnostics
If you experience pain in the neck, migraines and other manifestations of a hernia of the cervical spine of the 6th and 7th vertebrae, you should contact a neurologist or vertebrologist. After collecting an anamnesis and a thorough examination with checking all reflexes, the doctor will be able to assume the presence of a hernia. To confirm the diagnosis are assigned:
- KT;
- MRI;
- x-ray;
- electromyography.
MRI provides the most complete and accurate information. CT may be used as an alternative only in mild cases or when the patient is unable to pay the cost of an MRI. Comprehensive data is provided by a study on a tomograph with a magnetic field strength of more than 1.5 T. Thanks to MRI images, it is possible to thoroughly study the type, location and size of a C6-C7 disc herniation, which allows you to choose the best treatment tactics.
Conservative therapy
Initially, patients are offered conservative treatment of hernia, provided that there are no serious neurological disorders, and the hernia has not passed to the stage of sequestration.
 With a small size of education, the following is recommended for patients:
With a small size of education, the following is recommended for patients: - drug therapy;
- spinal traction.
If the size of the protrusion reaches 5-7 mm, it is recommended to start exercise therapy, attend physiotherapy sessions and wear the Chance collar. Let’s consider each component of conservative treatment separately.
Drug treatment
The use of drugs with different pharmacological effects allows you to have a complex effect on the problem. Therefore, patients are prescribed the following:
- NSAIDs — drugs help relieve pain and have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- muscle relaxants — designed to eliminate muscle spasm, which helps to reduce the intensity of pain and the correct distribution of the load on the muscles;
- vitamins of group B — improve nerve conduction, which has a positive effect on the sensitivity of the hands;
- chondroprotectors — according to manufacturers, they contribute to the regeneration of cartilage tissue, but the effectiveness of their use has not yet been proven.

In case of severe, unbearable pain in the neck, blockades are indicated. The procedure is carried out in a medical institution by a nurse with special training. It consists in introducing solutions of analgesics and corticosteroids into special points in the area of the affected disc. As a result, the transmission of pain impulses is blocked, and the patient gets rid of severe pain.
Traction therapy
Spinal traction can only reduce pain if the disc herniation of the 6th and 7th vertebrae is small. The essence of the method is the vibration-mechanical effect on the spine, as a result of which the distance between individual vertebrae slightly increases. This leads to a decrease in pressure on the intervertebral discs and a stop of degenerative changes.
Physiotherapy
To improve the effectiveness of the treatment, patients may be prescribed a course of procedures:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetotherapy;
- phonophoresis, etc.

They contribute to the activation of blood circulation, the accumulation of drugs in the affected area and, as a result, an improvement in well-being.
exercise therapy
Regular physical therapy helps to strengthen the muscles, which will be an excellent support for the spine. This will improve the patient’s condition and prevent the formation of a hernia in other spinal motion segments.
C6-C7 herniated disc surgery
Approximately 20-30% of cases fail conservative treatment. If at the same time there is an attachment of neurological disorders, the patient’s quality of life suffers significantly and severe pain is present, a consultation with a neurosurgeon is required. If there is evidence, he will prescribe an operation of one kind or another.
Surgical intervention is urgently performed if the hernia of the cervical spine of the 6th, 7th or other segments has passed into the stage of sequestration.
Depending on the location, size of the hernia and the clinical picture, the neurosurgeon may recommend:
- nucleoplasty;
- endoscopic surgery;
- microdiscectomy.
In these operations, the herniated disc or the entire disc is removed. If it is not possible to save the cartilage, it is necessary to replace it with an artificial implant or fuse the vertebral bodies together (fusion). The first scenario is more preferable, since it allows you to maintain the natural mobility of the spine.
Recently, M6-C endoprostheses have been used for cervical intervertebral disc replacement. Their design allows you to perform movements in 6 axes, and high strength ensures uninterrupted use for many decades.
Nucleoplasty
Nucleoplasty is the least traumatic and safest method of surgical treatment of cervical C6–C7 hernia. Its essence lies in the introduction under local anesthesia through a puncture with a diameter of several millimeters into the center of the disc hollow inside the instrument. Through the action of a laser, cold plasma, radio waves, or the mechanical action of the pressure of saline, part of the nucleus pulposus is destroyed.
 This creates the prerequisites for the gradual reverse retraction of the hernia and the elimination of pain.
This creates the prerequisites for the gradual reverse retraction of the hernia and the elimination of pain. Recently, hydroplasty with the help of the SpineGet apparatus, i.e., the use of saline pressure, has been more often used, since this technique is not associated with high temperatures. This avoids overheating of surrounding tissues and minimizes intraoperative risks.
But any technique of puncture surgery can be applied only with small hernias and the absence of neurological complications.
Endoscopic surgery
C6-C7 foraminal hernias or large lesions are indicated for removal using endoscopic equipment. The manipulator is brought to the affected disc through a small round puncture. The neurosurgeon monitors each of his actions through a monitor connected to the video camera of the endoscope. Since a diamond shaver is used to create access, the risk of damage to the nerve roots is minimal.
Microdiscectomy
For neurological disorders, sequestered hernias and in some other cases, the use of minimally invasive methods is not possible.
 In such situations, microdiscectomy is indicated.
In such situations, microdiscectomy is indicated. The operation is performed under general anesthesia through an anterior approach. Layer-by-layer separation of tissues and good visualization of all anatomical structures makes it possible to remove all pathologically altered tissues, restore the normal anatomy of the spinal motion segment at the level of the 6th and 7th vertebrae, and also release all pinched nerve endings. After that, it becomes possible to replace an irreversibly changed intervertebral disc with an endoprosthesis or fix the vertebrae with titanium structures.
Rehabilitation
Any surgical intervention is a stress for the body, after which recovery is required. If, after hydroplasty or another type of nucleoplasty, it proceeds almost imperceptibly for the patient, then after an endoscopic operation or microdiscectomy, it is required to slightly adjust the lifestyle.
Initially, drug therapy is recommended for patients to eliminate postoperative pain and inflammation.

