AMD Ryzen 5 5600G Review
The Ryzen 5 5600G is about to hit the retail market as the most affordable part sporting the Zen 3 architecture for $259. Inside the little box you also receive the Wraith Stealth cooler, which is a pretty interesting proposition. But first, some context…
Last month we checked out the Ryzen 7 5700G, which is the other APU in the 5000 series so far. If you haven’t read that review, in short, we were disappointed by what’s on offer as we struggled to find a practical use case for it considering the $360 asking price. For our audience, I think it’s fair to say the 5700G is a niche product that only makes sense for ultra compact PCs, whether that be for home theater use, casual gaming, or some other that requires you to have a desktop PC that’s the size of a gourmet burger.
For everyone else, a mid-range 6-core/12-thread processor, such as the Intel Core i5-10400F and a second hand graphics card such as the GTX 1060 3GB will serve you far better, at least for gaming, offering roughly twice the performance for the same price.
The R7 5700G then really is a product for OEM system builders. They get to advertise their compact and affordable PCs as serious gaming systems featuring 8 cores of Ryzen 7 power, while also affording them the luxury of slapping on a Radeon graphics logo, so you know it’s ready for Cyberpunk 2077 or any other modern game that it can’t actually run at a satisfactory level, but of course that doesn’t mater, if just has to give the impression that it’s a serious gaming machine.
So for most of you, at $360 the 5700G is a bit pointless, but what about the $260 Ryzen 5 5600G, is it any better?
| Ryzen 9 5900X | Ryzen 7 5800X | Ryzen 5 5600X | Ryzen 7 5700G | Ryzen 5 5600G | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release | November 5, 2020 | April 13, 2021 | |||
| MSRP $ | $550 | $450 | $300 | $360 | $260 |
| Cores / Threads | 12 / 24 | 8 / 16 | 6 / 12 | 8 / 16 | 6 / 12 |
| iGPU | N/A | 512:32:8 (8 CU) |
448:28:8 (7 CU) |
||
| Base Frequency |
3. 7 GHz 7 GHz |
3.8 GHz | 3.7 GHz | 3.8 GHz | 3.9 GHz |
| Turbo Frequency |
4.8 GHz | 4.7 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 4.6 GHz | 4.4 GHz |
| L3 Cache | 32 MB per CCD (64MB Total) | 32 MB | 32 MB | 16 MB | 16 MB |
| TDP | 105 watts | 65 watts | |||
In terms of specifications, it’s pretty straightforward. The 5600G is a 6-core/12-thread part, though it retains the same 16MB L3 cache, which is half that of the 5600X. Then for the iGPU, the Vega graphics are downgraded from 8 CUs to 7, and the frequency has been reduced by 5%, down to 1.9 GHz, so overall we expect a ~10% drop in iGPU performance.
To find out if that’s indeed the case we need to get into the benchmarks, and for this we’ve split the testing up into three sections. First we’re going to look exclusively at CPU performance by testing the 5600G in applications so we can compare it with the rest of our CPU data.
First we’re going to look exclusively at CPU performance by testing the 5600G in applications so we can compare it with the rest of our CPU data.
Then we want to see how well it works with the Vega iGPU, and for this we’ll be comparing it against the Ryzen 5 3400G, Ryzen 7 5700G and Core i7-11700, all using integrated graphics.
Finally, we’ve run discrete GPU tests using a GeForce RTX 3090, allowing us to compare the 5600G to a range of competing CPUs with a powerful graphics card. That should be interesting and will give us a good idea of what kind of headroom this APU offers gamers, should they upgrade down the track. So let’s get into it…
Application Benchmarks
Starting as we often do with Cinebench, we see that the 5600G is comparable in this test to the Core i5-11600K and just a smidgen slower than the 5600X which is good considering the 5700G was quite a bit slower than the 5800X. I’m not entirely sure why this is, perhaps the 16MB L3 cache does a better job of servicing 6-cores opposed to 8, not sure on that one.
Interestingly, the single thread performance is down on the 5600X by a 7% margin which isn’t massive, but it’s more significant than what we saw in the multi-thread test and is comparable to the 5700G vs 5800X margin.
Moving on to the 7-zip file manager compression test we find that the 5600G is only comparable to the Core i5-11400F making it 17% slower than the 5600X, which is a similar margin to that seen between the 5700G and 5800X, suggesting that the L3 cache capacity plays a crucial role here.
Decompression performance is more impressive when compared to the Intel competition and this is due to AMD’s SMT implementation working better, and as a result the 5600G was just 8% slower than Intel’s previous generation 8-core Core i7-10700. Still, when compared to the 5600X, it was 10% slower which is disappointing.
Even when testing with After Effects we find that the 5600G is ~9% slower than the 5600X and because this is a more lightly threaded application, the 5600G is comparable to the 5700G.
It’s the same with Adobe Photoshop which is another lightly threaded application that typically only leans on 1 or 2 cores heavily. Therefore we’re looking at comparable performance between not just the 5600G and 5700G, but also the new Core i5-11400F.
Adobe Premiere is a little more core-heavy and as a result the 5600G falls behind the 5700G, but when compared to the 5600X, it’s only 4% slower and therefore is comparable to the Core i5-11600K in this test.
The last application benchmark we have is Blender, where the 5600G finds itself situated between the Core i5-11600K and 11400F, making it just 6% slower than the 5600X.
Power Consumption
Before we get to the gaming tests, here’s a brief look at power consumption. The 5600G did consume slightly more power than the 5600X in this test despite being 6% slower. But when compared to the Intel competition, it was considerably more power efficient, especially against the 11600K.
Integrated Graphics Testing
Moving on to test the Radeon integrated graphics, we’ll start with Assassin’s Creed Valhalla at 1080p using the lowest possible quality settings. If you’re happy with 30 fps on average with frequent dips into the mid 20s then then the 5600G will work, but for me personally I found it unplayable. I was unable to enjoy the game at those frame rates, ideally I’d want at least 40 fps on average to start enjoying this one.
If you’re happy with 30 fps on average with frequent dips into the mid 20s then then the 5600G will work, but for me personally I found it unplayable. I was unable to enjoy the game at those frame rates, ideally I’d want at least 40 fps on average to start enjoying this one.
Overclocking the Vega graphics to 2.5 GHz boosted performance by 13% and that’s a pretty typical GPU overclock. That said, we have increased the operating frequency by 32%, so you’d expect a more significant increase, but I’d say we’re bandwidth limited here.
This took us from 30 to 34 fps on average which certainly helped, but wasn’t enough to start enjoying this title. As far as iGPU performance goes, it was very good, destroying Intel’s best socketed desktop options available right now.
Where the 5600G is very usable, in my opinion, is with Rainbow Six Siege. Here the game was very enjoyable with almost 60 fps on average, so perhaps not at the level of competitive gameplay, but it was playable in the more casual sense. Overclocked we received a 12% boost taking the average to 66 fps and now the 5600G is able to match a stock 5700G as well as the discrete Radeon RX 550.
Overclocked we received a 12% boost taking the average to 66 fps and now the 5600G is able to match a stock 5700G as well as the discrete Radeon RX 550.
When compared to the 3400G, the 5600G was 26% faster out of the box and a massive 127% faster than the Intel Core i7-11700. So for an iGPU solution it’s very impressive, but when compared to three generation old budget graphics cards like the GTX 1060 3GB, it looks a bit pathetic offering half the performance.
Unfortunately games like Horizon Zero Dawn aren’t playable using integrated graphics. Here the 5600G was good for just 25 fps on average, and overclocking only boosted that to 28 fps, or the same performance you’ll receive from the RX 550.
You’re looking at twice the performance with an old GTX 1060 3GB, or slightly more in this example. At least the AMD iGPUs ran this game, the Core i7-11700 kept crashing out when I tried to load into a level.
Despite being a late 2018 release, Shadow of the Tomb Raider is another AAA title that simply can’t run on integrated graphics. The 5600G was good for just 29 fps on average and wasn’t much better than the 3400G, we did see an improvement in 1% low performance but that’s likely a result of the extra CPU cores. Even with the 5600G overclocked the GTX 1060 3GB was still able to provide 163% greater performance.
The 5600G was good for just 29 fps on average and wasn’t much better than the 3400G, we did see an improvement in 1% low performance but that’s likely a result of the extra CPU cores. Even with the 5600G overclocked the GTX 1060 3GB was still able to provide 163% greater performance.
Doom Eternal runs well using the lowest settings at 1080p, and this saw the 5600G render 46 fps on average and 52 fps once overclocked. That means stock the 5600G was 21% faster than the 3400G and RX 550.
Watch Dogs: Legion is another modern game that you won’t be running on integrated graphics, at least at 1080p. With the lowest quality settings enabled, the 5600G rendered just 26 fps on average and then 30 fps once overclocked with regular dips into the mid 20s. So once again we’re looking at just shy of half the performance you’d get from the GTX 1060 3GB.
Counter-Strike: Global Offensive is a good example of a game that plays really well on low-end graphics solutions, including iGPUs. Here the 5600G was good for 101 fps on average at 1080p using the medium quality settings and we were able to boost that a further 24% via overclocking, hitting 125 fps on average and at that point you’re receiving a high refresh rate experience.
Here the 5600G was good for 101 fps on average at 1080p using the medium quality settings and we were able to boost that a further 24% via overclocking, hitting 125 fps on average and at that point you’re receiving a high refresh rate experience.
F1 2020 also plays reasonably well with the 5600G, spitting out 53 fps on average when stock and that made it slightly faster than the RX 550. Our overclock boosted performance by 15%, allowing for 61 fps on average, and at this point the gaming experience is excellent for an iGPU.
Our last integrated graphics test is Dota 2, a game that’s known to run on basically anything and proving that point is the 5600G with 66 fps on average at 1080p using the highest possible in-game quality settings. The overclock allowed for a big 29% increase in performance hitting 85 fps on average, so very smooth playable performance.
Gaming Benchmarks (dGPU)
Time to check out discrete GPU performance with the GeForce RTX 3090, and we’ll start with F1 2020. Here the 5600G allowed for 240 fps on average which is about the same level of performance you receive with the Core i5-10400F. That means this APU is 11% slower than the 5600X, and 6% slower than the 5700G, which is not a bad result.
Here the 5600G allowed for 240 fps on average which is about the same level of performance you receive with the Core i5-10400F. That means this APU is 11% slower than the 5600X, and 6% slower than the 5700G, which is not a bad result.
The 5600G fairs better in Rainbow Six Siege, not only did it allow for 464 fps on average but it was also just 9% slower than the 5600X, allowing it to beat all 10th and 11th-gen Core i5 processors.
Moving on to Horizon Zero Dawn, we find that the 5600G is comparable to the Core i5-10400F and not a great deal faster than the older Ryzen 7 3700X. When compared to the 5700G, it was just 3% slower and 9% slower than the 5600X.
In Borderlands 3 the 5600G doesn’t look particularly impressive, allowing for 142 fps on average making it 11% slower than the 5600X and the Core i5-10400F. Of course, that’s still highly playable performance, but the fact that it was slower than the Ryzen 5 3600 is a little concerning.
The 5600G only matched the Ryzen 7 3700X when testing with Watch Dogs Legion, though that did mean it also matched the 5700G. It was 12% slower than the 5600X and just 8% faster than the older Ryzen 5 3600.
It was 12% slower than the 5600X and just 8% faster than the older Ryzen 5 3600.
The 5600G also looks fairly weak relative to many of the other CPUs tested in Death Stranding, averaging 158 fps and placing somewhere between the 3700X and 3600, though it was closer to matching the performance of the 8-core model. It was quite shocking to see the 5600G trailing the 5600X by a massive 20% margin in this game though.
The 5600G was also much slower than the 5600X in Shadow of the Tomb Raider, this time trailing by an 18% margin, rendering 130 fps on average which was comparable to that of the 5700G, 3700X and 10th gen Core i5 processors.
In Hitman 2 the 5600G is much slower than the 5600X once again, trailing by 19% with an average of 122 fps opposed to 150 fps for the 5600X. The 5600G is similar to the 3700X when it comes to high-end gaming performance, and while that’s not a terrible result, it’s not exactly what we’ve come to expect from the Zen 3 architecture.
dGPU Gaming Performance Overview
Finally, we have the 10 game average data and as expected given what we just saw, the 5600G is only comparable with the 3700X when it comes to high-end gaming using a powerful discrete graphics card. Of course that’s not bad, but it does mean cheaper parts like the 10400F will deliver comparable or often better performance.
It also means when CPU bound the 5600G was on average 14% slower than the 5600X, which is a reasonably large margin. Of course it’s well worth noting that for the majority of gamers, and hardware configurations, the performance difference between these two CPUs is going to be very small as you’ll almost always end up GPU limited.
So keep in mind the fact that we are testing with a GeForce RTX 3090 at 1080p, using a lower tier GPU such as the RTX 3070 at 1440p will see the margins shrink to less than half of what’s shown here.
What We Learned
It’s worth mentioning that AMD is positioning the 5000-G series as flexible, scalable and accessible APUs for PC enthusiasts, said to deliver exceptional price to performance for gaming focused PCs. They even go as far as to say «incredible gaming on Radeon IGP.» So make no mistake, AMD is pushing the 5600G and 5700G as gaming-focused products.
They even go as far as to say «incredible gaming on Radeon IGP.» So make no mistake, AMD is pushing the 5600G and 5700G as gaming-focused products.
How incredible the gaming experience is really depends on the game. In modern and even relatively modern AAA titles, you’re typically looking at around 30 fps at 1080p using the lowest quality settings. Now, that might be incredible by iGPU standards, but overall it’s pretty miserable when compared to multi-generation old discrete GPUs.
With the right selection of games though, the 5600G can look quite good — games like CS:GO, League of Legends, Dota 2, Fortnite and F1 2020, for example. So as long as you go into this with the right expectations, gaming can be enjoyable with the 5600G standalone.
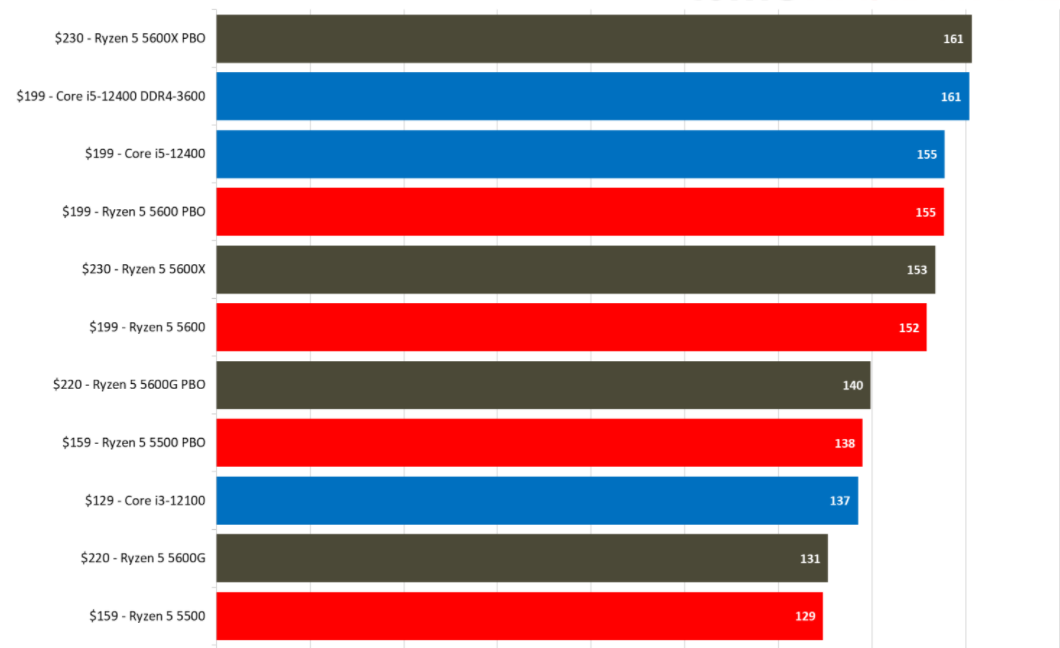
Priced at $260, it certainly makes a lot more sense than the 5700G, especially for gaming. These days you’re looking at ~$200 for a decent used graphics card — like the 3GB GTX 1060 — so it’s hard to beat the value of 5600G by doing what we suggested when reviewing the 5700G, which was to buy a Core i5-10400 and a second hand GPU.
Ideally, we’d prefer to see the 5600G priced closer to $200, but even if that’s not so, we can make a case for it at $260, and in our opinion that’s not possible for the 5700G at $360.
The Ryzen 5 5600G is also far more suitable than the 5700G as a stop-gap for those holding out for GPU pricing to recover, and it’s much more economical for use in home theater PCs. So as we see it, there’s far more use cases where the 5600G makes sense and that makes it a more valuable product in our opinion.
Shopping Shortcuts:
- AMD Ryzen 7 5800X on Amazon
- AMD Ryzen 5 5600X on Amazon
- Intel Core i7-11700 on Amazon
- Intel Core i7-10700K on Amazon
- AMD Radeon RX 6900 XT on Amazon
- AMD Radeon RX 6800 XT on Amazon
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 3080 on Amazon
- Nvidia GeForce RTX 3090 on Amazon
AMD Ryzen 5 5600G Specs, Price, and FPS in Games
Build a PC
| 6 | 12 | 3. 9 GHz 9 GHz |
4.4 GHz |
| Cores | Threads | Base Frequency | Turbo Frequency |
|---|
Geekbench 5 Single-Core
1466
64%
Geekbench 5 Multi-Core
7316
27%
Availability
AMD Ryzen 5 5600G 6-Core 12-Thread Unlocked Desktop Processor with Radeon Graphics
Buy on Amazon
$108.38
In Stock
Updated 78 minutes ago
Graphics Card
Resolution
Select game resolution
Graphics Settings
Select game graphics
Offset
…
Apply Offset
Value Rating
Performance Rating
Value per FPS
You will receive
… FPS
TOP 6 Games With AMD Ryzen 5 5600G
290
FPS
Grand Theft Auto V
1536
FPS
Minecraft
1155
FPS
League of Legends
506
FPS
VALORANT
313
FPS
Fortnite
319
FPS
Apex Legends
Alternatives For Ryzen 5 5600G
1080p, High
Intel Core i3-12100F
521
FPS
$
0. 21
21
/FPS
INTEL CORE I3-12100F DESKTOP
Buy on Amazon
$106.99
In Stock
Updated 78 minutes ago
Save $1.39
AMD Ryzen 5 5500
499
FPS
$
0.2
/FPS
AMD Ryzen™ 5 5500 6-Core, 12-Thread Unlocked Desktop Processor with Wraith Stealth Cooler
Buy on Amazon
$97.99
In Stock
Updated 78 minutes ago
Save $10.39
Intel Core i3-9350KF
461
FPS
$
0.23
/FPS
Intel Core i3-9350KF Desktop Processor 4 Core Up to 4.6GHz Unlocked Without Processor Graphics LGA1151 (999F4L)
Buy on Amazon
$104.03
In Stock
Updated 78 minutes ago
Save $4.35
Specifications
| General | |
|---|---|
| Release Date | Apr 13th, 2021 |
| Segment | Desktop |
| Socket | AMD Socket AM4 |
| Collection | Ryzen 5 |
| Codename | Cezanne |
| Performance | |
|---|---|
| Cores | 6 |
| Threads | 12 |
| Base Frequency | 3. 9 GHz 9 GHz |
| Turbo Frequency | 4.4 GHz |
| Other | |
|---|---|
| Power Consumption | 65 W |
| Overclockable | Yes |
| Integrated Graphics | Radeon Vega 7 |
Builds Using AMD Ryzen 5 5600G
1080p, High
Skytech Blaze II Gaming PC
273
FPS
$
3.66
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3060
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, 500 GB SSD
Buy on Amazon
$999.99
In Stock
Updated 73 minutes ago
iBUYPOWER Pro Gaming PC
273
FPS
$
4.76
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3060
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, 500 GB SSD
Buy on Amazon
$1,299. 99
99
In Stock
Updated 73 minutes ago
AVGPC Q-Box Series Gaming PC
273
FPS
$
3.4
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3060
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, N/A Storage
Buy on Amazon
$929
In Stock
Updated 73 minutes ago
AVGPC Hellfire Series Gaming PC
225
FPS
$
3.77
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3050
Ryzen 5 5600G
8 GB, N/A Storage
Buy on Amazon
$849
In Stock
Updated 73 minutes ago
Skytech Blaze Gaming PC
273
FPS
$
3. 66
66
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3060
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, 500 GB SSD
Buy on Amazon
$999.99
In Stock
Updated 71 minutes ago
HP Victus 15L Gaming Desktop PC
273
FPS
$
3.11
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3060
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, 1 TB SSD
Buy on Amazon
$849.99
In Stock
Updated 71 minutes ago
CYBERPOWERPC Gamer Master Gaming PC
225
FPS
$
7.11
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3050
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, 2 TB HDD
Buy on Amazon
$1,599.98
In Stock
Updated 75 minutes ago
HP Pavilion Gaming Desktop PC
176
FPS
$
5. 39
39
/FPS
Radeon RX 550
Ryzen 5 5600G
32 GB, 1 TB SSD
Buy on Amazon
$948
In Stock
Updated 71 minutes ago
HP OMEN 30L- Gaming Desktop PC
273
FPS
$
4.84
/FPS
GeForce RTX 3060
Ryzen 5 5600G
16 GB, 1 TB SSD
Buy on Amazon
$1,322.02
In Stock
Updated 74 minutes ago
HP 2022 OMEN Gaming Desktop PC
372
FPS
$
3.98
/FPS
Radeon RX 6600 XT
Ryzen 5 5600G
64 GB, 2 TB SSD + 2 TB HDD
Buy on Amazon
$1,479
In Stock
Updated 73 minutes ago
Find out which of the 2 CPUs performs better, view a side-by-side specification comparison.
Ryzen 5 5600G
$108.38
Ryzen 5 3600
$111.44
Ryzen 5 5600G
$108.38
Core i3-12100F
$106.99
Ryzen 5 5600G
$108.38
Ryzen 5 5500
$97.99
Ryzen 5 5600G
$108.38
Core i5-10400F
$112.23
Ryzen 5 5600G
$108.38
Core i5-10400
Ryzen 5 5600G
$108.38
Core i3-10100
Refine results to filter 1678 processors by performance, release date, price, and value. Click on a CPU to view more in-depth specifications and game FPS.
Calculation Parameters
Graphics Card
Resolution
Select game resolution
Graphics Settings
Select game graphics
Sort By
Popularity
Filters
Performance Rating
Value Rating
CPU Type
Desktop
25
Mobile
0
Server
0
Found 1678 CPUs.
Popularity
Processor
Performance
Ryzen 7 5700X
Apr 4th, 2022
Performance Rating
$189 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 7 5800X3D
Apr 20th, 2022
Performance Rating
$323 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 5 5600X
Nov 5th, 2020
Performance Rating
$166 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 5 5600G
Apr 13th, 2021
Performance Rating
$108.38 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i9-13900K
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$599.97 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 9 5900X
Nov 5th, 2020
Performance Rating
$340 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 7 5700G
Apr 13th, 2021
Performance Rating
$178 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i7-12700K
Nov 4th, 2021
Performance Rating
$298. 99 on Amazon
99 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i7-13700K
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$417.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 7 7700X
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$343.62 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i5-13600K
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$319.84 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 7 5800X
Nov 5th, 2020
Performance Rating
$233.01 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i5-12400
Jan 4th, 2022
Performance Rating
$182.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 5 5600
Apr 20th, 2022
Performance Rating
$139.79 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i7-12700KF
Nov 4th, 2021
Performance Rating
$276.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 9 7900X
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$419.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 9 7950X
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$589 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 5 3600
Jul 7th, 2019
Performance Rating
$111. 44 on Amazon
44 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i7-13700KF
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$398.88 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i5-12600K
Nov 4th, 2021
Performance Rating
$238.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Ryzen 5 7600X
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$244.19 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i9-13900KF
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$568.74 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i3-12100F
Jan 29th, 2022
Performance Rating
$106.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i5-13600KF
Sep 27th, 2022
Performance Rating
$296.99 on Amazon
In Stock
Core i9-12900K
Nov 4th, 2021
Performance Rating
$416.53 on Amazon
In Stock
- Previous
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 66
- 67
- 68
- Next
AMD Ryzen 5 5600G processor and similar AMD and Intel models without a discrete graphics card
Once upon a time, we conducted all tests of computer systems and processors for them with the same discrete graphics cards. This approach did not cause problems — basically, I had to work with modular desktop computers, which also provided the necessary flexibility in configuring them. Yes, and fixing the video card was required mainly for games — other applications at that time, as a rule, did not rely on their capabilities. And then games were part of the standard methodology — which is why it was required. Yes, and integrated graphics then took its first steps, and many of its implementations simply “slowed down” processors in general-purpose programs as well. nine0003
This approach did not cause problems — basically, I had to work with modular desktop computers, which also provided the necessary flexibility in configuring them. Yes, and fixing the video card was required mainly for games — other applications at that time, as a rule, did not rely on their capabilities. And then games were part of the standard methodology — which is why it was required. Yes, and integrated graphics then took its first steps, and many of its implementations simply “slowed down” processors in general-purpose programs as well. nine0003
Later, the ability to maintain this approach disappeared as the number of “non-configurable” systems under study grew. However, the GPU still did not affect the work of the vast majority of programs, but the games had to be moved to the optional set. Outside of it, it remains possible to compare the performance of processors directly with each other — regardless of the specific GPU. At one time, most tests, even on desktop systems, could be carried out exclusively with a focus on the IGP. Simply because in the period from 2014 to 2017, most of the new products were supplied with it: AMD then developed only APUs, while Intel supplied all desktop processors with an integrated GPU. HEDT, as well as special game tests, did not fit into the main canvas, but both could be done according to locally adapted methods .
Simply because in the period from 2014 to 2017, most of the new products were supplied with it: AMD then developed only APUs, while Intel supplied all desktop processors with an integrated GPU. HEDT, as well as special game tests, did not fit into the main canvas, but both could be done according to locally adapted methods .
AMD Ryzen 5 3400G and Intel Core i5-9600K with integrated and discrete graphics in applications of our test method
But after 2017, we had to return to the original approach. To the extent that it was possible, of course, compact and / or portable systems cannot be flexibly configured, so you have to use as is. But already adjusted for the GPU — which many programs gradually began to use, shifting part of the work from the processor to it. However, as our last year’s testing of the AMD Ryzen 5 3400G and Intel Core i5-9 showed600K with integrated graphics and two discrete video cards, this is not particularly difficult: most of the programs of the test method do not care about the specific model of the video card: it is either not used at all, or it is used in the same way. Only Adobe Premiere Pro and Magix Movie Edit Pro work significantly differently: the versions we use already know how to use the Intel GPU, but still ignore all other solutions. Now the situation is gradually changing, but we will find out how and by how much within the framework of the new testing methodology, which will soon be ready. In the meantime, this moment should simply be taken into account, but it makes sense to return to the topic again, since both companies have updated their processors. This is Intel’s first microarchitecture change in five years, and AMD last year increased the number of cores in APUs from four to eight — and also transferred them to a new microarchitecture this year. It is clear that the «pure» processors of the company can have a larger number of cores — and if they are equal, they are cheaper, while maintaining an advantage in the amount of cache memory, support for PCIe 4.0, etc. Intel has a different problem — graphics are everywhere (just in terms of processors blocked — but without changing other characteristics), but its performance, to put it mildly, leaves much to be desired.
Only Adobe Premiere Pro and Magix Movie Edit Pro work significantly differently: the versions we use already know how to use the Intel GPU, but still ignore all other solutions. Now the situation is gradually changing, but we will find out how and by how much within the framework of the new testing methodology, which will soon be ready. In the meantime, this moment should simply be taken into account, but it makes sense to return to the topic again, since both companies have updated their processors. This is Intel’s first microarchitecture change in five years, and AMD last year increased the number of cores in APUs from four to eight — and also transferred them to a new microarchitecture this year. It is clear that the «pure» processors of the company can have a larger number of cores — and if they are equal, they are cheaper, while maintaining an advantage in the amount of cache memory, support for PCIe 4.0, etc. Intel has a different problem — graphics are everywhere (just in terms of processors blocked — but without changing other characteristics), but its performance, to put it mildly, leaves much to be desired. And in models until last year, the same problem concerned even functionality. It would seem that the choice is obvious: if it is possible to install a video card, then it should be done. Even if there are no serious requirements for it — at least inexpensive. But precisely what «seemed» — since there are practically no inexpensive on the modern market. There are, perhaps, budget “plugs” that have not been updated for a long time — which, in some respects, are even worse than integrations (even Intel ones) — but in modern conditions they cost almost like real . And in such circumstances, focusing on integrated graphics (at least for a while — to wait for the normalization of prices) is fully justified. And just then the new Ryzen 5 5600G came to us, which (unlike the previous generation of APUs) the company plans to actively sell at retail, so it was decided to start working with it with just such material. For which it was necessary to test a few more AMD and Intel processors, but still they were going to do it for a long time.
And in models until last year, the same problem concerned even functionality. It would seem that the choice is obvious: if it is possible to install a video card, then it should be done. Even if there are no serious requirements for it — at least inexpensive. But precisely what «seemed» — since there are practically no inexpensive on the modern market. There are, perhaps, budget “plugs” that have not been updated for a long time — which, in some respects, are even worse than integrations (even Intel ones) — but in modern conditions they cost almost like real . And in such circumstances, focusing on integrated graphics (at least for a while — to wait for the normalization of prices) is fully justified. And just then the new Ryzen 5 5600G came to us, which (unlike the previous generation of APUs) the company plans to actively sell at retail, so it was decided to start working with it with just such material. For which it was necessary to test a few more AMD and Intel processors, but still they were going to do it for a long time. nine0003
nine0003
Note that we will not touch on game tests today — we have already dealt with this recently with respect to most of the subjects. With the exception of the 5600G, the GPU hasn’t changed much in the new line. Over time (no later than we collect the entire new collection) we will work on this issue in more detail. In the meantime — the processor part, since this is just the main change in both AMD Cezanne and Intel Rocket Lake.
Test participants
| Intel Core i5-9600K | Intel Core i5-10600K | Intel Core i5-11600K | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core name | Coffee Lake Refresh | Comet Lake | Rocket Lake |
| Production technology | 14 nm | 14 nm | 14 nm |
| Core frequency, GHz | 3.7/4.6 | 4.1/4.8 | 3.9/4.9 |
| Number of cores/threads | 6/6 | 6/12 | 6/12 |
| L1 cache (total), I/D, KB | 192/192 | 192/192 | 192/288 |
| L2 cache, KB | 6×256 | 6×256 | 6×512 |
| L3 cache, MiB | 9 | 12 | 12 |
| RAM | 2×DDR4-2666 | 2×DDR4-2933 | 2×DDR4-3200 |
| TDP, W | 95 | 125 | 125 |
| Number of PCIe lanes | 16 (3. 0) 0) |
16 (3.0) | 20 (4.0) |
| Integrated GPU | UHD Graphics 630 | UHD Graphics 630 | UHD Graphics 750 |
Last time we settled on the Core i5-9600K, however, as part of the transition from LGA1151 to LGA1200, the manufacturer first endowed this family with Hyper-Threading support (more precisely, stopped blocking it) without significantly changing anything in the chip, and then to replace Comet Lake came Rocket Lake. In which the microarchitecture of the processor cores is already new, and the GPU is new, and the PCIe controller is already Gen4 … In general, everything is beautiful, except for one thing: all the splendor is based on the same 14-nanometer process, so the crystal turned out to be very large and voracious. Everything is like in a joke about a new comfortable airliner: now fasten your seat belts and we’ll try to take off with all this aboard . We already know this well — since all these three processors have been tested more than once.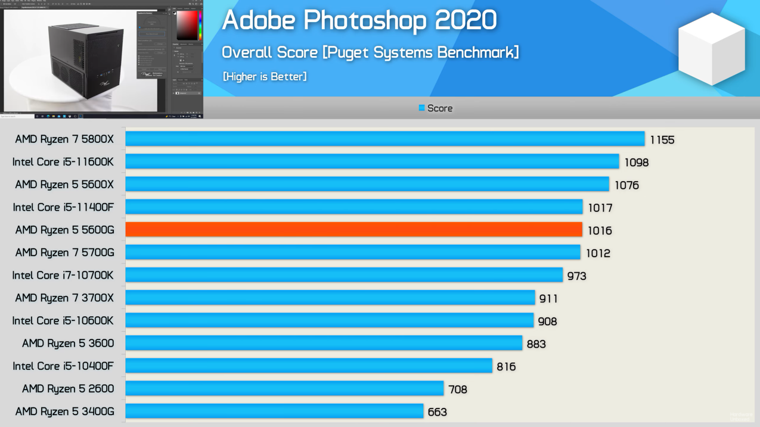 But two of them — only with a discrete graphics card.
But two of them — only with a discrete graphics card.
| AMD Ryzen 5 Pro 4650G | AMD Ryzen 7 Pro 4750G | AMD Ryzen 5 5600G | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Core name | Renoir | Renoir | Cezanne |
| Production technology | 7 nm | 7 nm | 7 nm |
| Core frequency, GHz | 3.7/4.2 | 3.6/4.4 | 3.9/4.4 |
| Number of cores/threads | 6/12 | 8/16 | 6/12 |
| L1 cache (total), I/D, KB | 192/192 | 256/256 | 192/192 |
| L2 cache, KB | 6×512 | 8×512 | 6×512 |
| L3 cache, MiB | 8 | 8 | 16 |
| RAM | 2×DDR4-3200 | 2×DDR4-3200 | 2×DDR4-3200 |
| TDP, W | 65 | 65 | 65 |
| Number of PCIe lanes | 20 (3. 0) 0) |
20 (3.0) | |
| Integrated GPU | Radeon | Radeon | Radeon |
Initially, it was decided to limit ourselves to six-core processors, since the 5600G (and today it is the main character — since it is the only completely new one) is exactly like that, however, on reflection, we added last year’s older APU to the set, even though it has eight cores. But the old ones — actually the year before last, and in desktop processors of the 3000 line (which are also Zen2) and in 2019year there were up to 16 cores. But there it happened thanks to the chiplet layout. And all APUs are more like Intel processors — they use one monolithic crystal. The 7-nanometer process technology made it possible to “shove” eight cores along with the GPU there, but more is still difficult. And without that, I had to greatly limit the capacity of the cache memory, and they still do not have support for PCIe 4.0 APUs. When switching from Renoir to Cezanne, nothing has changed significantly — for this, the company also needs new technical processes. But the cores are now Zen3, not Zen2 — and in the form of a single block: without splitting into quad-core CCX, as before. There is also a single cache of the third level, and its capacity has doubled. Despite the limited transistor budget, it was necessary to go for it — the low capacitance of L3 was perhaps the weakest point of Renoir. In chipsets of «clean» processors of both lines, we recall, it is generally 32 MiB, so the gap from them has only been reduced, but not eliminated. But this should also have a beneficial effect — as well as the new microarchitecture itself. nine0003
When switching from Renoir to Cezanne, nothing has changed significantly — for this, the company also needs new technical processes. But the cores are now Zen3, not Zen2 — and in the form of a single block: without splitting into quad-core CCX, as before. There is also a single cache of the third level, and its capacity has doubled. Despite the limited transistor budget, it was necessary to go for it — the low capacitance of L3 was perhaps the weakest point of Renoir. In chipsets of «clean» processors of both lines, we recall, it is generally 32 MiB, so the gap from them has only been reduced, but not eliminated. But this should also have a beneficial effect — as well as the new microarchitecture itself. nine0003
Test procedure
Methodology for testing computer systems of the 2020 sample
The testing methodology is described in detail in a separate article, and the results of all tests are available in a separate table in Microsoft Excel format. Directly in the articles, we use the processed results: normalized with respect to the reference system (Intel Core i5-9600K with 16 GB of memory, AMD Radeon Vega 56 video card and SATA SSD — this article is also directly involved in today’s article) and grouped by areas of application of the computer. Accordingly, all diagrams related to applications have dimensionless scores — so more is always better. And starting from this year, we are finally transferring game tests to an optional status (the reasons for which are discussed in detail in the description of the test methodology), so that only specialized materials will be available for them. nine0003
Accordingly, all diagrams related to applications have dimensionless scores — so more is always better. And starting from this year, we are finally transferring game tests to an optional status (the reasons for which are discussed in detail in the description of the test methodology), so that only specialized materials will be available for them. nine0003
iXBT Application Benchmark 2020
The task is primarily for calculations, and multi-threaded calculations — therefore the number of cores and threads is important. Can we increase their number? This is more efficient than improving the quality of the kernels. That’s why the 4750G remains the leader (since it’s the only one with the 8C/16T formula), and Intel processors benefited more from the return of Hyper-Threading than from a deep upgrade. But in general, the latter is clearly visible in both companies — and the efficiency is almost the same. And the performance is at the same level: if the 4600G/4650G were direct competitors to the Core i5-10600K, then the 5600G is already head to head with the i5-11600K.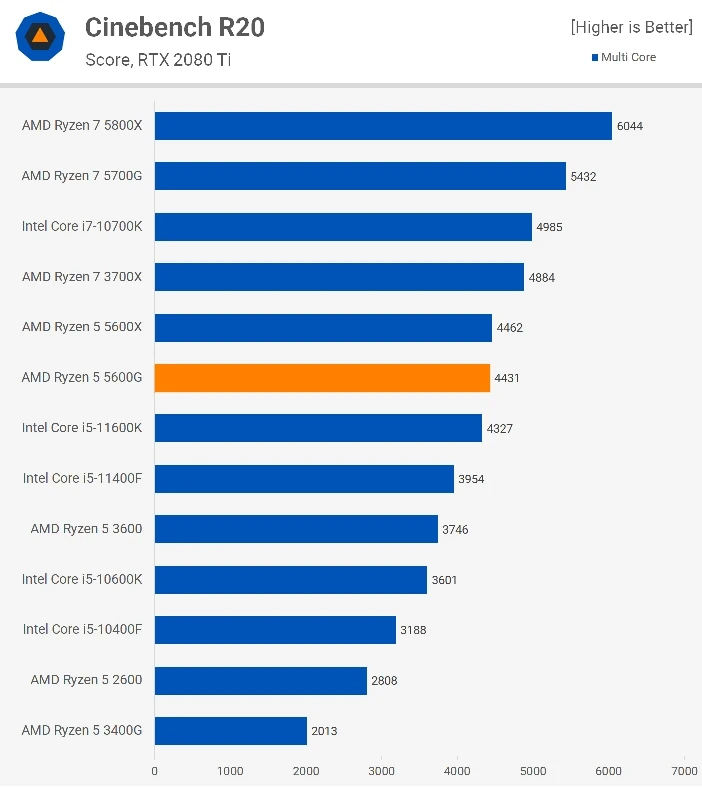 nine0003
nine0003
Nothing has changed. Although it couldn’t. Theoretically, software optimization could allow the Core i5-11600K to speed up somewhere (thanks to AVX512 support), but for now, parity. More precisely, its preservation is the same as last year. It was worse the year before last — then AMD APUs contained only four cores of the «old» architecture, much less efficient than Skylake. Therefore, the Ryzen 5 CPUs were at least as good as the Core i5 (in fact, at one time they competed well with the more expensive Core i7), and the Ryzen 5 APUs were incapable of such feats. Now, in pairs (2020 or 2021 edition) are the same, i.e. when choosing, first of all, you need to look at other circumstances. nine0003
Pogrom 🙂 The reasons for which are indicated above — in two out of five programs in Intel processors, the GPU took over the lion’s share of the work, but the versions used still cannot work in the same way with discrete or integrated solutions from AMD and Nvidia. It happens so — we warned more than once. However, it is clear that this is nothing more than a temporary state — Intel generally took care of video encoding and decoding issues before others, and the company’s market share has always been too large to ignore, and AMD has just yet to «convince» all programmers it is more responsible to treat (at least) APU. But, by the way, the effect of the upgrade of Intel processor cores turned out to be blurry — AMD has a larger increase. And it is clearly seen that not everything is decided by the quantity here: the new Ryzen 5 even managed to outperform last year’s Ryzen 7 even a little.0003
However, it is clear that this is nothing more than a temporary state — Intel generally took care of video encoding and decoding issues before others, and the company’s market share has always been too large to ignore, and AMD has just yet to «convince» all programmers it is more responsible to treat (at least) APU. But, by the way, the effect of the upgrade of Intel processor cores turned out to be blurry — AMD has a larger increase. And it is clearly seen that not everything is decided by the quantity here: the new Ryzen 5 even managed to outperform last year’s Ryzen 7 even a little.0003
In this case, single-threaded performance generally comes first. And it is clear that Intel is doing better with this at times — depending on other conditions, of course. But the difference of the order of 5% can not be taken into account — all the same, you will not notice its without devices .
And again we return to the exact equality. But only in the 11600K-5600G pair — last year’s products differed slightly not in favor of AMD. Remembering the «cache-loving» nature of this program — and the fact that Cezanne L3 has doubled, the mechanism for solving the problem is clear. nine0003
Remembering the «cache-loving» nature of this program — and the fact that Cezanne L3 has doubled, the mechanism for solving the problem is clear. nine0003
And here doubling the cache is clearly not enough. Inside AMD’s own lineup, it (together with the improvement of the cores) worked perfectly — the new Ryzen 5 managed to overtake the Ryzen 7 from the previous collection. But Intel processors are still noticeably faster. Note that «pure» AMD processors do not have such a problem — but there is also L3 32 MiB, and not 16 and not, especially 8. Moreover, the archivers themselves are no longer very relevant for many users today (and when they are needed — in practice, weaker processors do just fine), but this can also manifest itself in other classes of software. For example, the behavior of games has much in common with just these programs. And how things are going there — we will definitely check in a configuration with a discrete graphics card. nine0003
And we are back to normal again, even with a slight advantage of APU. It used to be, and here Intel even “won back” a little backlog — but such a difference can hardly be considered significant.
It used to be, and here Intel even “won back” a little backlog — but such a difference can hardly be considered significant.
Like this, it won’t work. However, it is due to literally two groups of applications — archivers and video editors. The first problem is “hardware” — it cannot be solved, at least until it is possible to speed up the memory system and, in particular, increase caches. It just has to be taken into account. And the second is purely software. And, in the process of updating the software, it can resolve itself, since this is purely a matter of compatibility. What is in newer versions of programs — as already mentioned, we will try to check soon. For now, let’s just say that the possibility of such a development of events cannot be ruled out. Under normal conditions, we can talk about parity between Core i5 and APU Ryzen 5.
Testing in 10 games on integrated GPUs of AMD and Intel processors and discrete GeForce GT 730, 740 and 1030
As for the processor part, as far as GPU performance is concerned, there is no “parity”, as we well know. Rocket Lake has only learned how to overtake Athlon — but at least Ryzen 3 (including the very first three-year-old models) is still far away. And this is not the only problem.
Rocket Lake has only learned how to overtake Athlon — but at least Ryzen 3 (including the very first three-year-old models) is still far away. And this is not the only problem.
Power consumption and energy efficiency
0005 power consumption not important . In principle, if we are talking about a gaming PC with a top-end video card, then against its background … Maybe not very important. But if a simple (perhaps even compact) system is being assembled, then I would like to be smaller than .
But the old 14nm “smaller” manufacturing process does not allow. In general, and the models of three years ago did not look very good in this parameter, the LGA1200 was developed in many respects to feed the voracious updated models — but against the backdrop of Rocket Lake, this all pales. AMD APUs, on the other hand, have about twice as modest appetites (on average), so you can assemble a compact computer on AM4 and not suffer with all sorts of supercoolers. With Intel’s new products, it’s better not to be smart. With younger models and tightening the power consumption limits, if only — but in this case, performance will decrease. nine0003
With Intel’s new products, it’s better not to be smart. With younger models and tightening the power consumption limits, if only — but in this case, performance will decrease. nine0003
Just because the «old» 14 nm do not allow you to be both rich and healthy at the same time. You can make a low-power processor, or you can make a high-performance one — but these will be two completely different processors. Although once this technical process was the best in the industry, and until recently it allowed Intel to somehow get out. But it’s good that this horse skeleton can no longer be spurred on. Alas, not yet in the desktop segment. But AMD does not have such a problem — exactly the same crystals that are designed for the mobile market go to desktop APUs. Much more power efficient than existing Intel desktop solutions. nine0003
Total
If we ignore individual hacks, then the conclusion is simple — in terms of processor performance, Ryzen 5 APUs are equivalent to Core i5 of the corresponding year of manufacture. Over the past time, both companies have increased performance — but just in approximately equal proportions. So, most likely, the same can be extended to the competition of Ryzen 7 with Core i7. But in the budget segment, AMD already has the new Ryzen 3, while Intel remains with last year’s Core i3. With all the consequences. However, Alder Lake and LGA1700 will be released soon, which can greatly change the alignment. But all this will start, as usual, with top-end processors and motherboards, then prices will drop for several more months … In general, it is unlikely that many will assemble a computer on a new platform by the New Year. And without a discrete graphics card — almost no one is for sure. nine0003
Over the past time, both companies have increased performance — but just in approximately equal proportions. So, most likely, the same can be extended to the competition of Ryzen 7 with Core i7. But in the budget segment, AMD already has the new Ryzen 3, while Intel remains with last year’s Core i3. With all the consequences. However, Alder Lake and LGA1700 will be released soon, which can greatly change the alignment. But all this will start, as usual, with top-end processors and motherboards, then prices will drop for several more months … In general, it is unlikely that many will assemble a computer on a new platform by the New Year. And without a discrete graphics card — almost no one is for sure. nine0003
In such conditions, first of all, you have to pay attention to other parameters. For example, prices. Or prohibitive (for this segment) power consumption of Rocket Lake. Or significantly more powerful graphics in the APU — at the level of junior discrete video cards, which, in general, allows you to play many games. Although, for some, the greater functionality of Intel platforms may be more important — for example, support for PCIe 4.0 (AMD still has to choose between integrated graphics and a new interface — they do not live together) or USB3 Gen2 × 2. In general, it seems to us that AMD AM4 looks much better than the Intel LGA1200 as a platform for a home non-gaming (but with the ability to run some games) computer in terms of the totality of characteristics at the moment. In the case of the latter, the use of integrated graphics is rather a temporary measure: when a gaming system is planned, but there is no money for a gaming video card yet. And the APU is a balanced all-in-one solution: fast, inexpensive, economical. nine0003
Although, for some, the greater functionality of Intel platforms may be more important — for example, support for PCIe 4.0 (AMD still has to choose between integrated graphics and a new interface — they do not live together) or USB3 Gen2 × 2. In general, it seems to us that AMD AM4 looks much better than the Intel LGA1200 as a platform for a home non-gaming (but with the ability to run some games) computer in terms of the totality of characteristics at the moment. In the case of the latter, the use of integrated graphics is rather a temporary measure: when a gaming system is planned, but there is no money for a gaming video card yet. And the APU is a balanced all-in-one solution: fast, inexpensive, economical. nine0003
Another interesting point: although both companies have updated their processor lines this year, the old solutions still should not be discounted. Yes, they are slower — but also cheaper. At the same time, Intel’s «tenth» line is much more economical. And AMD’s IGP once again hasn’t changed much, so if you focus on it, then new items are not really needed. On the other hand, the 4000th line did not enter the mass retail market, but there will be no problems with the acquisition of the 5000th in ordinary retail stores. And this is good — many have been waiting for her there for a long time. nine0003
On the other hand, the 4000th line did not enter the mass retail market, but there will be no problems with the acquisition of the 5000th in ordinary retail stores. And this is good — many have been waiting for her there for a long time. nine0003
AMD Ryzen 5 5600X vs Ryzen 5 5600G:
performance comparison
VS
AMD Ryzen 5 5600X
AMD Ryzen 5 5600G
Which is better: AMD Ryzen 5 5600X at 3.7 GHz (with Turbo Core up to 4.6) or Ryzen 5 5600G at 3.9 GHz (with Turbo Core up to 4.4)? To find out, read our comparative testing of these 6-core desktop processors in popular benchmarks, games and heavy applications.
- Overview
- Differences
- Performance
- Features
- Comments (4)
Overview
Overview and comparison of the main metrics from NanoReview
Single -flow performance
Rating in tests using one nucleus
Ryzen 5 5600x
73
Ryzen 5 5600g
68
Multi -flow performance
Tests in benchmarks, where all nucleus 9000 are involved0003
RYZEN 5 5600X
47
Ryzen 5 5600g
Energy efficiency
Energy consumption chip
RYZEN 5 5600x
73 9000 9000 9000 9000 RIC
Ryzen 5 5600X
63
Ryzen 5 5600G
59
Key differences
What are the main differences between 5600G and 5600X
nine0003
Reasons to choose AMD Ryzen 5 5600X
- Has 16MB more L3 cache
- New PCI Express standard — 4.
0
- 11% faster in Geekbench v5 single-core test — 1654 and 1493 points higher 9032 frequency in Turbo Boost (4.6 GHz vs 4.4 GHz)
Reasons to choose AMD Ryzen 5 5600G
- Launched 6 months later than rival
- Has Radeon RX Vega 7 integrated graphics
nine0411
Benchmark tests
Compare the results of processor tests in benchmarks
Cinebench R23 (single core)
Ryzen 5 5600X
+3%
1546
Ryzen 5 5600G
1503
Cinebench R23 (multi-core)
Ryzen 5 5600X
+5%
11845
Ryzen 5 5600G
11240
Passmark CPU (Single Core)
Ryzen 5 5600X
+6%
3380
Ryzen 5 5600G
3186
Passmark CPU (multi-core)
Ryzen 5 5600X
+10%
21963
Ryzen 5 5600G
19960
Geekbench 5 (single core)
Ryzen 5 5600X
+10%
1654
Ryzen 5 5600G
1503
Geekbench 5 (multi-core)
Ryzen 5 5600X
+18%
8952
Ryzen 5 5600G
7584
Add your Cinebench R23 results
nine0003
Specifications
AMD Ryzen 5 5600X and Ryzen 5 5600G full technical specifications list
General information
| Manufacturer | AMD | AMD |
| Release date | October 8, 2020 | April 13, 2021 |
| Type | Desktop | |
| Instruction set architecture | x86-64 | x86-64 |
| Codename | Zen 3 (Vermeer) | Zen 3 (Cezanne) |
| Integrated graphics | No | Radeon RX Vega 7 |
Processor
| Core | 6 | 6 |
| threads | 12 | 12 |
| Frequency | 3. |
3.9 GHz |
| Max. frequency in Turbo Boost | 4.6 GHz | 4.4 GHz |
| Number of cores | 6 | |
| Number of threads | 12 | 12 |
| Bus frequency | 100 MHz | 100 MHz |
| Multiplier | 37x | 39x |
| Level 1 cache | 64KB (per core) | 64KB (per core) |
| Level 2 cache | 512KB (per core) | 512KB (per core) |
| Level 3 cache | 32MB (shared) | 16MB (shared) |
| Unlocked multiplier | Yes | Yes |
| Number of transistors | — | 10.7 billion |
| Process | 7 nanometers | |
| Socket | AM4 | AM4 |
| Power consumption (TDP) | 65 W | 45-65W |
| Critical temperature | 95°C | 95°C |
| Integrated graphics | — | |
| GPU frequency | — | 300 MHz |
| Boost GPU frequency | — | 1900 MHz |
| Shader blocks | — | 448 |
| TMUs | — | 28 |
| ROPs | — | |
| TGP | — | 10-45W |
Igpu Flops
Ryzen 5 5600x
N/D
Ryzen 5 5600g
1. 108 Teraflops
Memory Support
| Type of memory type | DDR4-3200 | DDR4-3200 |
| Max. size | 128 GB | |
| Number of channels | 2 | 2 |
| Max. bandwidth | 47.68 GB/s | — |
| ECC support | Yes | No |
Other
| Official site | AMD Ryzen 5 5600X | |
| PCI Express version | 4.0 | 3.0 |
| Max. PCI Express lanes | 20 | 24 |
Poll
What processor do you think is the best?
Ryzen 5 5600X
886 (43.8%)
Ryzen 5 5600G
1135 (56.
