DirectX 9 Download Offline Installer For Windows 7 & 10
Download DirectX 9 old version on Windows 64-bit and 32-bit OS.
Microsoft DirectX 9 for Windows is a group of technologies designed to make Windows-based computers. It’s an ideal platform for running and displaying applications rich in multimedia elements such as full-color graphics, video, 3D animation, and rich audio.
DirectX 9 includes security and performance updates, along with many new features across all technologies, which can be accessed by applications using the DirectX APIs.
Download DirectX 9 old version for Windows 7, Windows 10, WinXP & Vista. This offline installer standalone end user run time setup will work both for 32-bit & 64-bit Windows operating systems. Simply click the download button to grab Direct X 9 for your Windows PC.
DirectX 9 Free Download Review 2023
If you are a PC gamer then Direct X technologies shouldn’t be alien to you. It’s a set of drivers that especially revolves around graphics drivers to give you audio and graphics experience while playing games.
DirectX 9 contains multiple APIs that are developed to enhance game graphics. The APIs that you will get when you download Direct X 9:
- Direct 3D. The most popular API, used for three-dimensional graphics programming and processing.
- Direct Input. Processes data from the mouse, keyboard, joystick and other controls for computer games.
- Direct Play. Used in network communications.
- Direct Graphics. This allows images to be drawn in two flat dimensions, as well as the representation of these in three dimensions.
- Direct Music. Plays music tracks composed with the Direct Music Producer.
- Direct Sound. Plays and records soundwaves.
- Direct Show. Plays video and audio with network transparency.

- Direct Compute. It offers special jargon and instructions that allow different processing threads in the massive core processors to be handled.
- Direct Setup. It allows you to install other DirectX components.
- Direct ML. Performs artificial intelligence or AI processing, as well as other features. These have been added in the 2019 update for Windows 10.
- DirectX Raytracing. Also called DXR, this is a feature that allows for real-time hardware ray tracing. It delivers a breakthrough in consumer-level computer graphics on GPUs, such as the Nvidia GeForce 20 series in 2018. This feature will not be available when downloading DirectX in its latest version but is an extension compatible with DirectX 12.
Microsoft DirectX 9 is included in Windows 7, 10 both 64-bit and 32-bit OS. You can update your DirectX drivers by installing the service pack and update. To upgrade DirectX 11 and further, you need to upgrade your Windows operating system.
You can also Download Direct X 11, or Direct X12 according to your system requirements.
How to Install DirectX9
The DX9 installation process is very simple and easy, just follow these steps:
- Download a DirectX9 installation package.
- Launch the directx.exe file.
- Read the License Agreement. If you agree with the terms of the agreement, click the Yes button
- Click the Browse button in the new window and choose the folder you want to unpack the installation files to. Click OK.
- After the unpacking is complete, open the folder containing the installation files and launch DXSETUP.exe.
- Read the License Agreement. If you agree with the terms, choose “I accept the agreement” and click Next.
- Click Next again.
- The components will be installed.
- After the installation, this window will be shown.
- Click Done. DirectX 9 was installed successfully!
Microsoft DX 9 Supported Games For PC List
Below are the best DirectX 9 only games:
- Assassins Creed
- GTA Vice City
- Star Wars : Knight of the old republic
- Splinter Cell
- Call of Duty
- Rise Of Nation
- Half Life 2
- Unreal Tournament 2004
- World of Warcraft
- Farcry
- Doom 3
- Call of Duty : United Offensive
- GTA San Andreas
- Splinter Cell: Chaos Theory
- Battlefield 2
- Silent Hunter 3
- Call Of Duty 2
Download
DirectX 9
Old Version 9 For Windows PC
4 (11)
🛡️ Safe & Secure
Free Download
Download Specs
- License: Free
- Platform: Windows
- Language: English
- File Size: 95.
 6 MB
6 MB - Downloads: 45,901
- Developer: Microsoft
DirectX 9 System Requirements
The installation process requires you to have Windows 7 or 10 operating system on your PC. The minimum requirements are:
- CPU: Pentium 233 MHz processor
- RAM: at least 64MB.
- HDD: at least 1.5 GB.
Pages 1 2
DirectX 9 32/64-bit Offline Installer For Windows 7 & 10 Free Download for PC
- Z. Meer
DirectX 9.0c Free Download latest 2021 update package from Microsoft which many modern games require.
DirectX 9.0c Free Download latest 2021 update package from Microsoft which many modern games require.
Download DirectX 9 for PC
Safe & Secure DirectX 9 Free download 9. 0 c files. Compatible with Windows 7, 8.1, 10 & 11 32/64-bit OS.
0 c files. Compatible with Windows 7, 8.1, 10 & 11 32/64-bit OS.
Choose download option
Download DirectX 9 9.0 c from trusted servers. Get free, fast, trusted, virus-free, original file downloads.
Microsoft DirectX 9.0c is a supporting tool designed to make Windows operating system an ideal program for playing and displaying games and Apps with a rich output for multimedia such as full-HD graphics, 3D animation display, video, and audio.
DirectX 9 download Windows 7 32/64-bit includes updates for security and performance, along with multiple new features to support new technologies, those that can be accessed by apps using the DirectX APIs.
If you are looking for the latest DirectX 9.0 c direct download Windows 7 32 bit, Here is how you can get this for free. This package includes Downloading Directx 9 Windows 7 offline installer that provides access to Microsoft’s DirectX APIs.
DirectX 9.0 c Free Download Overview
DirectX 9.0 c is a requirement of most latest and modern games, As usually it comes built-in with the latest versions of Windows but in case you are facing any problems, you can use the latest package of DirectX 9.0 c to satisfy these requirements. However, modern computers include a more recent version of Direct X like Directx 11.
DirectX 9 free download includes Pixel Shader 3.0 support along with many latest features. Free DirectX 9.0 Download (DX9.0 c) for Windows 32 & 84 bit introduces significant improvements across its suite with APIs. DirectSound offers new audio capabilities to Windows operating systems.
Microsoft DirectX 9.0 c Free Download Features
Multi-Threading: This application provides the ability to scale across multi-core CPUs which will help developers to take better advantage of multi-core power within CPUs. This results in faster gaming framerates.
DirectCompute: You can utilize the full power of graphics cards to accelerate gaming and non-gaming applications. This improves graphics, and will help PC users to accelerate everyday system tasks, like audio, and video editing, on their Windows 7 PC.
DirectX 9 Download Builds
Direct X 9.29.1974 – DirectX 9.0 c (Oct 2006) – MIcrosoft DirectX 9.0 c (Oct 2005) – Free DirectX 9 (Nov 2008) – DirectX 9.0 c (Nov 2007) – DirectX 9 (Mar 2009) – DirectX 9.0c (Mar 2008) – DirectX 9.0c (Jun 2010) – directx 9 free download windows 7 64 bits – DirectX 9.0c (Jun 2008) – DirectX 9.0 c (Jun 2007) – DirectX 9.0 c (Jun 2006) – DirectX 9.0c (Jul 2004) – DirectX 9.0 c (Feb 2010) – microsoft directx 9.0 c download windows 7 32 bits – DirectX 9.0 c (Feb 2007) – DirectX 9.0 c (Feb 2006) – DirectX 9.0 c (Dec 2006) – DirectX 9.0 c (Dec 2005) – DirectX 9.0c (Aug 2009) – DirectX 9.0c (Aug 2008) – directx 9.0 c windows 10 32 bit download – DirectX 9.0 c (Aug 2007) – DirectX 9.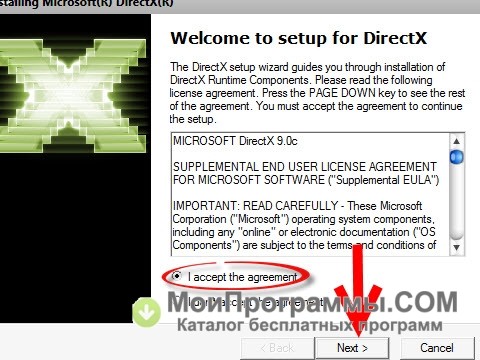 0 c (Aug 2006) – DirectX 9.0 c (Aug 2005) – DirectX 9.0c (Apr 2007) – DirectX 9.0 c (Apr 2006)-DirectX 9.0 c- directx 9.0 c free download for windows 7 32 bit -Downlaod DirectX 9.0 Windows 7 b-DirectX 9.0a-DirectX 8.2-DirectX 8.1b-DirectX 8.1 – DirectX 8.0a – DirectX 8.0 – DirectX 7.0a – DirectX 7.0 – DirectX 6.1 – DirectX 6.0 – DirectX 5.2 – DirectX 5.0 – DirectX 3.0 – DirectX 2.0 – DirectX 1.0
0 c (Aug 2006) – DirectX 9.0 c (Aug 2005) – DirectX 9.0c (Apr 2007) – DirectX 9.0 c (Apr 2006)-DirectX 9.0 c- directx 9.0 c free download for windows 7 32 bit -Downlaod DirectX 9.0 Windows 7 b-DirectX 9.0a-DirectX 8.2-DirectX 8.1b-DirectX 8.1 – DirectX 8.0a – DirectX 8.0 – DirectX 7.0a – DirectX 7.0 – DirectX 6.1 – DirectX 6.0 – DirectX 5.2 – DirectX 5.0 – DirectX 3.0 – DirectX 2.0 – DirectX 1.0
This Download will work on.
Windows 95 / Windows 98 / Windows 2000 / Windows XP / Windows Vista / Windows Vista x64 / Windows XP x64 / Windows ME / Windows NT 4.0 / Windows 7 / Windows 7 x64 / Windows 8 / Windows Server 2003 x64 / Windows Server 2003 / Windows Server 2008 / Windows 8 x64 / Windows NT / Windows 2000 x64.
Pages 1 2
# Direct X Setup Download# Direct3D Download# DirectX Download# ISO
DirectX won’t install: causes and solution
Contents
- DirectX won’t install
- Cause 1: Antivirus
- Cause 2: System
- FAQ
Many users, when trying to install or update DirectX components, are faced with the inability to install the package. Often, this problem needs to be fixed immediately, as games and other programs that use DX refuse to work properly. Consider the causes and solutions of errors during DirectX installation.
Often, this problem needs to be fixed immediately, as games and other programs that use DX refuse to work properly. Consider the causes and solutions of errors during DirectX installation.
nine0003
The situation is painfully familiar: it became necessary to install the DX libraries. After downloading the installer from the official Microsoft website, we try to run it, but we get a message like this: «DirectX installation failed: an internal system error occurred» .
The text in the dialog box may be different, but the essence of the problem remains the same: the package cannot be installed. This is because the installer is blocked from accessing the files and registry keys that need to be changed. Both the system itself and anti-virus software can limit the capabilities of third-party applications. nine0003
Reason 1: Antivirus
Most free antiviruses, despite their inability to intercept real viruses, often block those programs that we need like air.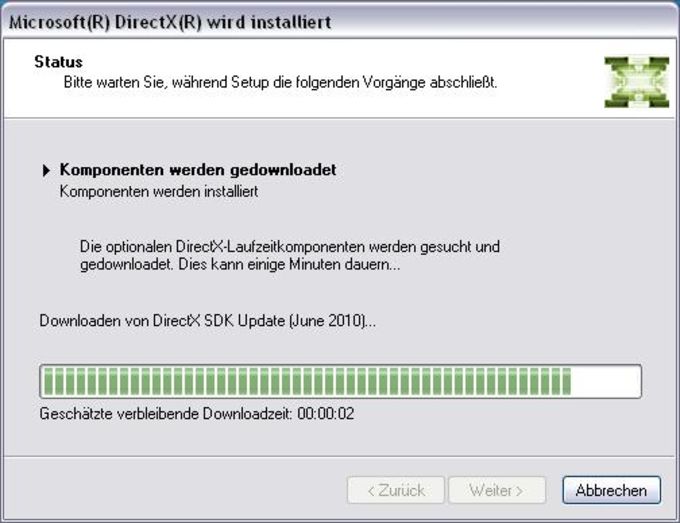 Their paid counterparts also sometimes sin with this, especially the famous Kaspersky.
Their paid counterparts also sometimes sin with this, especially the famous Kaspersky.
In order to bypass the protection, it is necessary to disable the antivirus.
Read more:
Disabling antivirus
How to disable Kaspersky Anti-Virus, McAfee, 360 Total Security, Avira, Dr.Web, Avast, Microsoft Security Essentials. nine0003
Since there are a lot of such programs, it is difficult to give any recommendations, so refer to the manual (if available) or to the software developer’s website. However, there is one trick: when booting into safe mode, most antiviruses do not start.
Read more: How to enter safe mode on Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows XP
Reason 2: System
In the Windows 7 operating system (and not only) there is such a thing as «access rights». All system and some third-party files, as well as registry keys are blocked for editing and deletion. This is done so that the user does not accidentally harm the system by his actions. In addition, such measures can protect against virus software that “targets” these documents. nine0003
In addition, such measures can protect against virus software that “targets” these documents. nine0003
When the current user does not have the rights to perform the above actions, any programs that try to access system files and registry branches will not be able to do this, the DirectX installation will fail. There is a hierarchy of users with different levels of rights. In our case, it is enough to be an administrator.
If you are the sole user of the computer, then most likely you have administrator rights and you just need to tell the OS that you allow the installer to perform the necessary actions. You can do this in the following way: call the explorer context menu by clicking RMB on the DirectX installer file, and select «Run as administrator» .
In the event that you do not have «admin» rights, you need to create a new user and assign him the administrator status, or give such rights to your account. The second option is preferable because it requires less action.
- Open «Control Panel» and go to the applet «Administration» .
- Next we go to «Computer Management» .
- Then we expand the branch «Local Users» and go to the folder «Users» .
- Double-click on item «Administrator» , uncheck the box next to «Disable account» and apply the changes.
- Now, at the next boot of the operating system, we see that a new user with the name 9 has been added to the welcome window0019 «Administrator» . This account is not password protected by default. Click on the icon and log in.
- Again we go to «Control Panel» , but this time we go to the applet «User Accounts» .
- Next, follow the link «Manage another account» .
- Select your «account» in the list of users.
- Follow link «Change account type» .

- Here we switch to parameter «Administrator» and press the button with the name, as in the previous paragraph.
- Now our account has the required rights. We log out or reboot, log in under our «account» and install DirectX.
Please note that the Administrator has exclusive rights to interfere with the operation of the operating system. This means that any software that is launched will be able to make changes to system files and settings. If the program turns out to be malicious, the consequences will be very sad. The Administrator account, after performing all the actions, must be disabled. In addition, it will not be superfluous to switch the rights for your user back to «Normal» .
Now you know what to do if the message «DirectX setup failed: An internal error has occurred» appears during DX installation. The solution may seem complicated, but it is better than trying to install packages obtained from unofficial sources or reinstalling the OS.
Once again about IP addresses, subnet masks and in general / Habr
A bit of educational program. Inspired by previous copy-pastes of various nonsense on this topic. Excuse me, nosing staff. nine0003
The IP address (v4) consists of 32 bits. Any self-respecting administrator, and indeed an IT specialist (I am silent about network engineers) should be able to correctly answer the question “how many bits an IP address consists of” being woken up in the middle of the night or being in a state of extreme intoxication. It is desirable, in general, about IPv6 too: 128 bits.
The first circumstance. Total theoretical IPv4 addresses can be:
2 32 = 2 10 *2 10 *2 10 *2 2 = 1024*1024*1024*4 ≈ 1000*1000*1000*4 = 4 billion
Below we will see that quite a lot of them are «eaten up» for all sorts of garbage.
Write down the IPv4 address, I think everyone knows how. Four octets (same as bytes, but if you want to flash, then say «octet» — you will immediately pass for your own) in decimal notation without leading zeros, separated by dots: «192.168.11.10».
Four octets (same as bytes, but if you want to flash, then say «octet» — you will immediately pass for your own) in decimal notation without leading zeros, separated by dots: «192.168.11.10».
The IP packet header has source IP and destination IP fields: source (who sends) and destination (to whom) addresses. Like a postal envelope. Within packets, IP addresses do not have any masks. There are no separators between octets either. Just 32 bits for the destination address and another 32 bits for the source address. nine0031
However, when an IP address is assigned to an interface (network adapter or whatever it is called) of a computer or router, then in addition to the address of this device itself, it is also assigned a subnet mask. Once again: mask not is sent in IP packet headers .
Computers need a subnet mask to define the boundaries of—you never know what—subnets. So that everyone can determine who is in the same [under] network with him, and who is outside it. (Actually, you can just say “networks”, often this term is used precisely in the meaning of “IP subnet”.) The fact is that within one network, computers exchange packets “directly”, and when you need to send a packet to another network, they send their default gateway (the third configurable option in the network properties, if you remember). Let’s see how this happens. nine0003
(Actually, you can just say “networks”, often this term is used precisely in the meaning of “IP subnet”.) The fact is that within one network, computers exchange packets “directly”, and when you need to send a packet to another network, they send their default gateway (the third configurable option in the network properties, if you remember). Let’s see how this happens. nine0003
The subnet mask is also 32-bit. But unlike an IP address, zeros and ones cannot alternate in it. There are always some ones first, then some zeros. The mask cannot be
120.22.123.12=01111000.00010110.01111011.00001100.
But the mask may be
255.255.248.0=11111111.11111111.11111000.00000000.
First N ones, then 32-N zeros. It is easy to guess that this form of notation is redundant. The number N, called the length of the mask, is quite sufficient. They do it: they write 192.168.11.10/21 instead of 192.168.11.10 255.255.248.0. Both forms carry the same meaning, but the first is noticeably more convenient./i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2021/J/C/Rz9JeURAiJTP0FN9h1Og/2016-01-14-instalando-directx-9.png)
To determine the boundaries of a subnet, the computer does a bit-by-bit multiplication (logical AND) between the IP address and the mask, resulting in an address with zero bits in the zero positions of the mask. Consider the example 192.168.11.10/21:
11000000.10101000.00001011.00001010
11111111.11111111.11111000.00000000
---------------------------------------------- nine0031
11000000.10101000.00001000.00000000 = 192.168.8.0
Second circumstance. Any self-respecting administrator must be able to translate IP addresses from decimal to binary and vice versa in the mind or on a piece of paper, and also be good at binary arithmetic.
The address 192.168.8.0, with all bits set to zero in positions corresponding to zeros in the mask, is called the subnet address. It (usually) cannot be used as an address for a particular host’s interface. If, on the contrary, these bits are set to ones, then address 19 will be obtained./i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2021/l/W/KizwYHQOyaoyaIomy1xg/2016-01-14-instalando-directx-9-concluido.png) 2.168.15.255. This address is called directed broadcast (broadcast) for this network. Its meaning in modern times is very small: there was once a belief that all hosts on a subnet should respond to it, but this was a long time ago and not true. However, this address also cannot (usually) be used as a host address. In total, two addresses in each subnet are in the trash. All other addresses in the range 192.168.8.1 through 192.168.15.254 inclusive are full host addresses within subnet 192.168.8.0/21, they can be used for assignment on computers.
2.168.15.255. This address is called directed broadcast (broadcast) for this network. Its meaning in modern times is very small: there was once a belief that all hosts on a subnet should respond to it, but this was a long time ago and not true. However, this address also cannot (usually) be used as a host address. In total, two addresses in each subnet are in the trash. All other addresses in the range 192.168.8.1 through 192.168.15.254 inclusive are full host addresses within subnet 192.168.8.0/21, they can be used for assignment on computers.
Thus, the part of the address that corresponds to the ones in the mask is the address (identifier) of the subnet. It is also often called the word prefix. And the part that corresponds to the zeros in the mask is the host ID within the subnet. A subnet address in the form 192.168.8.0/21 or 192.168.8.0 255.255.248.0 is quite common. Routers operate with prefixes, laying traffic routes through the network. Only the subnet’s default gateway (via some link-layer technology) knows about the location of hosts within subnets, not transit routers. But the host address in isolation from the subnet is not used at all. nine0003
But the host address in isolation from the subnet is not used at all. nine0003
The third circumstance. The number of hosts on a subnet is defined as 2 32-N -2, where N is the length of the mask. The longer the mask, the fewer hosts it contains.
From this circumstance, in particular, it follows that the maximum mask length for a subnet with hosts is N=30. It is the /30 networks that are most often used for addressing on point-to-point links between routers.
Although most modern routers work fine with /31 masks, using the subnet address (zero in the one-bit host part) and broadcast (one) as interface addresses, administrators and network engineers are often simply afraid of this approach, preferring to be guided by the principle of «little whether that. nine0003
But the /32 mask is used quite often. Firstly, for any official needs when addressing the so-called. loopback interfaces, secondly, from curvature: /32 is a subnet consisting of one host, that is, no network, in fact.
The more often the network administrator operates not with groups of hosts, but with individual machines, the less the network is scalable, the more snot, mess and incomprehensible rules in it. The exception, perhaps, is writing firewall rules for servers, where specificity is a good thing. But it is better to deal with users not individually, but en masse, entire subnets, otherwise the network will quickly become unmanageable. nine0003
The interface on which an IP address is configured is sometimes referred to as an IP interface or L3 interface («el-three», see OSI model).
Before sending an IP packet, the computer determines if the destination address is on «its own» subnet. If it hits, then it sends the packet “directly”, if not, it sends it to the default gateway (router). Typically, although not required, the default gateway is assigned the first host address on the subnet: in our case, 192.168.8.1 for beauty.
Fourth circumstance. From what has been said, in particular, it follows that the router (the gateway and the router are the same thing) with the interface address 192.
168.8.1 knows nothing about the traffic transmitted between, for example, hosts 192.168.8.5 and 192.168.8.7. A very common mistake novice administrators make is to want to block or otherwise control traffic between hosts within the same subnet using a gateway. For traffic to pass through the router, the destination and the sender must be on different subnets. nine0002 Thus, a network (even the smallest enterprise) should usually have several IP subnets (2+) and a router (more precisely, a firewall, but in this context these words can be considered synonyms) that routes and controls traffic between subnets.
The next step is to break the subnets into smaller subnets. The 192.168.8.0/21 network that we love can be divided into 2 /22 subnets, four /23 subnets, eight /24 subnets, etc. The general rule, as you might guess, is: K=2 X-Y , where K is the number of subnets with mask length Y that fit into a subnet with mask length X.
Fifth circumstance.
Like any decent IT guy, a network administrator, unless he’s on a paycheck for pretty eyes, is supposed to know powers of two from 0 to 16 by heart. (with a short mask, in which there are many hosts) is called aggregation or summation (that’s not summation!). This is a very important process to minimize the amount of information a router needs to find a path through a network. So, let’s say providers issue thousands of small blocks like /29 to clients, but the entire Internet does not even know about their existence. Instead, large prefixes like /19 and larger are assigned to each provider. This allows you to reduce the number of entries in the global Internet routing table by orders of magnitude.
The sixth circumstance. The longer the mask length, the fewer hosts can be on the subnet, and the greater the share of addresses «eating» into the addresses of the subnet, directed broadcast and default gateway. In particular, in the subnet with the mask /29 (2 32-29 = 8 combinations) there will be only 5 addresses available for real use (62.
5%). Now imagine that you are an ISP issuing thousands of /29 blocks to corporate customers. Thus, the competent partitioning of the IP space into subnets (drawing up an address plan) is a whole little science, including the search for compromises between various complex factors.
If there is a large enough range of addresses, usually private blocks 10.0.0.0/8, 172.16.0.0/12 and 192.168.0.0/16, of course, it is convenient to use masks that match the length of the octet boundaries: /8, /16, /24 or, respectively, 255.0.0.0, 255.255.0.0 and 255.255.255.0. When using them, you can make the work of the brain and the calculator easier, getting rid of the need to work with the binary system and bits. This is the right approach, but do not forget that the abuse of relaxation rarely leads to good.
And the last. Notorious address classes. Dear comrades, forget this word altogether! At all. It has been almost 20 years (!) since there have been no classes. Exactly since it became clear that the length of the prefix can be any, and if you distribute addresses in blocks of / 8, then no Internet will work.
nine0003
Sometimes «experienced experts» like to flash the words «network of class such and such» in relation to a subnet with a particular mask length. Let’s say you often hear the word «class C network» about something like 10.1.2.0/24. The class of the network (when it was) had nothing to do with the length of the mask and was determined by completely different factors (combinations of bits in the address). In turn, classful addressing obligated to have masks of only the length prescribed for a given class. Therefore, the specified subnet 10.1.2.0/24 never belonged and never will belong to class C.0003
But it’s better not to think about all this. The only thing you need to know is that there are different global conventions, collected under one roof in RFC3330, about the special meanings of certain address blocks. So, for example, the mentioned blocks 10/8, 172.16/12 and 192.168/16 (yes, you can write prefixes like that, completely discarding the host part) are defined as ranges for private use, prohibited from routing on the Internet.

