power supply — Can I safely use a PSU with an ATX 12v 4-pin for a board that has a EPS 12v 8-pin?
Information:
Page 16 of the manual to the motherboard says that the 8-pin connector is for supplying power to the CPU.
Method 1:
If you look at the pinout of the 8-pin socket and the 4-pin cable (figures 1 and 2 below respectively), you will notice that physically, it should be compatible. I found a page (figure 3) that indicates that it can be done, but strongly advises using a proper 8-pin cable. This makes sense because the connector is generally for providing the CPU with extra power (as opposed to any power), so while it may work, the system may suddenly shut down if CPU usage goes up to 100% (eg while doing a virus-scan, watching YouTube videos, etc.)
Method 2:
Another option I have found is some discussions (like this one) about using an adapter (figure 4) to connect the 4-pin cable to both halves of the 8-pin connector. In fact, there are plenty such adapters on eBay for as little as $1 (and free shipping). Newegg also has a couple. Of course the problem with this method is the same as the previous one in that there is no additional power being supplied; this method simply splits the power from one source across the two halves of the connector.
Like you said, a Molex-to-8pin adapter is a good option too. There are different ones available which either split a single cable across the two halves of the 8-pin connector (which is generally not going to be a problem since that is what happens when you plug the three or four connectors on one cable into multiple drives, etc. anyway). There are others (figure 5) that have two separate Molex connectors (one for each half of the 8-pin) which you can plug into Molex connectors from different cables from the PSU for extra peace of mind. These are fairly cheap too (~$2 with shipping). It also has similarly good reviews.
In fact, there are also 6-pin PCI-E to 8-pin ATX12V adapters as well, and probably others (though you indicated that the PSU does not have this)..jpg)
Recommendation:
The difference between the two methods gets to be somewhat complicated if you are not familiar with electronic engineering, but suffice it to say that method two is the better one in most circumstances. Using a PSU with an actual, dedicated 8-pin cable is the best solution of course, but if you look at the reviews at Newegg for the adapters, you will see that all of the reviews are positive, indicating that an adapter will likely be a good way to solve this problem for next to nothing.
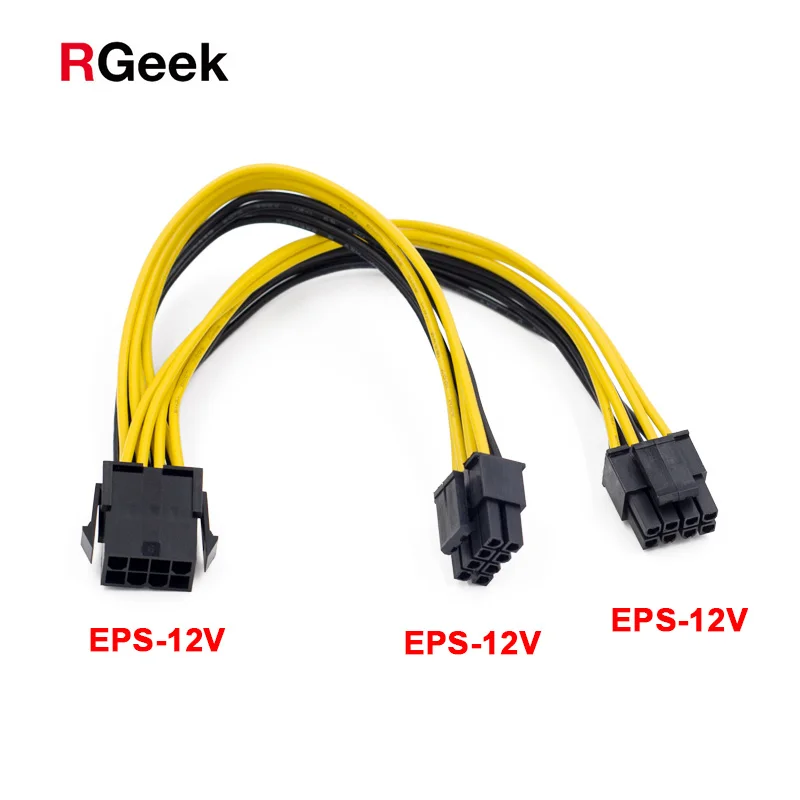
Figure 1: 8-pin EPS ATX_12v motherboard connector
Figure 2: 4-pin ATX 12v auxiliary connector
Figure 3: Using a 4-pin cable in an 8-pin plug
Figure 4: 4-pin to 8-pin ATX 12V adapter
Figure 5: Molex to 8-pin adapter
Is using 4-pin connector for 8-pin ATX 12V power connector ok?
Ask Question
Asked
Modified
6 years, 11 months ago
Viewed
37k times
My new computer rig has a power supply with just 1 4-pin connector but the motherboard, a GIGABYTE GA-MA785GM-US2H has an 8-pin ATX 12V power connector.
Is using only the 4-pin connector enough?
Edit:
The motherboard has a 2×12 main power connector and a 2×4 12v power connector for the CPU. According to the manual, its not even supposed to be able to be turned on without the 12V cable.
Edit 2:
- CPU: AMD Athlon II X3 435 Rana 2.9GHz
- PSU: 400W OCZ StealthXstream
- power-supply
1
IT depends on your CPU. The additional 4 pins were added to support the higher power draw of newer (at the time) Core 2 Quads. The 4 pins will happily provide power to most lower end CPUs, but if you have a Quad I would double check the TDP and make sure you can provide enough power with the 75W that the 4-pin can provide and that you don’t need the 150W that the 8-pin provides.
Either way, I would upgrade your PSU. You can get a good, brand name, high efficiency PSU with the proper connectors for well under $100 and you will be all set in the event that you upgrade down the road.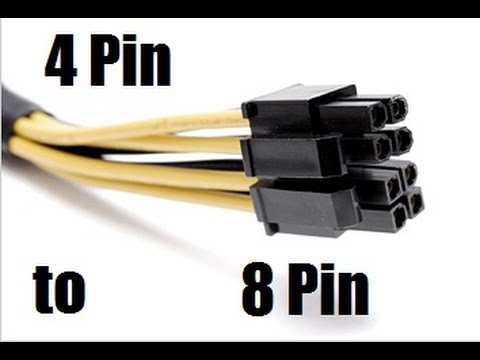
Edit: The Rana has a 95W TDP, this means that your CPU will consume 95W on max load. Your 24 pin power connector provides 144W max on the 12V rail. 75 of these Watts are used by PCIe, which leaves ~69W for the CPU (though other components will use some of this so in reality it’s probably closer to 60W). This means that with the additional 75W from the 4-pin you can ~135W available to the CPU under max load. This should be plenty assuming you are doing no overclocking and your motherboard and you don’t have any other major 12v draws in your system (like an additional video card).
Seriously though, you should still get a new PSU. They can be reused in newer computers if you upgrade and there’s no guarantee that you aren’t voiding your motherboard warranty even though it should work.
6
The CPU power connector is used to power the voltage regulators for the CPU. This is a seperate rail on the motherboard from the 12V rail on the ATX power connector so you can’t just add together the capacity of this connector and the capacity of the 12V line on the main ATX power connector.
Molex «mini fit JR» connectors are supposed to be good for about 9A per pin which would allow for arround 200W on a 4 pin connector (2 power 2 ground). That should be more than enough for nearly all CPUs. Unfounrtately however many power supplies have cheap clones of a minin fit JR which can’t tolerate such high currents. Also the inside of PC cases can be quite warm which reduces the safe current a bit. Combine this with enthusiasts overclocking/overvolting their CPUs and burned out connectors started to become a problem. In response motherboard vendors started fitting the 8 pin «EPS» connector (which was originally intended for high power server CPUs).
In general if you aren’t overclocking/overvolting you should be fine with the 4 pin connector.
Power supplies with motherboard power 24+8+4+4 pin
Power supplies with motherboard power 24+8+4+4 pin — buy cheap, price from 4 230 rubles. -39 models-photos, reviews, characteristics in the online store 123.ru compound for PC
- Components for PC
- Power Blocks
- 24+4+4+PIN
Sortifiers
50017 5 480 c
add to cart
14 970 c
in basket
14 080 C
in basket
7 620 C 800 C
in basket
11 870 C
in the corner 13 440 C
in the basket
10 570 C 12 280 C
in basket
18 170 C 21 380 C
in the basket
090 C
in the basket
44 850 C
in the basket
35 330 C
in basket
14 680 C
9 C
in the basket
14 210 C
in the basket
950 C 10 820 C
in basket
6 370 C
in CARSE
017 6 670 C
in the basket
7 160 C 8 530 C
In basket
6 530 C
5 990 C 9 6 080 C 900 C 900 C 9 In the basket
19 280 C
in the basket
14 060 C
in the basket
6 080 C 7 08
900 basket
11 550 C
in the basket
8 440 C
in basket
4 230 C
in the basket
15 010 C 9ATHER 9ATH
19 040 C
in the basket
58 800 C
in basket
Show more goods
- 1
- 2
Popular brands
- 93)
- Purchase on credit
- Installment plan with Conscience card
- Installment plan from Halva
RUB 6,410
Add to cart
PSU ATX 700 W Aerocool CYLON 700
Add to cart
CROWN Power supply CM-PS450W PLUS (PEAK 450W, 20+4in 500mm, 4+4pin*1, SATA*3, MOLEX*2, 120mm FAN, I/O, bubble pack)
1 550 rubles
Add to cart
PSU ATX 550 W Aerocool VX PLUS 550 RGB
Add to cart
PSU ATX 750W Zalman GigaMax ZM750-GVII
RUB 5,880
Add to cart
PSU ATX 400 W GINZZU SA400
Add to cart
PSU ATX 500 W GINZZU SB500
Add to cart
PSU ATX 450 W GINZZU SB450
add to cart
PSU ATX 500 W Exegate XP500
Add to cart
Official warranty
Cables in your PC power supply, explanation • Oki Doki
So, you are building a new gaming PC. For a beginner, this can be a daunting task. After all, there are a lot of components, and if you don’t know what you’re doing, you can mess things up. Thus, it is important to become familiar with all the components inside a PC, how they work and what goes where.
For a beginner, this can be a daunting task. After all, there are a lot of components, and if you don’t know what you’re doing, you can mess things up. Thus, it is important to become familiar with all the components inside a PC, how they work and what goes where.
Case in point: the power supply you just unpacked and a bunch of cables coming out of it. What are all these power supply cables and connectors, and what are they for? nine0013
20/24-pin motherboard cable
First, the cable that probably caught your attention the most is the wide 24-pin cable, whether you bought a modular or non-modular power supply. And this is actually the most important cable.
Programs for Windows, mobile applications, games — EVERYTHING is FREE, in our closed telegram channel — Subscribe 🙂
This cable is the main connector that provides power to your PC motherboard. While this isn’t the only connector your PC needs (other components will require additional power, as you’ll see shortly), it’s the main connector responsible for supplying the correct voltage to your motherboard and, by extension, to most of your PC’s components. . This includes your RAM, storage devices, unpowered PCIe devices, and pretty much everything else on your motherboard. nine0013
. This includes your RAM, storage devices, unpowered PCIe devices, and pretty much everything else on your motherboard. nine0013
This connector is usually located in a prominent position on the edge of the motherboard. On older ATX motherboards, as well as cheaper ones, you will find that the main connector actually has 20 pins, not 24. Similarly, some PSUs come with a 20+4 connector (with 4 pins that can be split) . instead of straight 24 pin. This is because older PCs with lower power requirements can get by with 20 pins instead of 24, and PSUs have basically stayed the same over the years (and not for lack of trying). nine0013
The power supplies are more or less compatible with the old ones thanks to the ATX standard, and this has stuck in the minds of some power supply manufacturers. After all, old PSUs die over time, and when that happens, being able to use a new PSU can probably save it from ending up in a landfill.
4/8 pin CPU connector
Next we have the CPU connector. The CPU is one of the few parts of your PC that needs additional power beyond the power supplied to the motherboard. The CPU socket is here to intervene. nine0013
The CPU is one of the few parts of your PC that needs additional power beyond the power supplied to the motherboard. The CPU socket is here to intervene. nine0013
The CPU socket is usually located next to your PC’s CPU socket. Just plug it in after you’re done with the motherboard connector and you’re done.
Depending on the computer, this connector may differ slightly. In lower end PCs, you will find a 4-pin header on the motherboard, which should provide enough power for those lower end chips. On mid-range and high-end processors, you can find an 8-pin header instead, providing enough power for just about every chip. nine0013
Almost always, your PC power supply includes an 8-pin connector that breaks into two parts, known as 4+4-pin. This allows you to connect it to both 4-pin and 8-pin connectors — just set one aside if you don’t need it.
You may find more than one CPU cable on some power supplies. Similarly, some motherboards may have 8-pin and 4-pin connectors, or come with a 12-pin connector instead. Although this is not the norm, some PCs require a lot of power for the processor, especially those who overclock. nine0013
Although this is not the norm, some PCs require a lot of power for the processor, especially those who overclock. nine0013
PCI Express 6/8-pin cable (GPU cable)
Technically, all PCI Express power needs are already served by the motherboard connector. After all, if you put something like a Wi-Fi card there, it will work fine. However, some devices (most commonly GPUs) require additional auxiliary power in addition to what the motherboard provides. This is where PCIe cables come in. They are sometimes referred to as GPU cables as they are primarily used by GPUs. nine0013
They will come with both 6-pin and 8-pin connectors and plug in on top of the GPU. Depending on which GPU we’re talking about, you can get away with one connector, you might need two, or as many as three, depending on the power requirements of the particular card. If the card’s power requirements are not fully met, users may experience performance drops or even instability and frequent crashes. Luckily, most power supplies, especially higher wattage ones, come with multiple power supply cables. nine0013
Luckily, most power supplies, especially higher wattage ones, come with multiple power supply cables. nine0013
Other Power Supply Cables
While these are the three main cables you need to be aware of, there are some additional cables that you may or may not need depending on your use case. They are responsible for powering the secondary components of your PC.
SATA cable
First, we have the SATA power cable. These are still widely used in power supplies these days, and if the name SATA gives you clues as to what it’s for, then your hunch is probably correct. The SATA power cable is mainly responsible for supplying power to the hard drive or other SATA drive directly from the hard drive. It should not be confused with the SATA cable, which is the actual connection between your hard drive and computer — the SATA power cable provides power, while the SATA cable does everything else. nine0013
Recently, SATA power cables have found other uses. For example, some computer cases with addressable RGB lighting may come with a hub to connect all the outputs of RGB peripherals such as fans.
