The AMD Radeon R9 290 Review
by Ryan Smithon November 5, 2013 12:01 AM EST
- Posted in
- GPUs
- AMD
- Radeon
- Hawaii
- Radeon 200
295 Comments
|
295 Comments
The AMD Radeon R9 290 ReviewAMD’s Last Minute 290 Revision & Meet The Radeon R9 290AMD’s Gaming Evolved Application & The TestMetro: Last LightCompany of Heroes 2Bioshock InfiniteBattlefield 3Crysis 3Crysis: WarheadTotal War: Rome 2Hitman: AbsolutionGRID 2SyntheticsComputePower, Temperature, & NoiseOverclockingFinal Words
With the launch of AMD’s Radeon R9 290X less than 2 weeks ago, the video card marketplace has become very active very quickly. The 290X not only reasserted AMD’s right to fight for the video card performance crown, but in doing so it has triggered an avalanche of pricing and positioning changes that have affected both NVIDIA and AMD.
NVIDIA for their part cut the price of the GTX 780 and GTX 770 to $500 and $330 respectively, repositioning the cards and giving them their first official price cuts since their spring launches. Meanwhile AMD has also made some changes, and although 290X is unaffected for the moment, 290 was affected before it even launched, receiving an arguably significant specification adjustment. Consequently with GTX 780’s price cut being NVIDIA’s counter to 290X, 290 has gone from just being a lower tier Hawaii card to also being AMD’s counter-counter, and in the process has become a somewhat different card than what it was going to be just one week ago.
But before we get ahead of ourselves, let’s start at the beginning. With the successful launch of the 290X behind them, and the equally successful launch of their new flagship GPU Hawaii, AMD is ready to make their next move. Launching today will be the Radeon R9 290, the obligatory lower-tier part for AMD’s new flagship lineup. Making the usual tradeoffs for a lower-tier part, AMD is cutting down on both the number of functional units and the clockspeeds, the typical methods for die harvesting, in exchange for a lower price.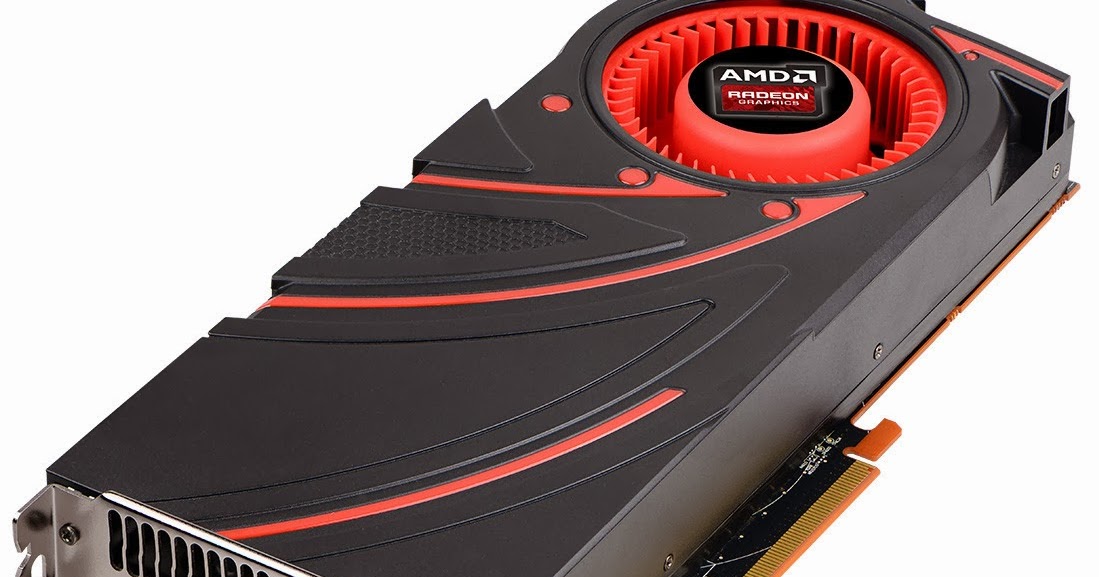 Now officially AMD has not announced the Radeon R9 290 in advance, but with listings for it having already gone up on the same day as the 290X, it’s something that everyone has been expecting.
Now officially AMD has not announced the Radeon R9 290 in advance, but with listings for it having already gone up on the same day as the 290X, it’s something that everyone has been expecting.
As always we’ll offer a full breakdown of performance and other attributes in the following pages, but before we even begin with that we want to point out that the 290 is going to be one of AMD’s most controversial and/or hotly debated launches in at least a couple of years. The merits of 290X were already hotly debated in some gaming circles for its noise relative to its performance and competition, and unfortunately 290 is going to be significantly worse in that respect. We’ll have a full rundown in the following pages, but in a nutshell AMD has thrown caution into the wind in the name of maximizing performance.
| AMD GPU Specification Comparison | ||||||
| AMD Radeon R9 290X | AMD Radeon R9 290 | AMD Radeon R9 280X | AMD Radeon HD 7970 | |||
| Stream Processors | 2816 | 2560 | 2048 | 2048 | ||
| Texture Units | 176 | 160 | 128 | 128 | ||
| ROPs | 64 | 64 | 32 | 32 | ||
| Core Clock | 727MHz | 662MHz | 850MHz | 925MHz | ||
| Boost Clock | 1000MHz | 947MHz | 1000MHz | N/A | ||
| Memory Clock | 5GHz GDDR5 | 5GHz GDDR5 | 6GHz GDDR5 |
5. 5GHz GDDR5 5GHz GDDR5 |
||
| Memory Bus Width | 512-bit | 512-bit | 384-bit | 384-bit | ||
| VRAM | 4GB | 4GB | 3GB | 3GB | ||
| FP64 | 1/8 | 1/8 | 1/4 | 1/4 | ||
| TrueAudio | Y | Y | N | N | ||
| Transistor Count |
6. 2B 2B |
6.2B | 4.31B | 4.31B | ||
| Typical Board Power | ~300W (Unofficial) | ~300W (Unofficial) | 250W | 250W | ||
| Manufacturing Process | TSMC 28nm | TSMC 28nm | TSMC 28nm | TSMC 28nm | ||
| Architecture | GCN 1.1 | GCN 1.1 | GCN 1.0 | GCN 1.0 | ||
| GPU | Hawaii | Hawaii | Tahiti | Tahiti | ||
| Launch Date | 10/24/13 | 11/05/13 | 10/11/13 | 12/28/11 | ||
| Launch Price | $549 | $399 | $299 | $549 | ||
Diving right into the hardware specifications, Radeon R9 290 is a bit more powerful than usual for a lower-tier part.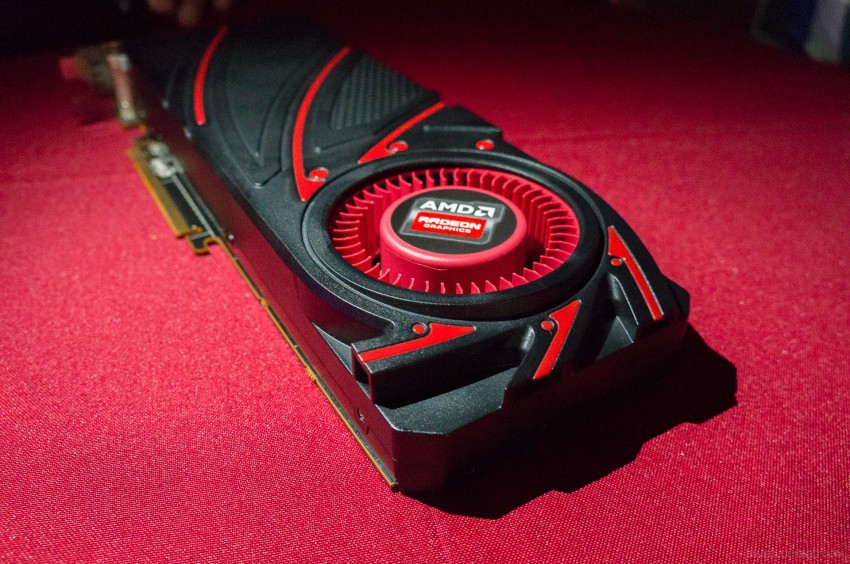 AMD has cut the number of CUs from 44 to 40 – disabling 1 CU per SE – while adjusting down the base GPU clockspeed and boost GPU clockspeed to from 727MHz and 1000MHz to 662MHz and 947MHz respectively. However AMD has not cut the amount of memory, the memory clockspeed, the memory bus width, or the number of ROPs, leaving those at 5GHz for the memory clockspeed, 512-bits for the memory bus width, and all 64 ROPs for the back-end hardware.
AMD has cut the number of CUs from 44 to 40 – disabling 1 CU per SE – while adjusting down the base GPU clockspeed and boost GPU clockspeed to from 727MHz and 1000MHz to 662MHz and 947MHz respectively. However AMD has not cut the amount of memory, the memory clockspeed, the memory bus width, or the number of ROPs, leaving those at 5GHz for the memory clockspeed, 512-bits for the memory bus width, and all 64 ROPs for the back-end hardware.
As a result the differences between the 290 and 290X are on paper limited entirely to the clockspeed differences and the reduced number of CUs. At their top boost bins this gives 290 95% the clockspeed of 290X, and 91% of the shader hardware, giving 290 100% of 290X’s memory performance, 95% of 290X’s ROP and geometry performance, and 86% of 290X’s shading/texturing performance.
Compared to AMD’s last generation offerings, the 290 is going to be closer to 290X than 7950 was to 7970. 290 retains a larger percentage of 290X’s shader and ROP performance, never mind the fact that the full 320GB/sec of memory bandwidth is being retained.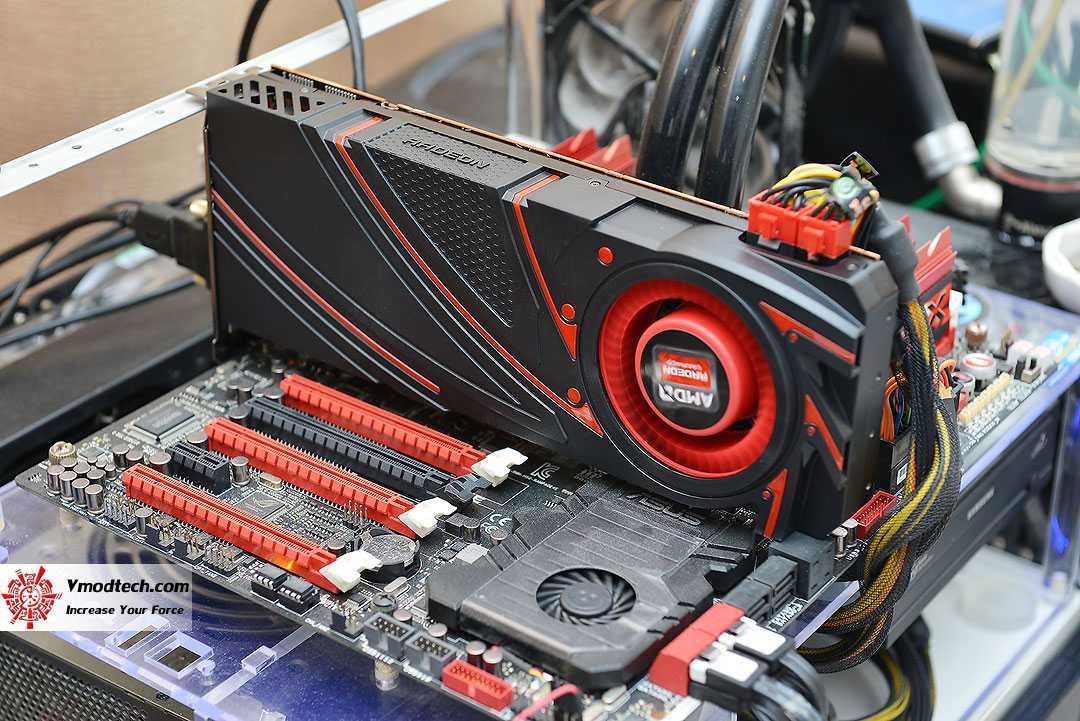 As such despite the wider price difference this time around, performance on paper is going to be notably closer. Paper will of course be the key word here, as in the case of 290 more so than any other card we’ve looked at in recent history theory and practice will not line up. Compared to the 290X, practice will be favoring the 290 by far.
As such despite the wider price difference this time around, performance on paper is going to be notably closer. Paper will of course be the key word here, as in the case of 290 more so than any other card we’ve looked at in recent history theory and practice will not line up. Compared to the 290X, practice will be favoring the 290 by far.
Moving on to power consumption, perhaps because of AMD’s more aggressive specifications for their lower-tier card this time around, power consumption is not dropping at all. AMD is still not throwing us any useful hard numbers, but based on our performance data we estimate the 290 to have a nearly identical TDP to the 290X, leading us to keep it at an unofficial 300W. Lower-tier parts typically trade performance for power consumption, but that will not be the case here. Power consumption will be identical while performance will be down, so efficiency will be slipping and 290 will have all the same power/cooling requirements as 290X.
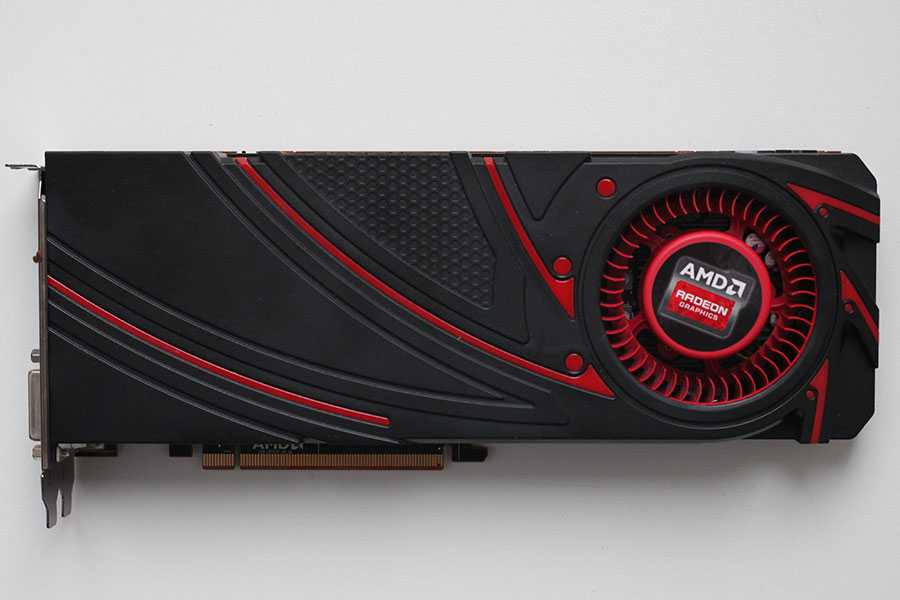
Meanwhile like the 290X launch, the 290 launch is going to be a hard launch, and a full reference launch at that.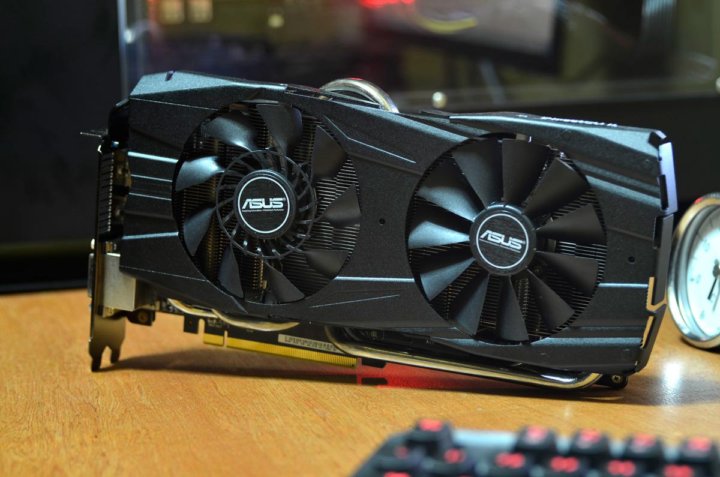 As such we’ll be seeing 290 cards go up for sale at the usual retailers today, with all of those cards using AMD’s reference cooler and reference board, itself unchanged from the 290X.
As such we’ll be seeing 290 cards go up for sale at the usual retailers today, with all of those cards using AMD’s reference cooler and reference board, itself unchanged from the 290X.
As for pricing and competitive positioning, AMD will be launching the 290 at what we consider to be a very aggressive price of $399. Based on the initial specifications, the performance, and the competition, we had been expecting AMD to launch this at $449, mirroring the launch of the 7950 in the process. But AMD has gone one step further by significantly undercutting both themselves and NVIDIA.
290’s immediate competition on the AMD side will be the $549 290X above it and the $299 280X below it, while on the NVIDIA side the competition will be the $499 GTX 780 above it and the $329 GTX 770 below it. Pricing wise this puts 290 as closer competition to 280X/GTX 770 than it does the high-tier cards, but as we’ll see in our benchmarks AMD is aiming for the top with regards to performance, which will make price/performance comparisons both interesting and frustrating at the same time.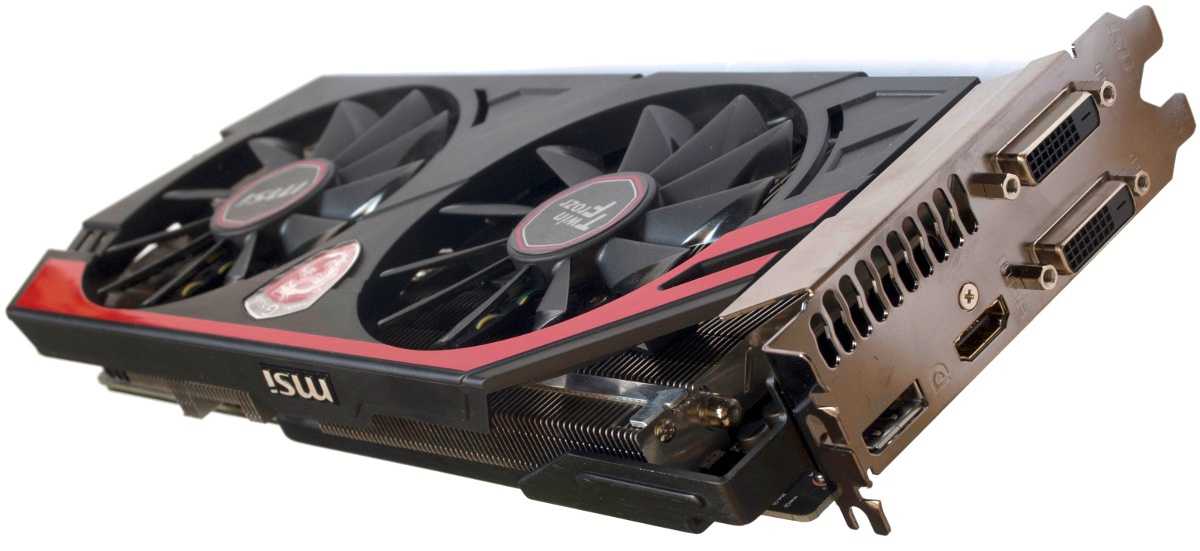
NVIDIA for their part will have their 3 game Holiday GeForce Bundle on the GTX 780 and GTX 770, presenting the same wildcard factor for overall value that we saw with the 290X launch. As always, the value of bundles are ultimately up to the buyer, especially in this case since we’re looking at a rather significant $100 price gap between the 290 and the GTX 780.
| Fall 2013 GPU Pricing Comparison | |||||
| AMD | Price | NVIDIA | |||
| Radeon R9 290X | $550 | ||||
| $500 | GeForce GTX 780 | ||||
| Radeon R9 290 | $400 | ||||
| $330 | GeForce GTX 770 | ||||
| Radeon R9 280X | $300 | ||||
| $250 | GeForce GTX 760 | ||||
| Radeon R9 270X | $200 | ||||
| $180 | GeForce GTX 660 | ||||
| $150 | GeForce GTX 650 Ti Boost | ||||
| Radeon R7 260X | $140 | ||||
AMD’s Last Minute 290 Revision & Meet The Radeon R9 290
The AMD Radeon R9 290 ReviewAMD’s Last Minute 290 Revision & Meet The Radeon R9 290AMD’s Gaming Evolved Application & The TestMetro: Last LightCompany of Heroes 2Bioshock InfiniteBattlefield 3Crysis 3Crysis: WarheadTotal War: Rome 2Hitman: AbsolutionGRID 2SyntheticsComputePower, Temperature, & NoiseOverclockingFinal Words
PRINT THIS ARTICLE
AMD Radeon R9 290 — Rasend schnelle Hawaii-Grafikkarte für 350 Euro
Anders als bei der Leistung unterscheidet sich die rund 350 Euro teure Radeon R9 290 äußerlich kaum vom AMD-Flaggschiff Radeon R9 290X (550 Euro).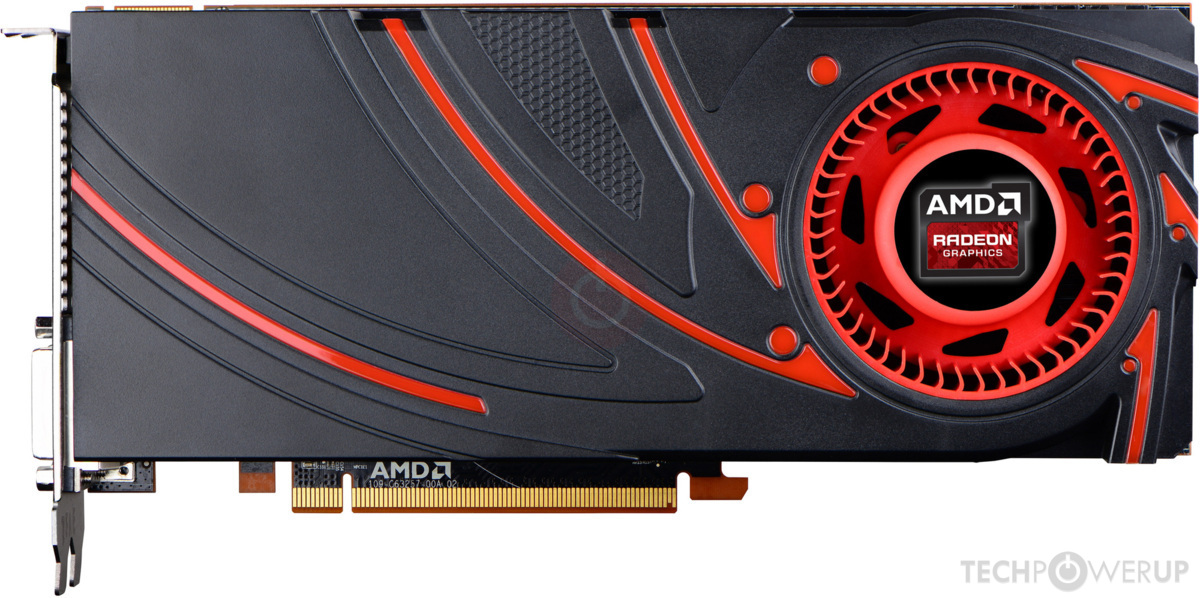
AMDs neue Radeon R-Karten stehen derzeit fast in allen Segmenten an der Preis-Leistungs-Spitze. Mit der Radeon R9 290 kommt jetzt die zweite Grafikkarte für den High-End-Bereich zum Test. AMD machte es uns und anderen Testern dabei allerdings nicht gerade nicht einfach und änderte im Vorfeld mehrfach das Veröffentlichungsdatum sowie die empfohlene Treiber-Version für die Radeon R9 290 — zuletzt wurde sogar noch die maximale Drehzahl des Lüfters angehoben.
Mit der unverbindlichen Preisempfehlung von 350 Euro liegt die Radeon R9 290 zwischen den kürzlich von Nvidia im Preis reduzierten Geforce GTX 770 (280 Euro) und der Geforce GTX 780 (440 Euro). Während die von uns bereits getestete Radeon R9 290X (550 Euro) das Geforce-Flaggschiff Geforce GTX Titan (850 Euro) in den Spiele-Benchmarks knapp schlagen konnte, soll die Radeon 290 ohne X die Geforce GTX 780 überholen. Der Hawaii-XT-Chip im Inneren der Radeon R9 290X treibt auch die Radeon R9 290 an, wurde bei der rund 200 Euro günstigeren Variante allerdings etwas beschnitten.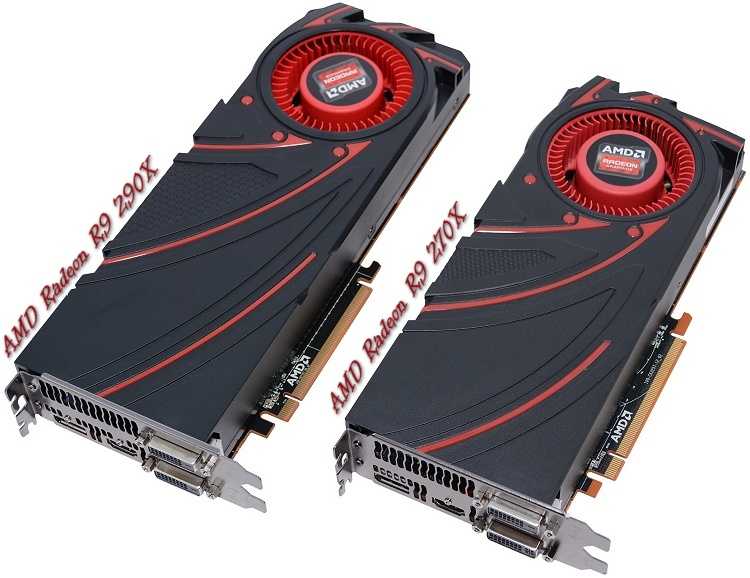
Statt den 2.816 Shadern der Radeon R9 290X finden sich bei der R9 290 nur 2.560 Einheiten und auch der Chip-Takt sinkt von 1.000 auf maximal 947 MHz. An der Speichergröße und dessen Takt ändert sich mit 4,0 GByte respektive 5.000 MHz hingegen nichts. Im Zusammenspiel mit dem 512 Bit großen Speicher-Interface kommt somit auch die Radeon R9 290 auf eine Speicherbandbreite von 320 GByte pro Sekunde. Außer der geringeren Shader-Zahl und Taktrate unterscheidet sich die Radeon R9 290 somit auf den ersten Blick kaum vom Radeon-Flaggschiff.
Neben AMDs API-Alternative »Mantle« unterstüzt die Radeon R9 290 dank integriertem DSP auch »TrueAudio«.
Beide Grafikkarten stecken im gleichen mattschwarzen Kunststoff-Gehäuse und werden von einem Radiallüfter gekühlt. Wie bei der Radeon R9 290X verzichtet AMD auch bei der Radeon R9 290 auf dedizierte Crossfire-Schnittstellen und überlässt den Datenaustausch zwischen mehreren Karten gänzlich der PCI-Express-Schnittstelle. Wie ähnlich sich Radeon R9 290 und 290X sind, zeigt sich auch am BIOS-Schalter auf der Oberseite der Radeon R9 290.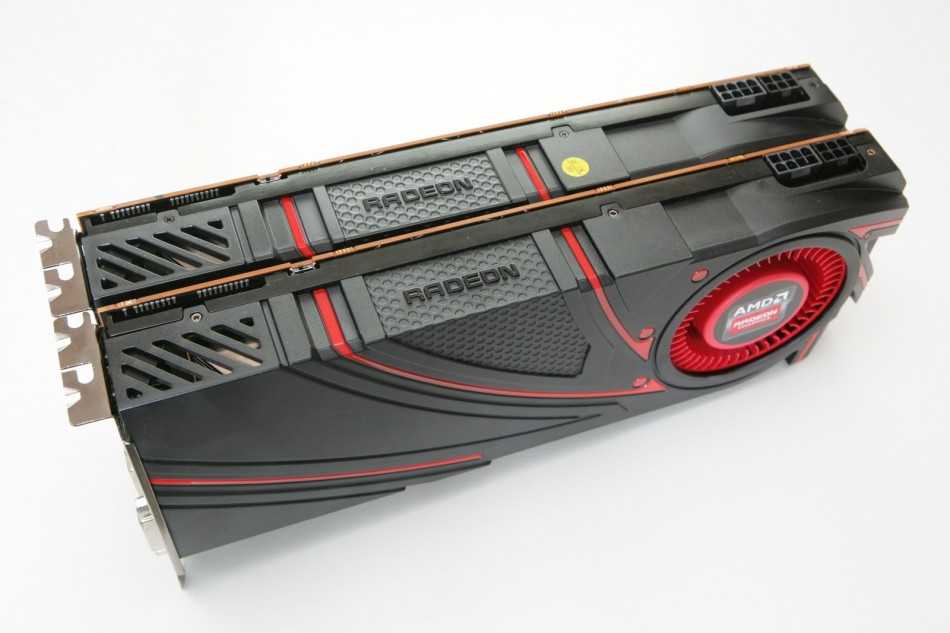
Während der bei der Radeon R9 290X das Umschalten zwischen »Uber-« und »Quiet-Modus« ermöglicht, verändert sich bei der R9 290 nach dem Umlegen nichts – in beiden Einstellungen erhalten wir die gleichen Werte für Temperatur, Stromverbrauch und Leistung. Der Schalter ist somit reine »Zierde«, könnte auf angepassen Herstellermodellen aber eventuell wieder funktionstüchtig gemacht werden.
Technische Daten
|
Radeon R9 290X |
Radeon R9 290 |
Geforce GTX 780 |
Geforce GTX 770 |
|
|
Grafikchip |
Hawaii XT |
Hawaii XT |
||
|
Fertigung |
||||
|
Chiptakt |
1. |
947 MHz |
863 MHz |
1.046 MHz |
|
Shader-Einheiten |
||||
|
Textur-Einheiten |
||||
|
GDDR5-Speicher |
4.096 MByte |
4.096 MByte |
3.072 MByte |
2.048 MByte |
|
Speichertakt (effektiv) |
5.000 MHz |
5.000 MHz |
6.008 MHz |
7.008 MHz |
|
Speicheranbindung |
512 Bit |
512 Bit |
384 Bit |
256 Bit |
|
Ca. |
550 Euro |
350 Euro |
440 Euro |
280 Euro |
Im Hinblick auf die vielen Gemeinsamkeiten zur Radeon R9 290X dürfte die Leistung der Radeon R9 290 durchaus mit der Geforce GTX 780 mithalten können. Ob die Grafikkarte dabei jedoch mit ähnlich hohen Temperaturen, Stromverbrauch und Lärmpegel wie die 290X zu kämpfen hat oder ob es AMD auch im Preisbereich zwischen 300 und 500 Euro gelingt, einen Preis-Leistungs-Tipp zu platzieren, werden die Benchmarks auf den nächsten Seiten zeigen.
Radeon Gaming Evolved
Ähnlich wie Nvidia mit »Geforce Experience« integriert auch AMD seit Kurzem ein zusätzliches Programm in den Grafikkarten-Treiber. Die »Gaming Evolved« genannte Funktion basiert auf der bereits etablierten Raptr-App und greift auch auf dessen Datenbank zu. Nach der Installation scannt das Programm die Hardware-Komponenten und erstellt somit ein Profil des Rechners.
Im Anschluss werden die auf der Festplatte installierten Spiele auf ihre Grafikeinstellungen überprüft und mit dem erstellten Profil und vergleichbaren Werten aus der Community abgeglichen. Per Knopfdruck lassen sich die vorgeschlagenen Einstellungen übernehmen und sollen so ohne weiteres Tüfteln die bestmögliche Performance und Grafikqualität gewährleisten. Hinzu kommen zahlreiche Extras wie News zu Spielen, Freundeslisten und Ingame-Chatfunktionen. Natürlich darf auch das obligatorische Achievement-System nicht fehlen. Noch befindet sich »Gaming Evolved« im Beta-Status und ähnlich wie bei Geforce Experience sollten Sie sich nicht blind auf die vorgeschlagenen Einstellungen verlassen. Da die Installation jedoch optional ist und die genannten Features teilweise durchaus sinnvoll sind, stellt das Programm eine nette Dreingabe zum Catalyst-Treiber dar.
Radeon Gaming Evolved Treiber — Bilder ansehen
Testsystem
Für unsere Grafikkarten-Tests nutzen wir wegen der besseren Vergleichbarkeit weiterhin einen 3,4 GHz schnellen Intel Core i7 2600K mit 8,0 GByte DDR3-RAM auf dem P67-Mainboard Maximus IV Extreme von Asus.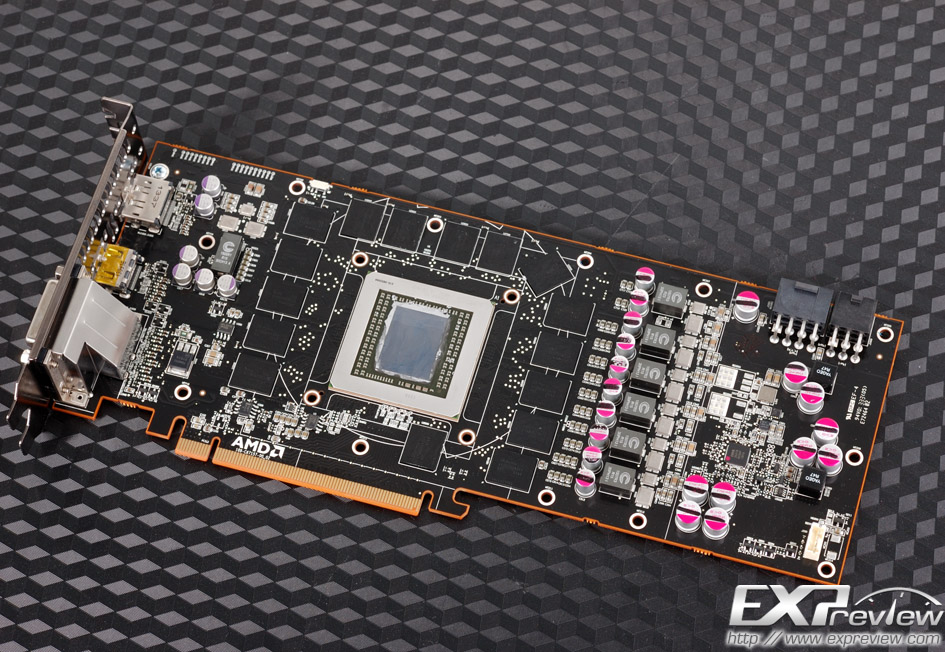 Die Intel-CPU spielt durch die geringen Leistungssteigerungen bei Prozessoren in den letzten Jahren noch immer auf Spitzenniveau mit.
Die Intel-CPU spielt durch die geringen Leistungssteigerungen bei Prozessoren in den letzten Jahren noch immer auf Spitzenniveau mit.
Betriebssystem, Spiele und Benchmark-Programme finden auf einer 512 GByte großen Samsung SSD 830 Platz. Wie andere in der Vergangenheit getestete Grafikkarten muss auch die Radeon R9 290 den Benchmark-Parcours aus den DirectX-11-Titeln Anno 2070, Crysis 3, Dirt 3, Max Payne 3, Metro: Last Light und The Elder Scrolls 5: Skyrim durchlaufen. Zwar befindet sich die Teststrecke für Battlefield 4 bereits im Aufbau, bis zur Fertigstellung nutzen wir jedoch noch das bewährte Battlefield 3. Alle genannten Titel testen wir mit maximalen Details in den Auflösungen 1680×1.050, 1920×1.080 und 2560×1.440. Dabei überprüfen wir die Leistung sowohl mit als auch ohne Kantenglättung und nehmen den Mittelwert aus mehreren Messungen.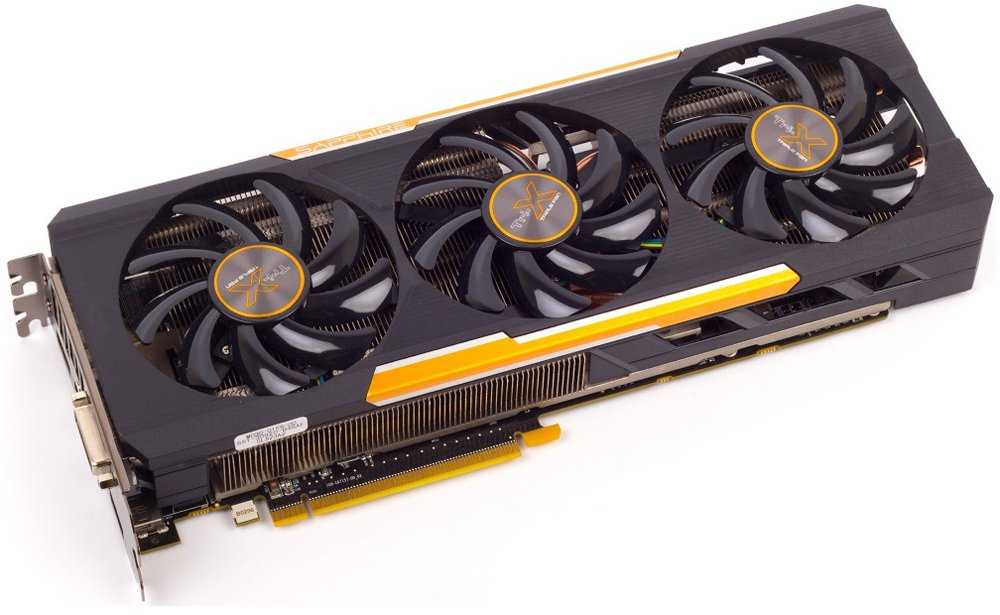
Overview of AMD Radeon R9 290
The Radeon R9 290 video card is AMD’s junior flagship of the new generation of the ninth series. This is a mid-range gaming video that is perfectly balanced in terms of technical parameters, which will quite pull most modern video games at maximum, ultra-high settings. Was released in 2013. The average cost in Europe is 280-290 dollars.
Overview, Specifications
Radeon R9 290 is a gaming graphics card released on the new Hawaii processor. The crystal is manufactured using a 28-nm process technology. Contains 6.2 billion transistors, and its area is 438 mm². Unlike AMD 290X, which has a bar frequency of 1000 MHz, this model has only 945 MHz. The amount of memory is 4096 megabytes. Connected to a 512-bit bus. Operates at a frequency of 1.250 MHz, which provides a throughput of 320 GB / s. It has support for all new features: TrueAudio, DirectSound 11.2 Tier 2.
In terms of technical parameters, AMD 290 can be compared with the Nvidia 780 graphics adapter, although in some parameters it is inferior to its competitor.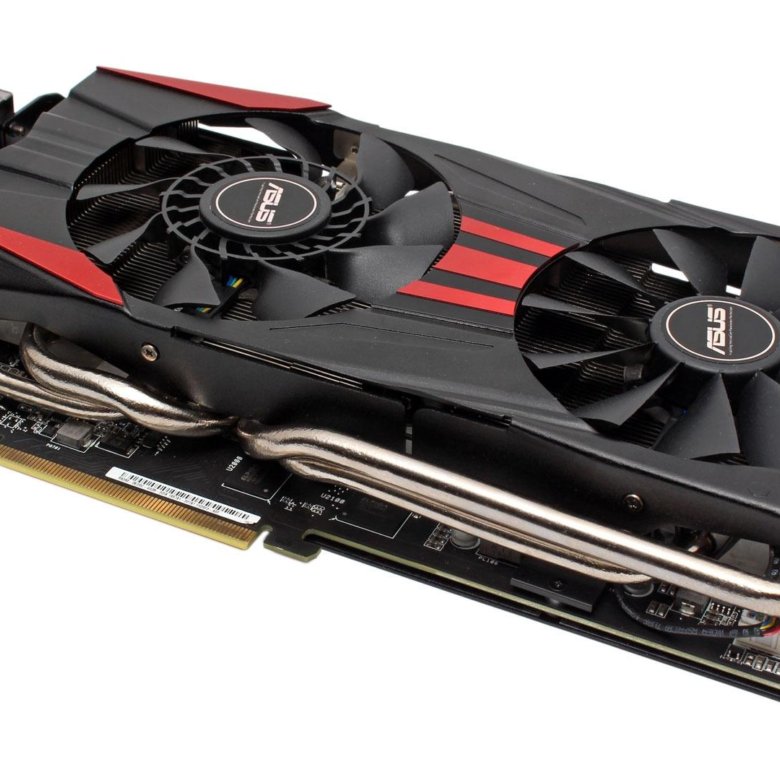 In addition, this model is not much different from AMD 290X, although the Boost frequency was reduced compared to the latter, the number of stream processors was cut from 2.816 to 2.560. The number of clock units is 160, while the number of raster operations pipelines (ROPs) is also 64.
In addition, this model is not much different from AMD 290X, although the Boost frequency was reduced compared to the latter, the number of stream processors was cut from 2.816 to 2.560. The number of clock units is 160, while the number of raster operations pipelines (ROPs) is also 64.
| Model | Radeon R9 280X | Radeon R 290 | Radeon R9 290X | HD 7990 |
| Main components | ||||
| GPU | Tahiti XTL | Hawaii | Hawaii XT | Malta |
| Number of transistors, million | 4313 | 6020 | 6020 | 2 x 4313 |
| Process technology, nm | 28 | 28 | 28 | 28 |
| GPU clock speed, MHz: High State / Boost State | 850/1000 | 947/ND | 1000/ND | 950/1000 |
| Stream Processors | 2048 | 2560 | 2816 | 2×2048 |
| Texture blocks | 128 | 160 | 176 | 2×128 |
| ROP | 32 | 64 | 64 | 2×32 |
| Video memory: type, size, MB | GDDR5, 3072 | GDDR5, 4048 | GDDR5, 4048 | GDDR5, 6144 |
| Memory clock: real (effective), MHz | 1500 (6000) | 1125 (5000) | 1125 (5000) | 1500 (6000) |
| Memory bus width, bit | 384 | 512 | 512 | 2×384 |
| Interface | PCI-Express 3. 0 x16 0 x16 |
PCI-Express 3.0 x16 | PCI-Express 3.0 x16 | PCI-Express 3.0 x16 |
| Image output | ||||
| Interfaces | 2 x DL DVI-D, 1 x HDMI 1.4a, 2 x DisplayPort 1.2 |
1 x DL DVI-I, 4 x Mini DisplayPort 1.2 |
||
| Max. resolution | VGA: 2048×1536, DVI: 2560×1600, HDMI: 4096×2160, DP: 4096×2160 |
VGA: 2048×1536, DVI: 2560×1600, HDMI: 4096×2160, DP: 4096×2160 |
||
| Typical power input, W | 250 | ID | ID | ID |
The Radeon R9 290, like the 290X, received a VID interface, thanks to which you can quickly, accurately adjust the voltage on the GPU, as well as a telemetry channel through which PowerTune receives voltage data from analog sensors.
R9 290 PCB same as R9 290X. The frame buffer is made up of SK Hynix H5GQ1h34AFR-R0C microcircuits with a nominal clock frequency of 6 GHz.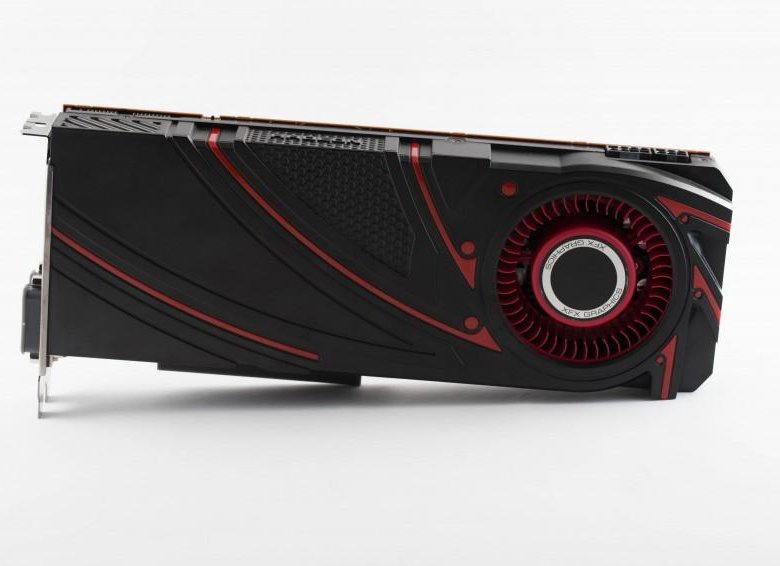 The components are powered according to the 5+1+1 scheme (GPU, memory chips, PLL).
The components are powered according to the 5+1+1 scheme (GPU, memory chips, PLL).
The specifications of the video adapter show the maximum frequency of the GPU, but in practice it can be limited by the power consumption limit and core temperature. Another variable is the fan speed limit: if the GPU temperature cannot be kept within the normal range at a given cooler speed, the frequency will be reduced. Therefore, if you manually adjust the PowerTune settings, you can give priority to either the performance or acoustic parameters of the video card. give priority to either performance.
Temperature, power consumption
Performance
Below is an overview of graphics cards from each manufacturer.
Radeon R9 290 Benchmarks
The R9 290 was originally intended to be similar in performance to the GeForce GTX 770, but as a result, the graphics adapter has been upgraded to rival the GTX 780, as evidenced by numerous tests.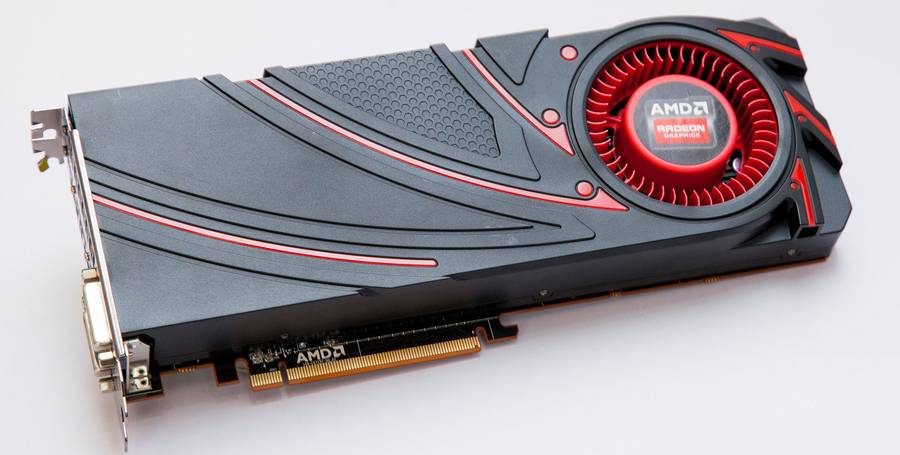
Before the release of the Radeon R9 290, AMD decided to boost performance by changing the fan speed limit from 40% to 47%. The original limit of 40% corresponds to the so-called Quiet Mode Radeon R9 290X, but the actual speeds differ: 1987 rpm for the R9 290X at 2172 rpm for the R9 290.
Under increased loads, the core temperature approaches the allowed 95 ° C , which is considered normal for a Hawaii processor. But at the same time, the fan can no longer spin faster, which leads to active “throttling” of the frequency. During a test run in the game Crysis 3, a drop to 851 MHz was noticed from the original 947 MHz.
Given that the frequencies of AMD 290 and 290X differ by only 5%, the power figures for both video cards are almost the same.
Performance, gaming tests
3DMark 2011, focused on DirectX 11, did not support AMD’s ambitious plans: the Radeon R9 290X was ahead of the GeForce GTX 780, but the R9 290 lags behind in some respects. The newer version of 3DMark also found a noticeable difference between the R9 290 and R9 290X. At the same time, the AMD 290 significantly outperforms the GeForce GTX 780 and practically reaches the GTX TITAN.
The newer version of 3DMark also found a noticeable difference between the R9 290 and R9 290X. At the same time, the AMD 290 significantly outperforms the GeForce GTX 780 and practically reaches the GTX TITAN.
The victory of the Radeon R9 290 over the GTX 780 came at the cost of running the cooling system at high speeds. But if you limit the fan speed to 40% of the nominal value, according to the benchmark results, overclocking the cooler did not have a significant effect, and only in some tests did it lead to a slight increase in frame rate. However, this was quite enough to establish an unconditional superiority over the GeForce GTX 780.290X has a very noticeable effect on performance both in synthetic benchmarks and in real modern video games, including in 4K resolution.
Radeon R9 290 peak processing power (4.9 TFLOPS) is 87.5% of R9 290X (5.6 TFLOPS). The GeForce GTX 780 is roughly related to the GeForce GTX TITAN (89%), and the difference between them in video games such as: Battlefield 3, Far Cry 3, Tomb Raider, Crysis 3, Metro: Last Light, Unigine Heaven 2, Batman: Arkham City is practically non-existent. Users can safely set games at maximum settings.
Users can safely set games at maximum settings.
If we talk about the overall performance of the tested model in games, then it will be enough to get acquainted with almost all the new products both in the multi-monitor configuration mode with a total resolution of 5760 x 1080, and on displays with a resolution of 2560 x 1600.
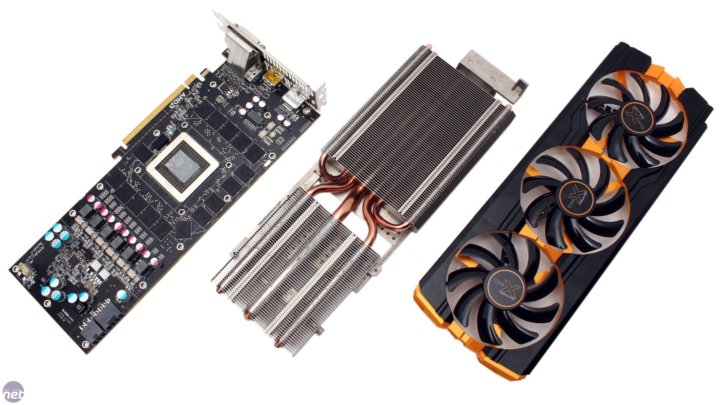
SAPPHIRE R9 290 4GB
SAPPHIRE R9 290 4GB graphics accelerator — model with «reference» cooling system. Occupies two slots for expansion cards. The video card has a reference frequency scheme without the use of any factory overclocking, which means that all overclocking is carried out by users.
The SAPPHIRE R9 290 4GB GDDR5 video adapter is equipped with AMD Hawaii PRO graphics chip, which is manufactured in 28nm process technology. Includes 2560 universal shader processors, 160 texture units, 64 raster units. Depending on the load and heating, the clock frequency of the graphics core changes dynamically, reaching a maximum of 947 MHz.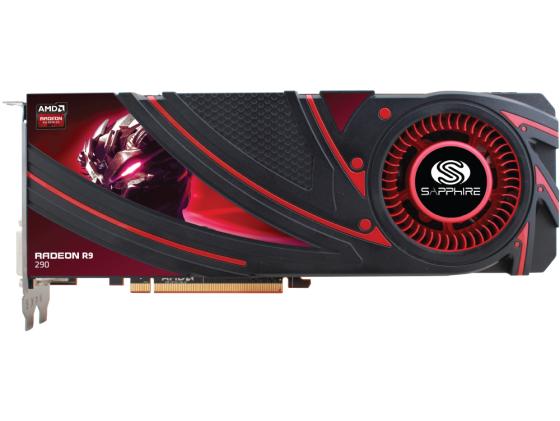
Set of video card interface panel ports:
- 2 x Dual-link DVI-D;
- 1 x HDMI;
- 1 x DisplayPort.
HDMI, DisplayPort connectors support 4K Ultra HD (4096×2160) resolution. In AMD Eyefinity mode, via the DisplayPort interface, special adapters can connect four monitors, TVs, using all connectors of the interface panel directly.
PCB height is 112 mm. The length of the video card is 290 mm. In the center is a graphic chip equipped with a metal frame for safe installation and removal of the cooling system. The power subsystem of the video card is built according to a seven-phase scheme: five phases for the graphics core, one for the memory and one for the PLL. To power the graphics adapter, in addition to the PCI Express 3.0 x16 slot, two additional 6- and 8-pin PCIe connectors are used.
In terms of performance, SAPPHIRE R9 290 is about 6% ahead of NVIDIA GTX 770, but 9-12% behind NVIDIA GTX 780. At the same time, gaming tests showed that most new video games on displays with a resolution of 5760 x 1080 and 2560 x 1600 runs steadily at maximum settings.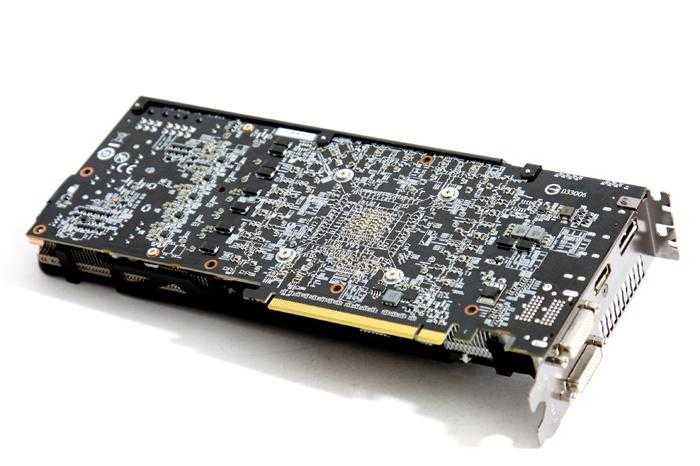 During overclocking, we managed to increase the GPU frequency to 1190 MHz (25%;) which can be called a very good result. The video memory frequency was fixed at 1400 MHz (+12%).
During overclocking, we managed to increase the GPU frequency to 1190 MHz (25%;) which can be called a very good result. The video memory frequency was fixed at 1400 MHz (+12%).
The main advantage of this model is a high degree of performance in computer games, which allows you to assemble a completely balanced gaming system that will satisfy both professional gamers and beginners. Minus — a high level of CO noise.
ASUS RADEON R9 290 OC
ASUS Radeon R9 290 OC (R9290-DC2OC-4GD5) is a perfectly balanced gaming video card suitable for comfortable gaming at maximum, ultra-maximum settings.
The model is equipped with a DirectCU II open-type cooling system with two Everflow fans, a massive aluminum heatsink with five heat pipes. Direct contact technology is used, while three out of five tubes are involved in the heat sink.
The main advantages of ASUS Radeon R9 290 OC include:
- high performance;
- fresh GPU architecture;
- relatively low cost;
- quality power system.

Disadvantages: modest configuration, average CO efficiency, increased noise at maximum load.
The length of the graphics accelerator is 287 mm. Two DVI-D connectors are responsible for image output — HDMI, DisplayPort.
The hinged elements of the printed circuit board are located as tightly as possible, which is explained by the large dimensions of the graphics processor, as well as a large number of different microcircuits, and a complex power supply system. The BIOS switch is located on the top of the PCB. Available performance or quiet modes.
The AMD Hawaii processor has a very large core surface area and is equipped with a protective metal frame. 2560 universal stream processors, which are located in the core package, provide maximum video performance. The frequency of the graphics chip of the video card is increased compared to the reference, it is 1000 MHz.
When the video card is loaded at 100% using the MSI Combuster utility, the AMD Hawaii video chip warmed up to 81 degrees Celsius.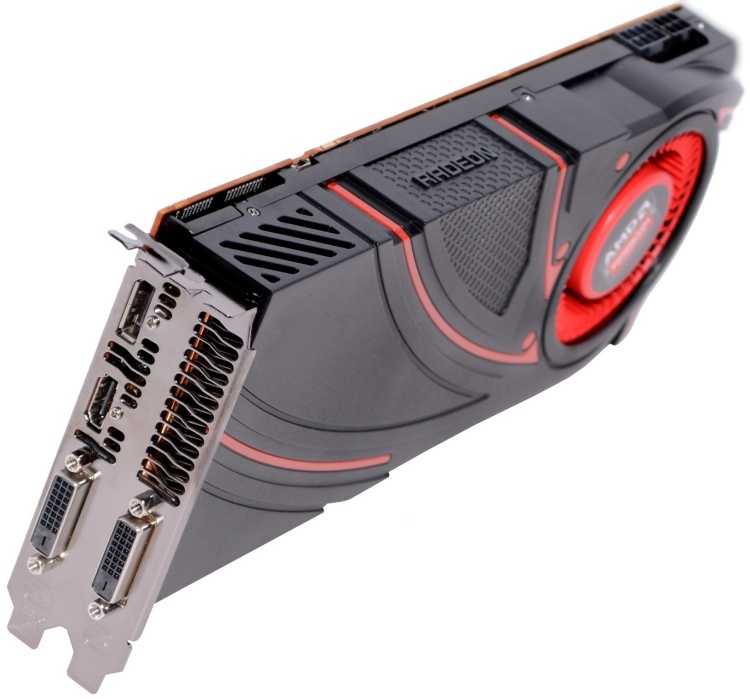 The level of heating in the load shows that the installed DirectCU II CO does not look as confident on AMD Hawaii as the cooling systems in similar video cards from other manufacturers. During overclocking, the frequency of the graphics chip increased to 1150MHz, the memory frequency to 6000MHz.
The level of heating in the load shows that the installed DirectCU II CO does not look as confident on AMD Hawaii as the cooling systems in similar video cards from other manufacturers. During overclocking, the frequency of the graphics chip increased to 1150MHz, the memory frequency to 6000MHz.
In gaming tests, the model showed excellent results. ASUS Radeon R9 power290 OC is enough for a comfortable game in such heavy projects as Metro Last Light, Hitman Absolution.
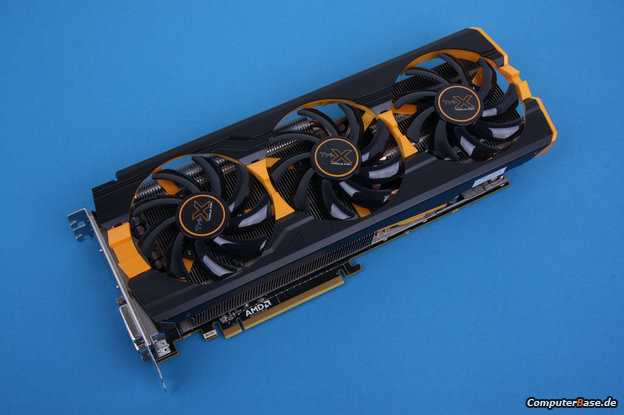
GIGABYTE Radeon R9 290
When planning to assemble a high-performance gaming system, users can choose the GIGABYTE Radeon R9 290 graphics accelerator, which attracts with good value for money. Thanks to a high degree of performance, you can run your favorite modern video games at maximum, ultra-high settings without dropping FPS.
Based on the revolutionary GCN architecture, the GIGABYTE Radeon R9 290 is equipped with an excellent, efficient Windforce 3X cooling system that keeps the temperature of the device low even at maximum graphics settings and at the same time provides almost silent operation.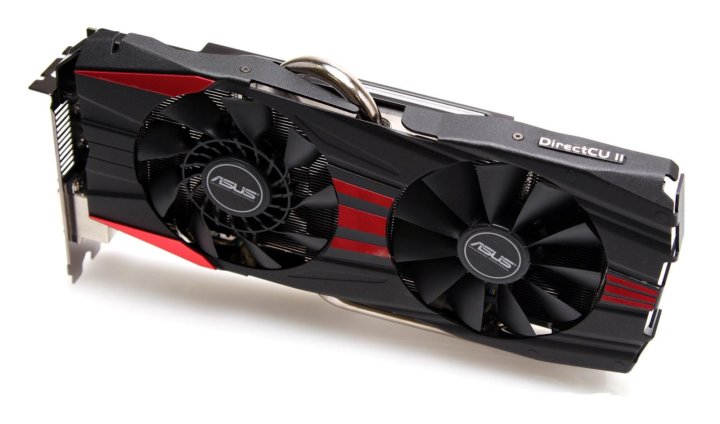 AMD TrueAudio technology will allow you to get the highest quality, clear, surround sound.
AMD TrueAudio technology will allow you to get the highest quality, clear, surround sound.
The video card model is quite massive and weighty, which is explained by the size of the CO and the casing made of metal. The heatpipes and cooling shroud protrude slightly from the PCB. At the same time, thanks to the well-thought-out design of the casing, the weight is distributed more evenly. The cooling system consists of three branded 75mm fans and a massive radiator, consisting of two sections, interconnected by five heat pipes with a diameter of 5 and 8 mm.
Video memory size — 4 GB. There is support for SLI / CrossFire, CrossFire X, DirectX 12, OpenGL 4.5 modes. Interfaces for connecting to monitors are represented by two DVI connectors, one HDMI and Display Port.
Extreme profiles were used in the benchmarks on the Intel i7-3930K, 4 GHz processor. In Crysis 3, Metro Last Light Redux, Sleeping Dogs, Tomb Raider 2013, and other modern games at maximum FPS settings, the FPS is confidently kept at 70-80.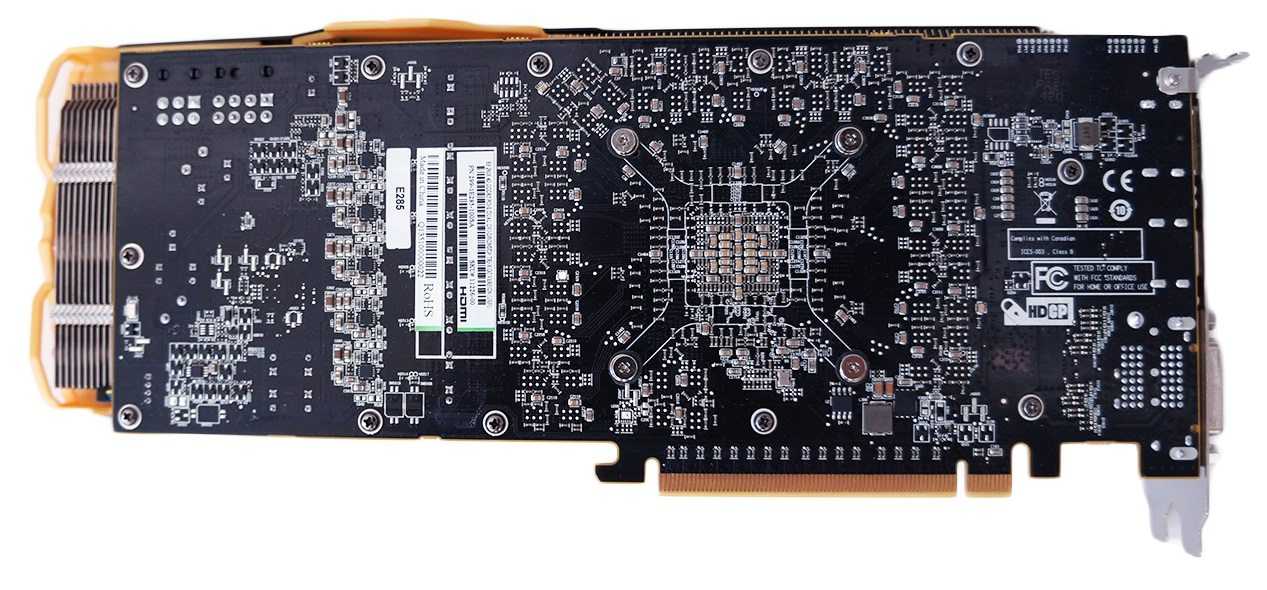 The temperature under load increased, but the noise level was lowered.
The temperature under load increased, but the noise level was lowered.
Total
As you can see, the difference from 290X is insignificant. even in a “lite” form, the GPU Hawaii does not lose its ambitions for leadership in 4K resolutions. AMD does not disclose the TDP of the card, but if the Radeon R9 290X consumes no less than 280 W in the load, then the Radeon R9 290 is not far behind in this regard.
AMD Radeon R9 290 vs Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060: What is the difference?
37 points
AMD Radeon R9 290
58 points
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 9more memory bandwidth?
288GB/s vs 192.2GB/s
512bit vs 192bit
2560 vs 1280
6200 million vs 4400 million
160 vs 80
64 vs 48
Why is Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060 better than AMD Radeon R9 290?
- GPU frequency 844MHz higher?
1506MHz vs 662MHz - 30.
 6 GPixel/s higher pixel rate?
6 GPixel/s higher pixel rate?
72.3 GPixel/s vs 41.7 GPixel/s - 130W below TDP?
120W vs 250W - 877MHz faster memory speed?
2002MHz vs 1125MHz - 2GB more VRAM?
6GB vs 4GB - 3508MHz higher effective clock speed? Is
8008MHz vs 4500MHz - 0.8 a newer version of DirectX?
12 vs 11.2 - Supports ray tracing?
What are the most popular comparisons?
AMD Radeon R9 290
vs
AMD Radeon Vega 8
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
AMD Radeon RX 580
AMD Radeon R9 290
vs
AMD Radeon RX 550
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1650
AMD Radeon R9 290
vs
AMD Radeon RX 580
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3050 AMD 903 Laptop 20
vs
AMD Radeon R9 290X
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1650 Ti Laptop
AMD Radeon R9 290
vs
Nvidia GeForce GTX 960
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
AMD Radeon RX 570
AMD Radeon R9 290
VS
AMD Radeon RX 570
NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 1060
VS
NVIDIA GEFORCE GTX 105000
AMD RADEN RADEN RADEN RADEN RADEN290
vs
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1050
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
Manli GeForce GTX 1650
AMD Radeon R9 290
vs
Nvidia GeForce GTX 970
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3050 Ti Laptop
AMD Radeon R9 290
vs
AMD Radeon RX 470
Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
vs 90903
Nvidia GeForce RTX Ol000 /10
7 Votes
performance
10. 0 /10
0 /10
1 votes
8.3 /10
7 Votes
Remediness of work
10.0 /10
1 Votes
8.4 /10
7 Votes
Reliability
10.0 /10
1 Votes
8.1 /10 9000 9000 9000 GPU
662MHz
1506MHz
The graphics processing unit (GPU) has a higher clock speed.
turbo GPU
947MHz
1708MHz
When the GPU is running below its limits, it can jump to a higher clock speed to increase performance.
pixel rate
41.7 GPixel/s
72.3 GPixel/s
The number of pixels that can be displayed on the screen every second.
FLOPS
4.85 TFLOPS
3.85 TFLOPS
FLOPS is a measure of GPU processing power.
texture size
152 GTexels/s
120. 5 GTexels/s
5 GTexels/s
Number of textured pixels that can be displayed on the screen every second.
GPU memory speed
1125MHz
2002MHz
Memory speed is one aspect that determines memory bandwidth.
Shading patterns
Shading units (or stream processors) are small processors in a graphics card that are responsible for processing various aspects of an image.
texture units (TMUs)
TMUs take texture units and map them to the geometric layout of the 3D scene. More TMUs generally means texture information is processed faster.
ROPs render units
ROPs are responsible for some of the final steps of the rendering process, such as writing the final pixel data to memory and for performing other tasks such as anti-aliasing to improve the appearance of graphics.
Memory
effective memory speed
4500MHz
8008MHz
The effective memory clock is calculated from the size and data transfer rate of the memory. A higher clock speed can give better performance in games and other applications.
A higher clock speed can give better performance in games and other applications.
maximum memory bandwidth
288GB/s
192.2GB/s
This is the maximum rate at which data can be read from or stored in memory.
VRAM (video RAM) is the dedicated memory of the graphics card. More VRAM usually allows you to run games at higher settings, especially for things like texture resolution.
versions of GDDR memory
Later versions of GDDR memory offer improvements such as higher data transfer rates, which improve performance.
memory bus width
512bit
192bit
A wider memory bus means it can carry more data per cycle. This is an important factor in memory performance, and therefore the overall performance of the graphics card.
Supports memory troubleshooting code
✖AMD Radeon R9 290
✖Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
Memory troubleshooting code can detect and fix data corruption.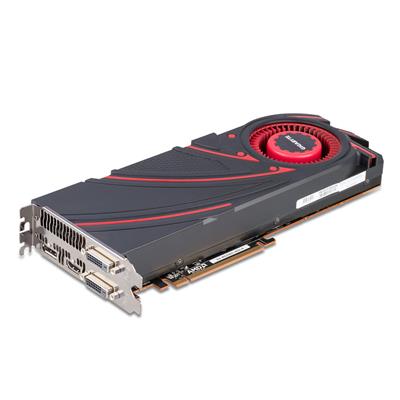 It is used when necessary to avoid distortion, such as in scientific computing or when starting a server.
It is used when necessary to avoid distortion, such as in scientific computing or when starting a server.
Functions
DirectX version
DirectX is used in games with a new version that supports better graphics.
OpenGL version
The newer the OpenGL version, the better graphics quality in games.
OpenCL version
Some applications use OpenCL to use the power of the graphics processing unit (GPU) for non-graphical computing. Newer versions are more functional and better quality.
Supports multi-monitor technology
✔AMD Radeon R9 290
✔Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
The video card has the ability to connect multiple screens. This allows you to set up multiple monitors at the same time to create a more immersive gaming experience, such as a wider field of view.
GPU boot temperature
Lower boot temperature means the card generates less heat and the cooling system works better.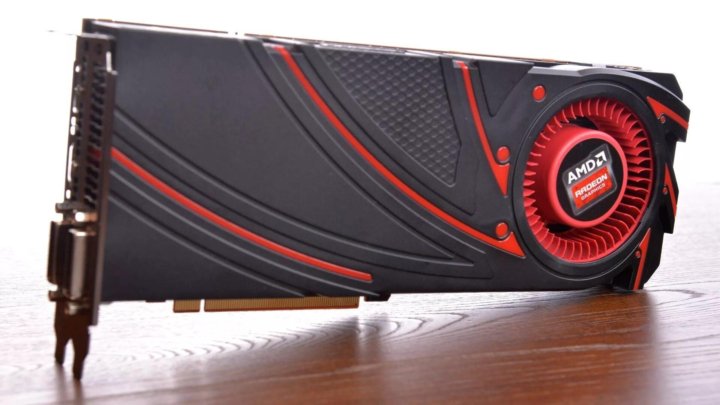
supports ray tracing
✖AMD Radeon R9 290
✔Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
Ray tracing is an advanced light rendering technique that provides more realistic lighting, shadows and reflections in games.
Supports 3D
✔AMD Radeon R9 290
✔Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
Allows you to view in 3D (if you have a 3D screen and glasses).
supports DLSS
✖AMD Radeon R9 290
✖Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
DLSS (Deep Learning Super Sampling) is an AI based scaling technology. This allows the graphics card to render games at lower resolutions and upscale them to higher resolutions with near-native visual quality and improved performance. DLSS is only available in some games.
PassMark (G3D) result
This test measures the graphics performance of a graphics card. Source: Pass Mark.
Ports
has HDMI output
✔AMD Radeon R9 290
✔Nvidia GeForce GTX 1060
Devices with HDMI or mini HDMI ports can stream HD video and audio to an attached display.
 000 MHz
000 MHz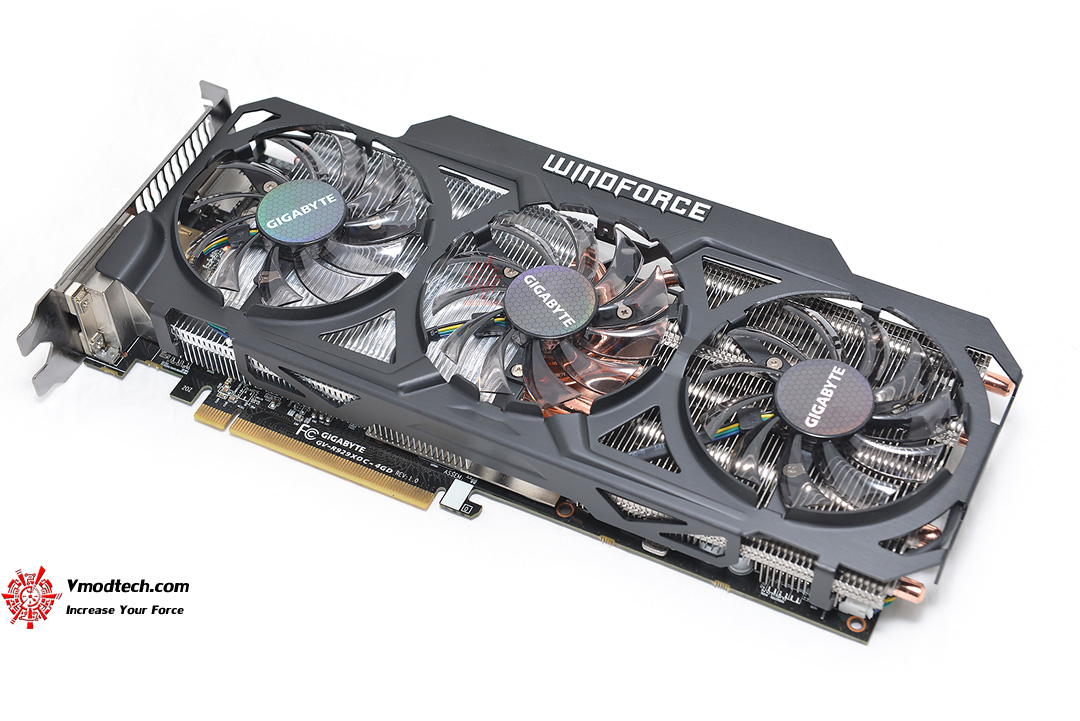 Preis
Preis